Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Prev Med Public Health > Volume 55(3); 2022 > Article
-
Special Article
Cohort Profile: Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort Constructed by Linking the Korean National Tuberculosis Surveillance System and National Health Information Database -
Dawoon Jeong1
 , Hee-Yeon Kang2
, Hee-Yeon Kang2 , Jinsun Kim3
, Jinsun Kim3 , Hyewon Lee3
, Hyewon Lee3 , Bit-Na Yoo4
, Bit-Na Yoo4 , Hee-Sun Kim4
, Hee-Sun Kim4 , Hongjo Choi5
, Hongjo Choi5
-
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health 2022;55(3):253-262.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.21.635
Published online: April 22, 2022
1The Korean Institute of Tuberculosis, Korean National Tuberculosis Association, Cheongju, Korea
2Department of Health Policy and Management, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Division of Tuberculosis Prevention and Control, Bureau of Infectious Disease Policy, Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Cheongju, Korea
4National Evidence-based Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea
5Department of Preventive Medicine, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- Corresponding author: Hee-Sun Kim, Department of Health Policy Research, National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, 400 Neungdong-ro, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul 04933, Korea, E-mail: hskim7336@neca.re.kr
- Co-corresponding author: Hongjo Choi, Department of Preventive Medicine, Konyang University College of Medicine, 158 Gwanjeodong-ro, Seo-gu, Daejeon 35365, Korea, E-mail: hongjo@konyang.ac.kr
- * Jeong & Kang contributed equally to this work as joint first authors.
Copyright © 2022 The Korean Society for Preventive Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- We aimed to review the current data composition of the Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort, which was constructed by linking the Korean Tuberculosis Surveillance System (KNTSS; established and operated by the Korean Disease Control and Prevention Agency since 2000) and the National Health Information Database (NHID; established by the National Health Insurance Service in 2012). The following data were linked: KNTSS data pertaining to patients diagnosed with tuberculosis between 2011 and 2018, NHID data of patients with a history of tuberculosis and related diseases between 2006 and 2018, and data (obtained from the Statistics Korea database) on causes of death. Data from 300 117 tuberculosis patients (177 206 men and 122 911 women) were linked. The rate of treatment success for new cases was highest in 2015 (86.7%), with a gradual decrease thereafter. The treatment success rate for previously treated cases showed an increasing trend until 2014 (79.0%) and decreased thereafter. In total, 53 906 deaths were confirmed among tuberculosis patients included in the cohort. The Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort can be used to analyze different measurement variables in an integrated manner depending on the data source. Therefore, these cohort data can be used in future epidemiological studies and research on policy-effect analysis, treatment outcome analysis, and health-related behaviors such as treatment discontinuation.
- A World Health Organization (WHO) report included tuberculosis (TB) among the top 10 leading causes of death worldwide. Approximately 6–7 million people are diagnosed with TB annually, and the number of TB-related deaths in 2020 was approximately 1.5 million. The Korea has the highest incidence and the third highest mortality rate due to TB among the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development member countries [1]. The Korean government announced the second National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Control (2018–2022) in 2018 and the Strengthening Measures of Tuberculosis Prevention and Management in 2019; it has promoted policies to reduce the incidence of TB and the associated mortality rate [2].
- The Korean National Tuberculosis Surveillance System (KNTSS), a web-based notification system, was established in 2000 [3]; it collects information on demographics, diagnostic test results, and final treatment outcomes of TB patients by mandatory notification of physicians according to Article 11 (Reporting by Physicians) of the Infectious Diseases Control and Prevention Act and Article 8 (Reporting Obligation of Medical Institutions) of the Tuberculosis Prevention Act.
- In the past, TB-related research that integrated national data sources was rarely conducted; thus, it was difficult to comprehensively study TB due to quality problems in TB notification data [4,5]. Various studies have used data from the KNTSS, but those studies could not assess patients’ socioeconomic position and treatment results (such as death) due to data unavailability. Moreover, assessment of data on TB diagnosis and treatment alone would be insufficient, as it is important to consider the presence of comorbidities and the relationship of TB with these conditions in an integrated approach for TB management. Therefore, the evidence referred to in clinical guidelines for TB was mostly generated from observational studies using individual patient data derived from single or multi-hospital medical records rather than population-level data. Recently, due to continuous efforts to improve the quality of KNTSS data, the data completeness of TB notifications in 2014—that is, the proportion of TB notified cases in KNTSS among the newly registered TB cases in the National Health Insurance (NHI)—improved to about 94% [6], which raised the need to use data linked with other representative data.
- The National Health Information Database (NHID) of the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) is a public database on healthcare utilization, medical examinations, socio-demographic variables, and information on deaths of Koreans; it includes data from >50 million people, which have been obtained since 2002 [7]. Despite the availability of these high-quality data sources, there is insufficient research on TB integrating these sources and utilizing their strengths. Linking each source enables researchers to measure the effectiveness of TB treatment for TB; demonstrates trends in the actual national disease incidence, morbidity, and mortality; and facilitates further investigation of the possible causes of TB [8–10]. The linkage of databases permits identifying deficiencies in each data system and can help devise solutions to improve the data sources. Therefore, it is necessary to combine the available information to accurately calculate statistical data [11].
- We aimed to establish the Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort by linking national representative data sources to create new population-level evidence for TB monitoring and management. This study was conducted to review the current status of the Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort, which was established by linking data in the KNTSS, NHID, and the Causes of Death Statistics databases.
INTRODUCTION
- Sources of Data
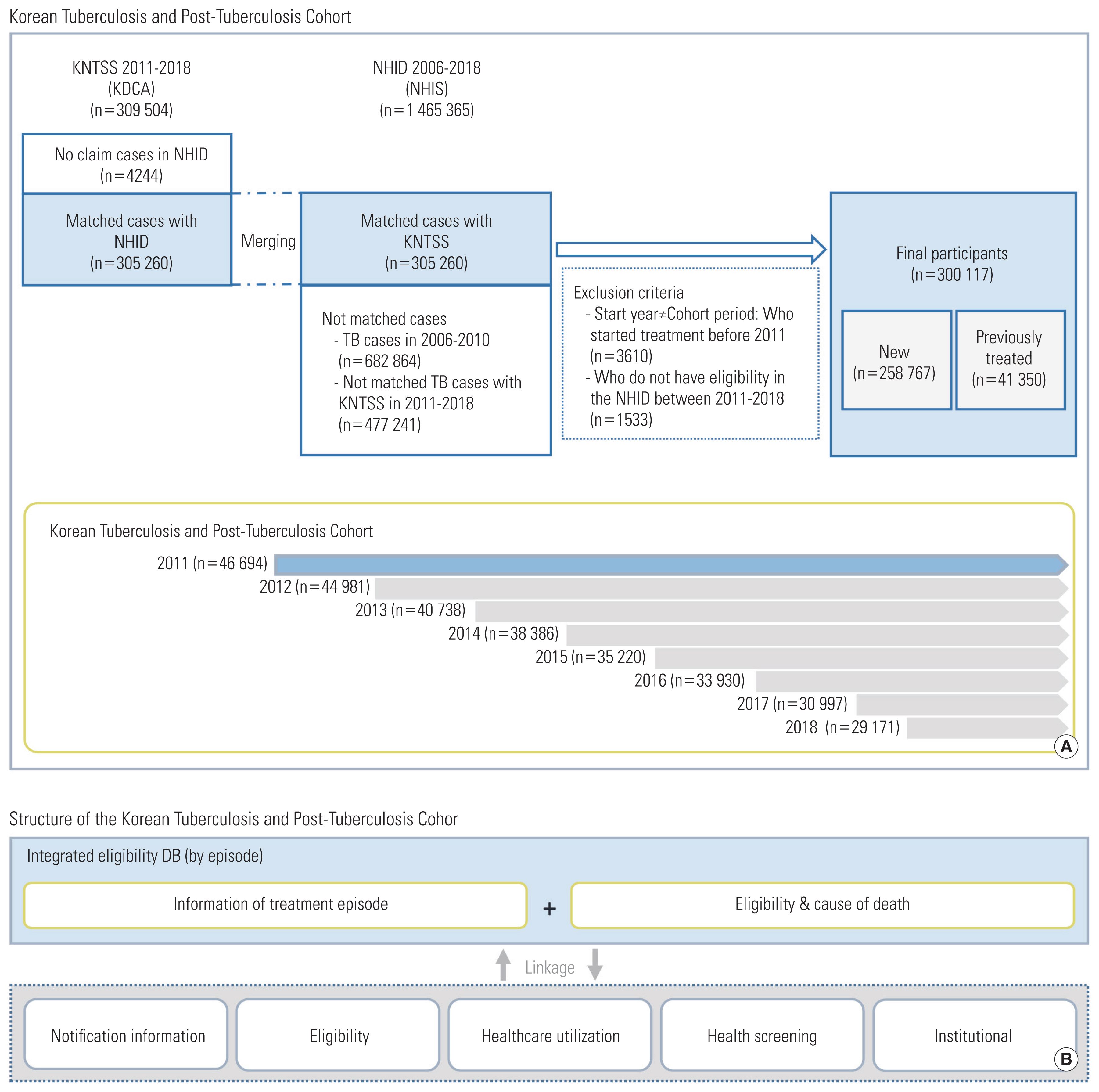
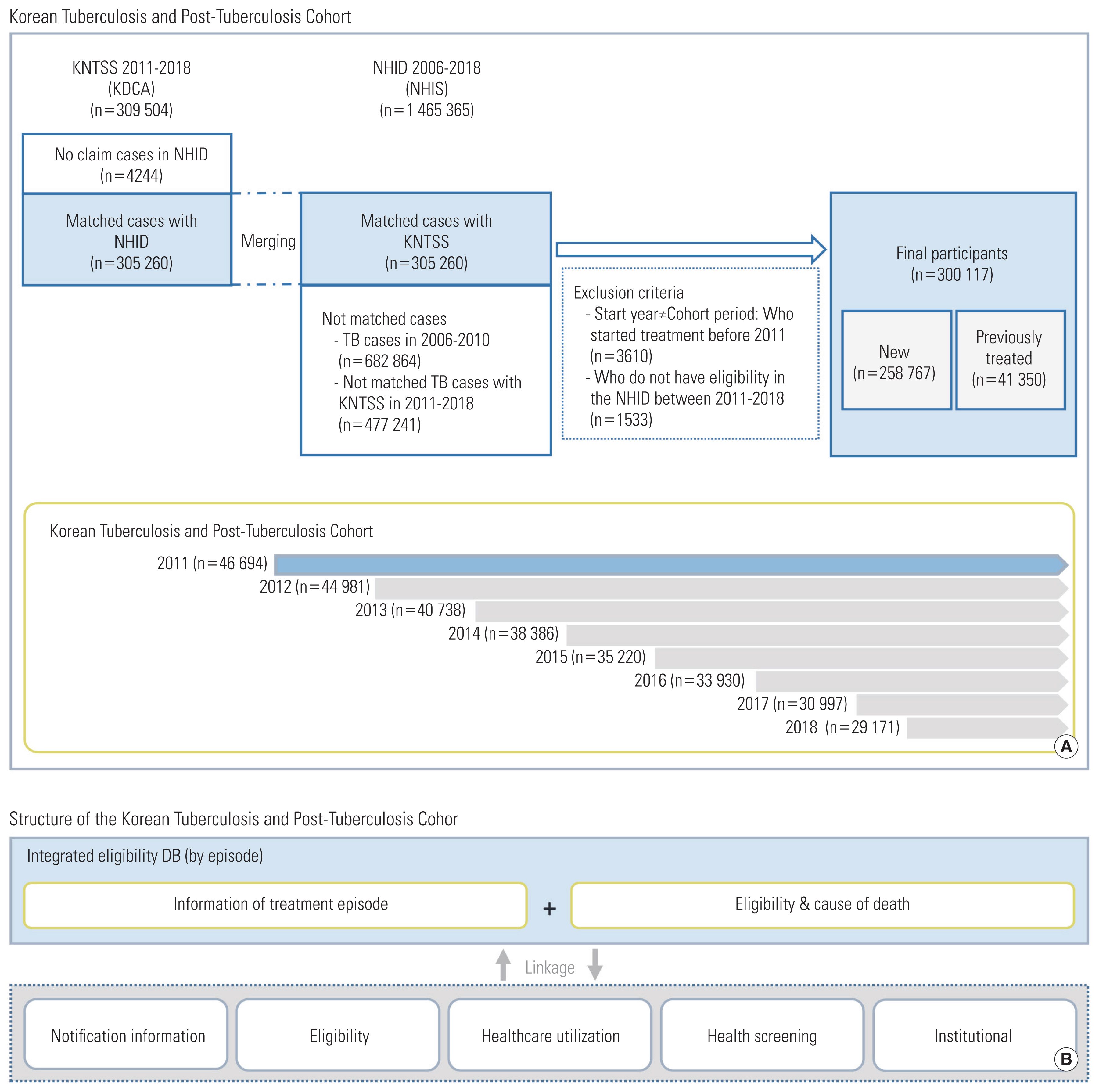
- The study cohort was constructed by linking data from (1) the KNTSS (data reported during 2011–2018), which was established by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA), (2) the NHID (data from 2006 to 2018), which was established by the NHIS, and (3) Statistics Korea database (data related to the cause of deaths, 2011–2018). Each data source contains nationwide representative data on the current status of TB patients and their insurance eligibility, medical history, and death-related information in Korea.
- TB notification data from KNTSS are currently collected and analyzed by the KDCA, which produces national statistics for monitoring and evaluating national TB management projects and supervises the publication of annual reports. The KNTSS records patients’ personal information, diagnostic test results (clinical, radiological, bacteriological, and histological examinations), diagnostic records, treatment information, and information on death during the treatment period, along with treatment outcomes [12]. TB patients from the KNTSS data are confirmed and reported as infected according to the tuberculosis diagnostic test standards at medical institutions. Unlike secondary data sources (e.g., NHID), it does not require an operational definition, so it was used as the main data source for study subjects for data linkage. We utilized data from 2011 to 2018 considering the data linkage available years.
- The NHID is a public database of personally unidentifiable data for research established by the NHIS. The NHID has data on claims of healthcare providers reported by the NHI process for a single insurer and information on the insurance eligibility, insurance contributions, medical history, and medical institution of all citizens. Thus, the NHID has been used for various studies at the individual level because it contains information on socio-demographic variables (health insurance, Medical Aid beneficiaries, insurance premiums), healthcare utilization, health screening, and mortality of citizens [7]. Therefore, TB-related utilization of TB patients not identified in KNTSS and diagnostic information of comorbidities, other diseases, drug prescriptions, and medical use can be identified. Of particular note, the insurance premium can be used as a proxy indicator for socioeconomic position. These data were linked to data from 2006 to 2018 to confirm the history of patients reported to KNTSS in 2011–2018.
- Information on causes of death was acquired by linkage with the Causes of Death Statistics report of Statistics Korea. Statistics Korea provides a variable for the cause of death through the NHIS only for studies linked with the NHID; it requires approval by the Microdata Integrated Service of Statistics Korea. We linked the TB patients confirmed as having died between 2011 and 2018 in the NHID with the cause of death variable, which was the underlying cause of death on death certificates, after the approval by Statistics Korea. Causes of death were available as International Statistical Classification of Disease and Related Health Problems, 10th revision (ICD-10) codes [13] to facilitate international comparisons according to the WHO classification guidelines [14]; these were converted to the Korean Standard Classification of Diseases and Causes of Death (KCD-7) for use in the Korean context.
- Data Linkage
- The data linkage process was led by the National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency (NECA), the research organizer, after the protocol was approved by the NECA Research Data Deliberation Committee. After obtaining approval from NHIS’s National Health Information Data Request Review Committee, TB report data were obtained through cooperation with the KDCA and linked to the NHIS for the final dataset. Data linkage was implemented through each data source’s resident registration number, which was converted into an alternative personal identification number after linkage to identify subjects from each data source in an anonymized analysis. Data linkage was established for the matched TB patients reported to the KNTSS from 2011 to 2018 and those with a medical claim for TB and TB-related diseases in the NHID from 2006 to 2018. The data of participants with confirmed deaths were linked with the cause-of-death variable from the Causes of Death Statistics of Statistics Korea (conducted by the NHIS).
- Participants
- The Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort comprised patients registered in the KNTSS from 2011 to 2018. Considering subjects identified in the KNTSS, those with at least one claim of TB-related diseases (ICD-10 codes A15-A19, B90, U84.3, U88) in the NHID (2006–2018) were included in the cohort. Subjects within NHID not linked through personal identification numbers were Koreans without information on the insurance type or foreigners (not included in the health insurance system) (Figure 1). These subjects were excluded because it was impossible to track their demographics and health-related results in the NHID or to check for duplicates among data sources.
- The cohort of TB patients identified through the two sources comprised individual integrated treatment episodes, from the first date of diagnosis (index date) to the date of treatment result (TB cured, treatment completion, failure, loss to follow-up, death during treatment, not evaluated, missing), considering 2011–2018 as each individual’s TB treatment episode (e.g., the treatment result was “treatment completion” in the first episode, but a second episode was counted if TB recurred later) (Supplemental Materials 1 and 2).
- The subjects were linked with NHID data from 2006 to 2018. Using NHID data, we collected data on the subjects’ changes in eligibility and insurance premiums, specific TB treatment details, treatment history, and treatment outcomes (e.g., death) during the study period.
- Variables
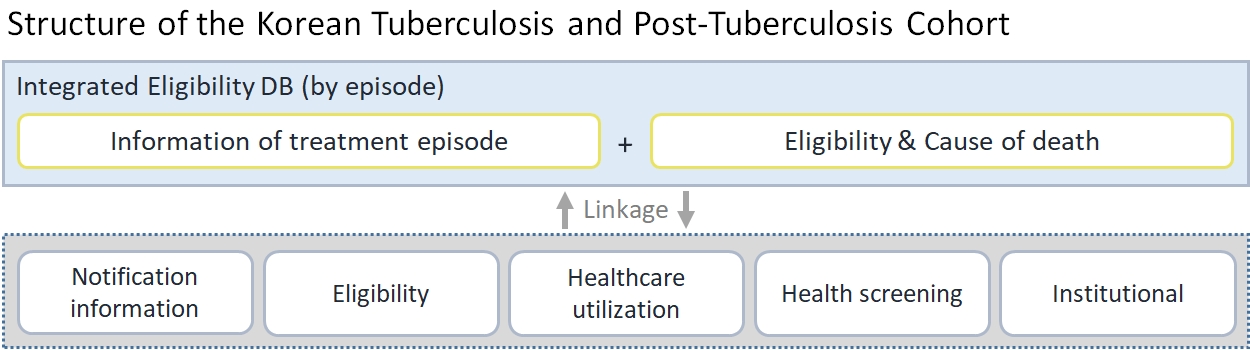
- The constructed database comprises integrated eligibility data of TB patients, KNTSS data, NHID data (healthcare utilization, health screening, and healthcare institution). The integrated TB data table includes both health insurance qualifications of NHID and notification data of KNTSS at the time of reporting based on the KNTSS notification date for each TB treatment episode. The database includes variables on demographic characteristics (personal de-identification number, gender, age, nationality, type of insurance [health insurance, Medical Aid], income decile based on monthly insurance premium on the first day of the year, residential area, disability information, death information [date and cause of death]) and KNTSS notification information (patient classification [new patient or previously treated patient], date of notification, index date, the number of re-treatments, end date of treatment, treatment result, public-private mix program medical institution, type of TB, primary diagnostic test results [radiology, sputum smear test, sputum culture test, polymerase chain reaction, Xpert]). The NHID variables correspond to eligibility data, healthcare utilization data, institutional data, health screening data, and death information (Table 1).
- The integrated table included eligibility and death from the NHID variables, and the health utilization data comprised claims data for medical history. Researchers can analyze medical status, treatment details, disease, and drug prescription history information by integrating these parameters with the “common key” variable. The incident and prevalent cases of diseases of interest, underlying diseases, or TB can be confirmed using the following criteria: the frequency of admissions or visits, diagnostic codes, and drug prescription details according to operational definitions from previous studies. Variables including comorbidities such as the Charlson comorbidity index can be defined. Moreover, therapeutic regimens and drug resistance patterns can be identified with drug resistance prescription details and Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classification codes.
- The integrated TB database constitutes a kind of individual treatment episode dataset by the year of the index date, which has personal yearly variables. It followed the main database, KNTSS, which is applicable only once a year for each patient. The eligibility data and health screening data also have the same structure. The daily healthcare service utilization data, generated at every visit, comprise the type of care (inpatient or outpatient), diagnostic codes, medical services, and prescriptions for drugs. Finally, mortality data (death and cause of death) are generated only once for the entire cohort period.
- Ethics Statement
- This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency (NECAIRB19-008-1). In order to study other research questions using the linked data, the data linkage procedures of KCDA, NHIS, and Microdata Integrated Service are required again after separate institutional review board approval.
COHORT DESCRIPTION
- Initially, 305 260 patients were linked through a combination of the KNTSS and NHID. In total, 300 117 patients were included after excluding 3610 patients who were reported in or started treatment outside the inclusion period (2011–2018) and 1533 patients without eligibility data in the cohort period (2011–2018) (Figure 1).
- The cohort contained more men (n=177 206) than women (n=122 911). Considering age, men aged 50–59 years (20.1%) and women aged 70–79 years (19.1%) showed the highest proportion of TB. There were more new TB cases than previously treated TB cases regardless of gender, although the percentage of re-treatments was higher in men (16.4%) than in women (10.0%). The number of patients gradually decreased over time, although this trend was not statistically significant; the difference in gender distribution was insignificant by year (0.1–0.2%p; Table 2). Details of the characteristics are shown in Supplemental Material 3.
- The treatment outcomes for TB patients were calculated according to the WHO definition. In the treatment results of the new TB patients in 2011–2018, the proportion of TB treatment success increased (from 77.9 to 86.7% by 2015) and then gradually decreased. The treatment success rates gradually increased from 75.8% to 83.6% in men and 80.8% to 85.6% in women. The highest rates were observed for both men and women in 2015 (85.4 and 88.4%, respectively). There was no significant change in the treatment failure rate. The loss to follow-up (LTFU) rate decreased from 5.3% to 1.8%, with a change from 6.0% to 2.0% among men and from 4.3% to 1.4% among women. TB-related deaths during treatment increased slightly until 2016 and then decreased. They had similar increasing trends followed by a decrease. The rate of other deaths gradually increased (from 3.7 to 10.2% overall, from 4.1 to 10.5% in men, and from 3.2 to 9.8% in women). The rate of undetermined evaluations gradually decreased (Table 3 and Supplemental Material 4).
- Re-treated patients had similar trends to those of new patients. The rates of treatment success increased from 2011 to 2014, and then decreased. Men (76.8%) had the highest treatment success rate in 2016 and women (84.7%) in 2014. The treatment failure rate decreased slightly, from 0.5% to 0.2% for men and from 0.4% to 0.2% for women. The LTFU rate declined and increased again in 2015, and then decreased from 7.5% to 6.7%. The LTFU rate by gender declined and increased again in 2015, then decreased from 8.1% to 6.2% in men. The LTFU rate in women slightly fluctuated, but increased from 3.7% to 7.8% from 2014 to 2018. There was no significant change in TB-related deaths during treatment. The proportion of other deaths during treatment gradually increased (from 4.2 to 10.6% overall, from 4.6 to 11.2% among men, and from 3.3 to 9.0% among women). The percentage of undetermined evaluations gradually decreased until 2016 (1.7%) and increased thereafter (Table 3 and Supplemental Material 4).
- Among the 300 117 subjects with matched data, the causes of death were confirmed in 53 906 cases in the NHID or KNTSS from 2011–2018; the number of deaths was 53 374 in the NHID and 26 461 in the KNTSS. However, regarding the KNTSS, when a registered person died during treatment, the relevant medical institution was required to record the death information, according to which deaths were classified as TB-related or non-TB-related. Therefore, it is difficult to follow up when the death occurred after treatment termination of LTFU. Regarding the proportion of TB deaths among the deaths of TB patients, 25.1% (n=13 423) of all deaths (n=53 374) were in the NHID, and 21.7% (n=5754) of the 26 461 deaths in the KNTSS were from TB (Supplemental Material 5). The proportion of TB deaths in the total number of deaths in NHID continued to decrease from 47.6% in 2011 to 16.7% in 2018. Accordingly, the proportion of people who died from causes other than TB increased.
- The most common non-TB-related causes of death were lung and bronchial cancer (8.2%), pneumonia (6.7%), cerebrovascular disease (4.7%), other cardiovascular diseases (4.0%), chronic lower respiratory disease (3.5%), ischemic heart disease (3.3%), and diabetes (3.0%) (Figure 2 and Supplemental Material 6). The leading causes of death from 2011 to 2018 in the general population were cerebrovascular disease, lung and bronchial cancer, pneumonia, ischemic heart disease, and intentional self-harm (suicide) [15,16]. Therefore, the distribution of deaths in the TB cohort showed a slightly different pattern from that in the general population.
FINDINGS
- The main advantage of our database is that the information possessed by the relevant data sources is linked. Since preliminary information on each data source is linked, various studies can use the strengths of each data source (e.g., an analysis of treatment outcomes according to socioeconomic variables can examine vulnerability factors). Potential findings from studies using this database would provide an opportunity to strengthen the KNTSS. The KNTSS has mainly focused on capturing epidemiological and clinical characteristics. However, future studies using our database could generate crucial evidence on issues including health inequity among TB patients and vulnerability factors associated with poor prognosis. Consequently, the KNTSS could fortify the surveillance system by measuring more variables. Next, the reliability of the key indicators for TB management can be improved. The information on patients with TB managed in separate data sources is linked; thus, the actual trends of TB in Korea can be determined. The severity of TB can be estimated at the time of diagnosis using information related to the diagnostic test results. The degree of disease progression at the time of diagnosis can be estimated using chest radiography findings, acid-fast bacilli smear results, and culture results. Finally, research can track long-term life after TB diagnosis and treatment. It would also be possible to analyze risk factors for patients who relapse or die after uneventful completion of TB treatment and to design a study tracking the re-treatment of TB patients who stop treatment or the emergence of drug resistance.
- However, the Korean Tuberculosis and Post-Tuberculosis Cohort has some limitations. First, the KNTSS was linked only to the first reported information of the notification year for each patient. If a patient was reported multiple times during the year, there would be no way to track changes in the values of the diagnostic tests performed at the time of each report. Nevertheless, this cohort contains information on the same patients, regardless of relapse or re-treatment, reported in different years. Second, data loss may occur because there are no data for non-claimed cases. The KNTSS covers all cases of TB infection in Korea, but the NHID contains data for claims from medical institutions. However, these account for less than 1.5% of all patients. Therefore, there is no apparent problem in testing the hypotheses of different studies using data from this cohort. Third, the information on health screening is included in 66.2% of the total cohort; thus, information on all patients’ examinations cannot be analyzed when using the data (Supplemental Materials 7 and 8). According to the National Health Examination Statistical Yearbook, the national health examination rate increased from 72.6% in 2011 to 76.9% in 2018. Since the health examination rate of our cohort was 66.2%, there should be no problem in conducting research using the examination data. Finally, by linking several sources in this cohort, socioeconomic levels, causes of death, and disease history can be studied together. However, both the NHID and Cause of Death Statistics data are secondary data, which are limited because they can only be used as proxy indicators or considered as operational definitions. Thus, additional verification and supplementation in the public health monitoring system established for TB elimination and management are needed, along with suggestions for a public health monitoring system based on cohort research results.
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES
- Cohort data can be used in various studies. Researchers can use this cohort data to identify the determinants of TB from an epidemiological perspective (e.g., studies can be conducted on seasonality and socioeconomic position of TB outbreaks in Korea, medical use patterns, and health outcomes according to the presence or absence of TB resistance, multidrug-resistant TB incidence rates, and differences in TB characteristics and treatment outcomes according to regions and income levels). Second, research on treatment methods can be conducted, including evaluating the compliance rate of standard treatment regimens during initial treatment for new patients; analyzing the risk factors of TB outbreak, recurrence, and death in patients with diabetes; treating TB patients with chronic diseases in multimorbidity; and evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of new TB drugs. Third, the cohort data can be used to facilitate research on multidrug-resistant TB, including an estimation of the medical cost burden for multidrug-resistant TB patients and risk factors for transfer, undetermined evaluation, and treatment discontinuation for patients with multidrug-resistant TB. Finally, studies on policy-related issues can be conducted to compare the characteristics of cases of death or to study the mechanisms of health inequalities.
CONCLUSION
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
-
FUNDING
This study was financially supported by the National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (grant No. NC19-002, NC20-003, and NC21-001) and by an intramural research grant from the Korean National Tuberculosis Association.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Kim HS, Choi H. Data curation: Jeong D, Kim J, Kang HY. Formal analysis: Jeong D, Kang HY. Writing – original draft: Jeong D, Kang HY, Choi H. Writing – review & editing: Jeong D, Kang HY, Kim J, Lee H, Yoo BN, Kim HS, Choi H.
Notes

- 1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report; 2020 [cited 2021 Nov 25]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131
- 2. Cho KS. Tuberculosis control in the Republic of Korea. Epidemiol Health 2018;40: e2018036ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Go U, Park M, Kim UN, Lee S, Han S, Lee J, et al. Tuberculosis prevention and care in Korea: evolution of policy and practice. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis 2018;11: 28-36ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Na BJ, Kang MY, Hong JY, Kim EY, Kim KY, Lee MS, et al. The ratio of medical aid over health insurance of age adjusted mortality rate of tuberculosis and related factors. J Agric Med Community Health 2006;31(1):9-20. (Korean)
- 5. Kim HJ. Current status of tuberculosis in Korea. Korean J Med 2012;82(3):257-262. (Korean)Article
- 6. Kang HY, Yoo H, Park W, Go U, Jeong E, Jung KS, et al. Tuberculosis notification completeness and timeliness in the Republic of Korea during 2012–2014. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2016;7(5):320-326ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Seong SC, Kim YY, Khang YH, Heon Park J, Kang HJ, Lee H, et al. Data resource profile: the national health information database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46(3):799-800PubMed
- 8. Chu H, Shih CJ, Lee YJ, Kuo SC, Hsu YT, Ou SM, et al. Risk of tuberculosis among healthcare workers in an intermediate-burden country: a nationwide population study. J Infect 2014;69(6):525-532ArticlePubMed
- 9. Lee CC, Lee MG, Hsu WT, Park JY, Porta L, Liu MA, et al. Use of calcium channel blockers and risk of active tuberculosis disease: a population-based analysis. Hypertension 2021;77(2):328-337ArticlePubMed
- 10. Chen YT, Kuo SC, Chao PW, Chang YY. Use of lipid-lowering agents is not associated with improved outcomes for tuberculosis patients on standard-course therapy: a population-based cohort study. PLoS One 2019;14(1):e0210479ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Lalor MK, Mohiyuddin T, Uddin T, Thomas HL, Lipman M, Campbell CN. The challenge of estimating tuberculosis mortality accurately in England and Wales. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2018;22(5):572-578ArticlePubMed
- 12. Yu S, Sohn H, Kim HY, Kim H, Oh KH, Kim HJ, et al. Evaluating the impact of the nationwide public-private mix (PPM) program for tuberculosis under National Health Insurance in South Korea: a difference in differences analysis. PLoS Med 2021;18(7):e1003717ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. World Health Organization. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems 10th revision; [cited 2021 Nov 25]. Available from: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en
- 14. Korea Informative Classification of Disease. Korean standard classification of diseases and causes of death (KCD-7); [cited 2021 Nov 25]. Available from: https://www.koicd.kr/kcd/kcds.do (Korean)
- 15. Shin HY, Lee JY, Kim JE, Lee S, Youn H, Kim H, et al. Cause-of-death statistics in 2016 in the Republic of Korea. J Korean Med Assoc 2018;61(9):573-584. (Korean)ArticlePDF
- 16. Korean Statistical Information Services. Deaths by cause (103 item); 2021 [cited 2021 Nov 25]. Available from: https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1B34E02&conn_path=I2&language=en
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- A Quasi-experimental Study on the Effect of Pre-entry Tuberculosis Screening for Immigrants on Treatment Outcomes in South Korea: A Difference-in-Differences Analysis
Sarah Yu, Dawoon Jeong, Hee-Yeon Kang, Young Ae Kang, Gyeong In Lee, Hongjo Choi
Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health.2024; 14(1): 154. CrossRef - Relationship between metformin use and mortality in tuberculosis patients with diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Eunki Chung, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Heejin Kim, Heesun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 39(2): 306. CrossRef - Trends in Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases in Humans and Animals during COVID-19 Pandemic, South Korea
Taehee Chang, Sung-il Cho, Dae sung Yoo, Kyung-Duk Min
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Beyond reducing direct medical cost: examining health outcomes in tuberculosis through a difference-in-differences analysis of South Korea’s out-of-pocket payment exception policy
Sarah Yu, Daseul Moon, Dawoon Jeong, Young Ae Kang, Gyeong In Lee, Hongjo Choi
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Timing and predictors of death during treatment in patients with multidrug/rifampin-resistant tuberculosis in South Korea
Eunjeong Son, Hongjo Choi, Jeongha Mok, Young Ae Kang, Dawoon Jeong, Doosoo Jeon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 39(4): 640. CrossRef - Sex differences in the impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis recurrence: a retrospective national cohort study
Dararat Eksombatchai, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 127: 1. CrossRef - Nationwide Treatment Outcomes of Patients With Multidrug/Rifampin-Resistant Tuberculosis in Korea, 2011–2017: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Korean TB-POST)
Hongjo Choi, Jeongha Mok, Young Ae Kang, Dawoon Jeong, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Doosoo Jeon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - Impact of Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Use on Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Pulmonary Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study with Propensity Score Matching
Hongjo Choi, Dawoon Jeong, Young Ae Kang, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeongha Mok
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2023; 86(3): 234. CrossRef - Retreatment after loss to follow-up reduces mortality in patients with multidrug/rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis
Hongjo Choi, Jeongha Mok, Young Ae Kang, Dawoon Jeong, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Doosoo Jeon
ERJ Open Research.2023; 9(4): 00135-2023. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and cause of death in patients with tuberculosis: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Se Hyun Kwak, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang, Frederick Quinn
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0295556. CrossRef
 KSPM
KSPM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite