Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Prev Med Public Health > Volume 53(6); 2020 > Article
-
COVID-19: Original Article
Anticipating the Need for Healthcare Resources Following the Escalation of the COVID-19 Outbreak in the Republic of Kazakhstan -
Yuliya Semenova1
 , Lyudmila Pivina2
, Lyudmila Pivina2 , Zaituna Khismetova3
, Zaituna Khismetova3 , Ardak Auyezova4
, Ardak Auyezova4 , Ardak Nurbakyt5
, Ardak Nurbakyt5 , Almagul Kauysheva6
, Almagul Kauysheva6 , Dinara Ospanova7
, Dinara Ospanova7 , Gulmira Kuziyeva8
, Gulmira Kuziyeva8 , Altynshash Kushkarova9
, Altynshash Kushkarova9 , Alexandr Ivankov10
, Alexandr Ivankov10 , Natalya Glushkova5
, Natalya Glushkova5
-
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health 2020;53(6):387-396.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.20.395
Published online: October 5, 2020
1Department of Neurology, Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology, Semey Medical University, Semey, Kazakhstan
2Department of Internal Medicine, Semey Medical University, Semey, Kazakhstan
3Department of Public Health, Semey Medical University, Semey, Kazakhstan
4Head Office, Kazakhstan Medical University Higher School of Public Health, Almaty, Kazakhstan
5Department of Epidemiology, Evidence Medicine and Biostatistics, Kazakhstan Medical University Higher School of Public Health, Almaty, Kazakhstan
6Department of Research and International Affairs Kazakhstan Medical University Higher School of Public Health, Almaty, Kazakhstan
7Department of Public Health, Kazakh Medical University of Continuing Education, Almaty, Kazakhstan
8Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Evidence-Based Medicine, Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, Almaty, Kazakhstan
9Medical College, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Shymkent, Kazakhstan
10Department of Postgraduate Education, Kazakh Medical University of Continuing Education, Almaty, Kazakhstan
- Corresponding author: Natalya Glushkova, MD, PhD Department of Epidemiology, Evidence Medicine and Biostatistics, Kazakhstan Medical University Higher School of Public Health, Utepova 19A, Almaty 050010, Kazakhstan E-mail: glushkovanatalyae@gmail.com
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Society for Preventive Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Objectives
- The lack of advance planning in a public health emergency can lead to wasted resources and inadvertent loss of lives. This study is aimed at forecasting the needs for healthcare resources following the expansion of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in the Republic of Kazakhstan, focusing on hospital beds, equipment, and the professional workforce in light of the developing epidemiological situation and the data on resources currently available.
-
Methods
- We constructed a forecast model of the epidemiological scenario via the classic susceptible-exposed-infected-removed (SEIR) approach. The World Health Organization’s COVID-19 Essential Supplies Forecasting Tool was used to evaluate the healthcare resources needed for the next 12 weeks.
-
Results
- Over the forecast period, there will be 104 713.7 hospital admissions due to severe disease and 34 904.5 hospital admissions due to critical disease. This will require 47 247.7 beds for severe disease and 1929.9 beds for critical disease at the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak. There will also be high needs for all categories of healthcare workers and for both diagnostic and treatment equipment. Thus, Republic of Kazakhstan faces the need for a rapid increase in available healthcare resources and/or for finding ways to redistribute resources effectively.
-
Conclusions
- Republic of Kazakhstan will be able to reduce the rates of infections and deaths among its population by developing and following a consistent strategy targeting COVID-19 in a number of inter-related directions.
- Many uncertainties originate from the possible scarcity of healthcare resources due to the rapid escalation of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by a novel coronavirus (CoV) associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) secondary to atypical pneumonia. This CoV belongs to the family Coronaviridae and is likely to be a zoonosis in nature, as it shares many similarities with SARS-CoV, which was spread to humans through palm civets and raccoon dogs as incidental hosts [1]. COVID-19 emerged in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and quickly spread globally, reaching the Republic of Kazakhstan (hereafter Kazakhstan) in March 2020 [2].
- On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic [3], and viral pandemics tend to present serious threats to healthcare systems by imposing extraordinary and sustained demands on them [4]. These demands can exceed the service capacity with regard to both inputs and outputs, undermining the availability of sufficient resources, infrastructure, technologies, and professional workforce. COVID-19 presents the enormous challenge of balancing between equality and equity for people in the distribution of risks and benefits. In view of the increasing frequency of COVID-19 cases among the country’s population, there is an urgent need to evaluate best practices in order to optimize the use of available means and resources. This is particularly true for intensive care unit (ICU) beds and related equipment that are at imminent risk of unavailability. Thus, it is essential to establish clinical, technical, and ethical criteria to make the best use of these resources in order to ensure the greatest possible benefits for COVID-19 patients [5].
- Some international professional associations have argued that, since the pandemic is an exceptional situation, it must be managed in the same way as any crisis situation and requires measures of conflict/catastrophe or disaster medicine [6,7]. However, to do so, solid technical and scientific criteria, strict ethical principles, and legal considerations must be taken into account. Besides, a fair allocation of available resources requires an ethical decision-making framework, which can be adapted and revised depending on the context of the developing situation. Healthcare systems and individual providers must be prepared to make the most of limited resources and to reduce the damage to people and society [5]. The weight of decisions about the allocation of available healthcare resources should not fall on the professionals who are in the front line of the epidemic and are already overburdened by the scenario that is unfolding, experiencing increased risks of failure and professional stress. In contrast, healthcare providers need to be protected in this process, since they are fundamental to face the issue of the escalating outbreak [8].
- The lack of advance planning in a public health emergency can lead to the waste of resources and inadvertent loss of lives, as well as jeopardizing the trust of the general public in medical services [9-11]. This study is aimed at forecasting the needs for healthcare resources following the escalation of the COVID-19 outbreak in the Kazakhstan, focusing on hospital beds, equipment, and the professional workforce, in light of the developing epidemiological situation and the data on resources currently available.
INTRODUCTION
- Data Sources
- Currently, the Ministry of Health of the Kazakhstan reports all COVID-19 cases registered in the country through a special website maintained by the National Center of Public Health [12]. In order to anticipate the need for healthcare resources, we built a real-time database from those data. We also used the World Bank data on the population size in Kazakhstan, which equaled 18 654 000 people in 2020 [13], as well as on available healthcare resources. As for the latter, we utilized the Republican Center for Health Development (RCHD) dataset to get information on the number of medical workforce in the Kazakhstan [14]. Data on available hospital beds in the country were also obtained from the RCHD [14], while the number of available beds in infectious disease units were extracted from the reports of the Ministry of Health, Kazakhstan [15].
- Mathematical Modeling
- The classic 4-compartmental susceptible (S) – exposed (E) – infected (I) – removed (R) (SEIR) model was utilized to estimate the spread of the COVID-19 outbreak in the Kazakhstan [16]. The SEIR model categorizes the country’s population into 4 broad compartments: susceptible (those who can develop the disease of interest), exposed (those who are already infected but are asymptomatic), infected (those who are infected and present with symptoms and signs), and removed (those who are recovered or dead) [17]. We updated an earlier published SEIR model on the COVID-19 outbreak in Kazakhstan [2] for the next 12 weeks, incorporating the latest epidemiological data, and included official data on the cumulative number of symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
- Thus, we entered the following variables into the SEIR model: cumulative number of infected, which equaled 131 596 (including asymptomatic polymerase chain reaction [PCR]-positive patients); duration of the incubation period (5 days); duration of mild and asymptomatic infections (5 days); proportion of infections that are asymptomatic (30%); proportion of infections that are severe (2%); duration of severe infection (hospital stays), which was estimated to be 10 days; proportion of infections that are critical (2%); duration of critical infections or ICU stays (15 days); death rate for critical infections (0.55%); the country’s population size (18 654 000); the maximum time of forecast (80 days); the transmission rate for infections that are asymptomatic (0.50 days), mild infections (0.39 days), severe infections (0.01 days), and critical infections (0.01 days); R0 (reproduction number)=2.12; T2 (doubling time)=8 days; and r (number of contacts a day)=0.091.
- To predict the number of COVID-19 cases in need of hospitalization versus healthcare capacity (number of severe and critically ill patients vs. the capacity of the healthcare system, which is constrained or capped by inpatient bed availability in the whole country or by the availability of beds provided for COVID-19 patients), the construction of the classic SEIR model was followed by analyses of general hospital beds and the number of available beds for COVID-19 patients in the Kazakhstan. We assumed that inpatient beds would be reserved solely for severe infections (symptomatic patients presenting with severe pneumonia associated with dyspnea, respiratory rate >30/min, blood oxygen saturation <93%, ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen [PaO2/FiO2] <300, and/or infiltrates exceeding 50% of the lung volume) and critical infections (symptomatic patients with respiratory failure, septic shock, and/or multiple organ dysfunction or failure) [18].
- Forecasting the Need for Healthcare Resources
- After a strict quarantine was imposed across the country from March 19, 2020 until mid-May 2020, its subsequent weakening was accompanied by the escalation of the COVID-19 outbreak, with a substantial increase in the number of infections and deaths. This returned the epidemic to the starting point and, for example, resulted in the shortening of T2 from 10 days to 7 days. The COVID-19 Essential Supplies Forecasting Tool (COVID-ESFT, version 2.0) [19] was used to generate a forecast model of the healthcare resources needed for the next 12 weeks, beginning on September 2, 2020. The COVID-ESFT helps to estimate the demand for essential supplies, including biomedical and diagnostic reagents and equipment, medical workforce, and infrastructure, based on a prior evaluation of COVID-19 patient numbers depending on their severity. The COVID-ESFT is best used for estimates over a short time period and does not take into account the already available resources, which must be factored in additionally. Clinical guidance, current practice, and international standards stand behind the assumptions for equipment and workforce needs, infrastructure required, and oxygen demands [19]. As the COVID-ESFT is not an epidemiological tool, we preliminarily constructed the SEIR model to ground our judgments regarding the need for healthcare resources. The variables needed for healthcare resource planning were acquired from the statistical compilation issued by the RCHD and were entered into the model manually [14]. The list of available healthcare resources and underlying assumptions are presented in Table 1.
- The Ministry of Health of the Kazakhstan made a number of provisions for a timely and adequate response to the COVID-19 outbreak. These included the allocation of additional inpatient beds with a maximum number of 20 000 [20]. To calculate the difference in the number of beds available for the COVID-19 response at its peak and the actual number of beds needed based on predictive modeling, we used the following formula:
- Percentage difference=(a/b-1)*100 %, where “a” is a bigger number and “b” is a smaller number
- Ethics Statement
- The permission from research ethics committee was not obtained since we only relied on official statistics presented in open data sources.
METHODS
- According to the mathematical model, over the forecast period there will be 104 713.7 hospital admissions due to severe disease and 34 904.5 hospital admissions due to critical disease. This will require 47 247.7 beds for severe disease and 1929.9 beds for critical disease at the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak. Out of the 20 000.0 beds allocated by the Ministry of Health, 11 336.0 will be occupied by severely ill patients and 664.0 will be occupied by critically ill patients. Thus, the expected shortage of beds for severe disease constitutes 35 912.0 or 316.8% while that for critical disease constitutes 1265.9 or 190.6% (Table 2).
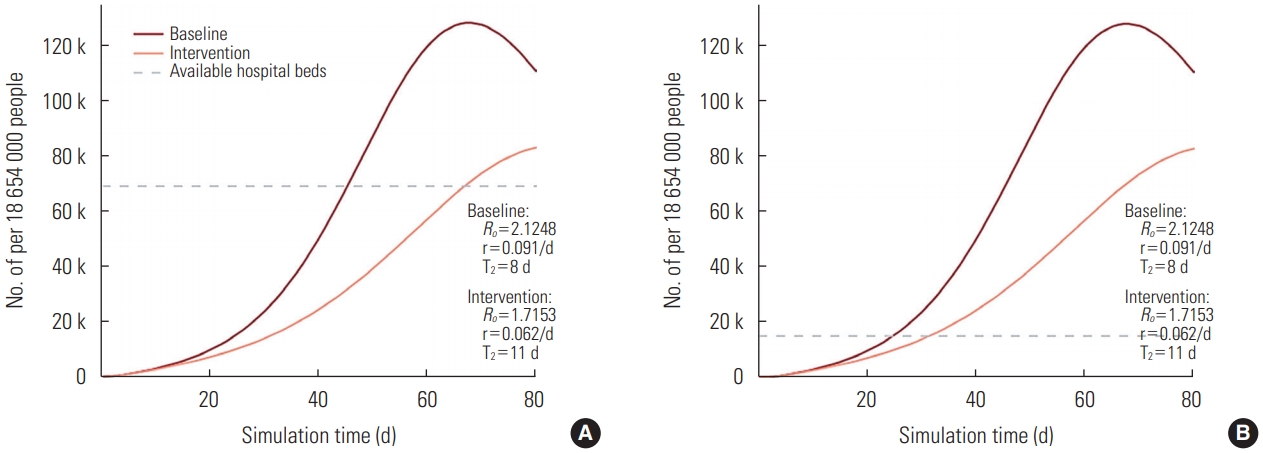
- Figure 1A depicts the number of all inpatient beds available in the country, including both governmental and private healthcare sectors, according to the outbreak progression. The dark red line is an outbreak forecast with no intervention measures being applied and the light red line represents the impact made by the introduction of quarantine measures. Both the dark red and light red lines present forecasts only for severe and critical cases, since mild and moderate cases are treated at the outpatient level. The gray dotted line displays the current number of all available inpatient beds (70 411), which is far beyond the need of severely and critically ill COVID-19 patients. According to the graph, the acute shortage of inpatient beds will start at day 46 of the forecast if no intervention measures are applied and at day 73 with the introduction of quarantine. Figure 1B depicts the number of inpatient beds available for COVID-19 treatment in Kazakhstan, based on the statement made by the Minister of Health. This number is equal to 20 000 and originates from the repurposing of provisional hospitals as infectious disease hospitals. In this case, the acute shortage of inpatient beds begins even earlier.
- The forecasted patient numbers and bed availability in Kazakhstan are presented in Table 3, according to which the demand for inpatient beds increases drastically following the growing numbers of severely and critically ill patients, reaching its peak in the second week of the forecast, with a subsequent rapid decline. This reflects a high need for all categories of healthcare workers, beginning from cleaners and caregivers and ending with the professional medical workforce (Table 3). The maximum demand for PCR testing, which is considered obligatory for the confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis in the Kazakhstan, follows in the second week of the forecast with a relatively gradual decline due to a decreasing number of COVID-19 patients. A detailed specification of the forecasted need for treatment equipment according to the total expected caseload is presented in Table 4. As the actual number of available equipment in the country has not been reported, it may be assumed that it will be necessary to procure additional equipment to deal with spillover of an outbreak.
RESULTS
- This research was conducted to evaluate the needs for healthcare resources following the expansion of COVID-19 outbreak in the Kazakhstan. The forecast was grounded on mathematical modeling of a rapidly developing epidemiological situation and used the WHO tool to anticipate the demands for hospital beds, equipment, and professional workforce. In essence, this research presents internationally comparable data on the epidemiology of the COVID-19 outbreak, complementing an earlier publication on the promising effects of mass quarantine in the Kazakhstan [2]. Still, after the early introduction of quarantine and other community protection measures, the decision was made to re-open the country by mid-May, which was followed by a rapid escalation of the outbreak with increasing numbers of deaths and severe and critical infections [21]. This required re-consideration of the outbreak scenario, including the need to estimate the availability of healthcare resources.
- The major finding of this study is that if the forecasted epidemic growth occurs in reality, the abundance of severely and critically ill patients will overwhelm the country’s healthcare system very quickly, leaving no free hospital beds for other patients. This dictates the need to act in 2 different directions: reducing the number of new COVID-19 cases and optimizing the existing healthcare services to make them more fit for the emerging situation [22]. The endorsement of communitywide and personal protective measures would perhaps be the best strategy to reduce the number of new disease cases. As these measures are more effective in combination, they should be repeatedly encouraged by both the country’s officials and opinion leaders. Timely identification and isolation of disease cases works better at the early stages of an outbreak and mass quarantine could be beneficial at any stage [23]. For more effective modeling of an outbreak forecast, a deterministic SEIR compartment model with quarantine measures could be used, if these data are available [24]. As for optimization of healthcare services, various approaches could be implemented, including construction of new hospitals, re-profiling of existing hospitals for COVID-19 patients, and considering all patients as potential cases with subsequent treatment based on their clinical presentation [25].
- Some other factors must be considered in the combat against the COVID-19 outbreak. Triage or sorting of patients is a common approach applied in public health emergencies. Determining the priority of treatment based on the disease severity or infection risk imposed on other people requires the development of very accurate standard criteria. Triage augments clinical and economic efficiency, safety, and availability of timely medical care [26]. Reverse triage is a way to reorient hospital resources to critically ill patients [27]. Emergency departments (EDs) of multidisciplinary hospitals, emergency medical services, and outpatient clinics are currently the main places where sorting of COVID-19 patients takes place [28]. This situation is complicated by a very limited number of unified clinical guidelines or care protocols devoted to the triage of patients with COVID-19 [29].
- The Australasian College for Emergency Medicine issued a clinical management guide for COVID-19 in EDs with limited resources that emphasizes the importance of maintaining control and standards for infection prevention, using personal protective equipment, and establishing isolation zones and waiting areas to minimize the number of patients and to separate patients with respiratory symptoms from others. There should also be clear criteria for hospitalization, isolation, and patient discharge, and every hospital is recommended to introduce an isolation ward to minimize COVID-19 spread. The staff of EDs must enable the timely identification of patients who present with fever or respiratory symptoms and show signs of shock or respiratory distress in order to transport them to the ICU without delay [27]. The clinical guideline entitled “COVID-19 pandemic: triage for intensive-care treatment under resource scarcity” proposes considering the short-term prognosis as a decisive criterion for patient sorting in ICUs. According to this guideline, age alone should not be used as a criterion as this may cause discrimination against older people, but it should be taken into account on the basis of short-term prognosis, since older people are more likely to suffer from concomitant diseases [30].
- As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread rapidly across the world, ICUs must be prepared for a large influx of patients and to withstand additional pressure imposed by the outbreak on both patients and medical personnel [31,32]. For this, it is necessary to provide training for other healthcare professionals on how to deal with critically ill patients in need of resuscitation. It is also important to enable the provision of mechanical ventilation and especially of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) to all critically ill patients with severe pneumonia, given the high effectiveness of these procedures. In many instances, this will require allocation of additional funds to procure lacking equipment [33]. Clear threshold indicators should be developed for transferring critically ill patients to ECMO and mechanical ventilation, and steps should be taken to ensure the possibility of bronchoscopy with disposable bronchoscopes.
- For the purpose of effective infection control in ICUs and in order to prevent cross-contamination among healthcare workers, it is necessary to train staff on how to use personal protective equipment and to provide the possibility for them to take a shower at the end of the working day. The movement of medical personnel within and outside the department should be strictly limited. Although in an ideal scenario the team would go through a 2-week observation period after the shift is over, this is not always possible in resource-poor settings, where healthcare workers stay on duty for prolonged time periods with no chance for replacement. It is also very important to pre-develop models of resuscitation scenarios with different specialists and to conduct appropriate training [34].
- The rapidly escalating COVID-19 outbreak poses many requirements for the procurement of medicines, devices and equipment. It is also necessary to make a sufficient number of beds available for patients with severe forms of the disease who need maintenance therapy and continuous monitoring of their vital functions and oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry or analysis of blood gas composition. All procedures should be carried out in a well-ventilated area (at least 12 air changes per hour and a controlled direction of air flow when using mechanical ventilation). The constant availability of oxygen and mechanical ventilation apparatus should be ensured, as well as a sufficient supply of sedatives for intubated patients [35].
- In extreme conditions such as a global pandemic, healthcare systems could be weakened to such an extent that they may not be able to provide all necessary resources. In such situations, there is a need to increase rapidly the available resources or to find ways for to redistribute them effectively. Even developed countries with the most advanced healthcare systems achieved only intermediate results in controlling the COVID-19 outbreak. As compared to such countries, the healthcare system of Kazakhstan is less developed and it has started to face the consequences of significant relaxation of COVID-19-focused communitywide protective measures. Still, Kazakhstan will be able to reduce the rates of infections and deaths among its population by developing and following a consistent strategy targeting COVID-19 in a number of inter-related directions.
DISCUSSION
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
-
FUNDING
None.
Notes
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: YS, NG. Data curation: NG, AI. Formal analysis: NG. Funding acquisition: None. Methodology: NG, YS. Project administration: NG. Visualization: AI, NG. Writing – original draft: YS, NG, LP, ZK, AA, AN, AK. Writing – review & editing: YS, NG, AK, DO, GK, AI.
Notes
| Input variable | n (no. of beds/cases) | Data source, specification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare staff | |||
| No. of HCWs | 208 510 | Statistical compilation of RCHD [14]; This figure does not account for dentists | |
| Proportion of HCWs available for COVID-19 response | 0.70 | Out of all HCWs in the country, including laboratory staff | |
| No. of HCWs per bed | 2.96 | There are 70 441 hospital beds in the Republic of Kazakhstan with exclusion of nursing care beds, rehabilitation beds, palliative care beds, and psychiatric beds; Three shifts per day are needed; The no. of HCWs per bed = 208 510/70 441 = 2.96 | |
| No. of caretakers per bed | 1.00 | One per patient by default | |
| No. of ambulance technicians per bed | 0.03 | Based on 1 ambulance per 100 bed hospital with 2 operators (driver+ ambulance technician) | |
| There are 2218 ambulances in the Republic of Kazakhstan (including specialized and non-specialized ambulances) | |||
| Ambulance technicians per bed = 2128/70 441 = 0.03 | |||
| No. of beds in infectious disease units | 20 000 | 60% utilization (Ministry of Health, Republic of Kazakhstan, 2020) [20] | |
| Proportion of hospital beds available for critically ill patients. | 0.02 | 100% utilization (Ministry of Health, Republic of Kazakhstan, 2020) [20] | |
| Infrastructure | |||
| No. of ICU beds per hospital | 8.94 | Out of 788 hospitals in the country, 557 are government-owned and the rest are private; The overall no. of beds is 70 441; No. of beds per hospital = 70 441/788 = 89.39; We assume that 10% of beds in any hospital could be reprofiled to ICU beds = 89.39*0.1 = 8.94; Thus, there are 9 ICU beds per hospital | |
| Beds per 1000 population | 3.78 | Statistical compilation of RCHD [14] | |
| Country population = 18 654 000 | |||
| Beds per 1000 population = 70 441/18 654 000*1000 = 3.78 | |||
| Consultations | |||
| No. of consultations per HCW per day, on an average | 20.00 | We assume that on an average, a doctor and a nurse consult 40 patients per day each | |
| Lab operation | |||
| No. of lab staff in the country | 12 511 | Statistical compilation of RCHD [14] | |
| Proportion of lab staff available for COVID-19 response | 0.67 | Lab staff in the country, the proportion of lab staff in the country that could be used empirically for the COVID-19 response | |
| No. of tests run by each lab per day | 400.00 | Based on 2 machines with throughput of 200 tests per day, by default | |
| No. of lab staff per lab | 3.00 | Based on current known staffing models by default | |
| General information on the country’s HCWs | |||
| No. of doctors | 72 877 | Statistical compilation of RCHD [14] | |
| No. of nurses and midwives | 175 705 | Statistical compilation of RCHD [14] | |
| No. of HCWs treating hospitalized COVID-19 inpatients | 0.55 | Based on calculations in the model of inpatient vs. outpatient staff needs | |
| Proportion of HCWs responsible for screening and triaging of COVID-19 suspects | 0.15 | Based on calculations in model of inpatient vs. outpatient staff needs | |
| No. of HCWs for outpatients | 8780 | Statistical compilation of RCHD [14]; We assume that this category is covered by general practitioners available in the Republic of Kazakhstan | |
- 1. Guan Y, Zheng BJ, He YQ, Liu XL, Zhuang ZX, Cheung CL, et al. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science 2003;302(5643):276-278ArticlePubMed
- 2. Semenova Y, Glushkova N, Pivina L, Khismetova Z, Zhunussov Y, Sandybaev M, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and forecast of COVID-19 outbreak in the Republic of Kazakhstan. J Korean Med Sci 2020;35(24):e227ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. [cited 2020 Aug 11] Available from: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020
- 4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National pandemic influenza plans. 2017 [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/pandemic-resources/planning-preparedness/national-strategy-planning.html
- 5. Emanuel EJ, Persad G, Upshur R, Thome B, Parker M, Glickman A, et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020;382(21):2049-2055ArticlePubMed
- 6. Berlinger N, Wynia M, Powell T, Hester DM, Milliken A, Fabi R, et al. Ethical framework for health care institutions & guidelines for institutional ethics services responding to the coronavirus pandemic: managing uncertainty, safeguarding communities, guiding practice. 2020 Mar. 16. [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.thehastingscenter.org/ethicalframeworkcovid19/
- 7. Rubio O, Estella A, Cabre L, Saralegui-Reta I, Martin MC, Zapata L, et al. Ethical recommendations for a difficult decision-making in intensive care units due to the exceptional situation of crisis by the COVID-19 pandemia: a rapid review & consensus of experts. Med Intensiva 2020;44(7):439-445. (Spanish)ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Satomi E, Souza PM, Thomé BD, Reingenheim C, Werebe E, Troster EJ, et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources during COVID-19 pandemic: ethical considerations. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2020;18: eAE5775ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Dauletyarova M, Semenova Y, Kaylubaeva G, Manabaeva G, Khismetova Z, Akilzhanova Z, et al. Are women of East Kazakhstan satisfied with the quality of maternity care? Implementing the WHO tool to assess the quality of hospital services. Iran J Public Health 2016;45(6):729-738PubMedPMC
- 10. Dauletyarova MA, Semenova YM, Kaylubaeva G, Manabaeva GK, Toktabayeva B, Zhelpakova MS, et al. Are Kazakhstani women satisfied with antenatal care? Implementing the WHO tool to assess the quality of antenatal Services. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018;15(2):325ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Gromova O, Doschanova A, Lokshin V, Tuletova A, Grebennikova G, Daniyarova L, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in Kazakhstan: cross-sectional study. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2020;199: 105565ArticlePubMed
- 12. National Center of Public Health, Kazakhstan. Coronavirus infection COVID-19. [cited 2020 May 8]. Available from: m: https://hls.kz/коронавирусная-инфекция-covid-19 (Russian)
- 13. World Bank. Kazakhstan. [cited 2020 May 8]. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/country/kazakhstan
- 14. Republican Center for Healthcare Development. Public health. [cited 2020 May 8]. Available from: http://www.rcrz.kz/index.php/en/
- 15. Ministry of Healthcare, Kazakhstan. The number of intensive care beds in Kazakhstan (Healthcare Ministry report). [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://liter.kz/tret-reanimaczionnyh-koek-v-strane-zanyato-bolnymi-koronavirusom-minzdrav/ (Russian)
- 16. Morris JS. Modeling COVID-19 spread vs healthcare capacity. 2020 Apr. 29. [cited 2020 May 8]. Available from: https://alhill.shinyapps.io/COVID19seir/
- 17. Bhanot G, DeLisi C. Predictions for Europe for the Covid-19 pandemic from a SIR model. medRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.26.20114058Article
- 18. Liang T; Yixueyuan Affiliated Hospital. Handbook of COVID-19 prevention and treatment: compiled according to clinical experience. 2020 [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://esge.org/documents/Handbook_of_COVID-19_Prevention_and_Treatment.pdf
- 19. World Health Organization. COVID-19 essential supplies forecasting tool. [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-essential-supplies-forecasting-tool
- 20. Minister of Health of Kazakhstan Alexey Tsoi. Six basic measures to strengthen the fight against COVID-19. [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.facebook.com/196849530492917/posts/1525472110963979/ (Russian)
- 21. Covid world map: tracking the global outbreak. New York Times; 2020 Aug. 10. [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/world/coronavirus-maps.html
- 22. Chowdhury R, Heng K, Shawon MS, Goh G, Okonofua D, Ochoa-Rosales C, et al. Dynamic interventions to control COVID-19 pandemic: a multivariate prediction modelling study comparing 16 worldwide countries. Eur J Epidemiol 2020;35(5):389-399ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Ngonghala CN, Iboi E, Eikenberry S, Scotch M, MacIntyre CR, Bonds MH, et al. Mathematical assessment of the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions on curtailing the 2019 novel coronavirus. Math Biosci 2020;325: 108364ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Ryu S, Ali ST, Lim JS, Chun BC. Estimation of the excess COVID-19 cases in Seoul, South Korea by the students arriving from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020;17(9):3113ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Paital B, Das K, Parida SK. Inter nation social lockdown versus medical care against COVID-19, a mild environmental insight with special reference to India. Sci Total Environ 2020;728: 138914ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Emergency Severity Index (ESI): a triage tool for emergency departments. 2020 [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/systems/hospital/esi/index.html
- 27. Australasian College of Emergency Medicine. Managing COVID-19 across the Indo-Pacific: a guide for emergency departments with limited resources. 2020 Mar. 20. [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: https://www.ipcrg.org/sites/ipcrg/files/content/attachments/2020-03-27/Managing-COVID-19-across-the-Indo-Pacific-%28G763%29.pdf
- 28. Cao Y, Li Q, Chen J, Guo X, Miao C, Yang H, et al. Hospital emergency management plan during the COVID-19 epidemic. Acad Emerg Med 2020;27(4):309-311ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Her M. How is COVID-19 affecting South Korea? What is our current strategy? Disaster Med Public Health Prep 2020;1-3ArticlePubMed
- 30. Swiss Academy Of Medical Sciences. COVID-19 pandemic: triage for intensive-care treatment under resource scarcity. Swiss Med Wkly 2020;150: w20229PubMed
- 31. Liu Y, Li J, Feng Y. Critical care response to a hospital outbreak of the 2019-nCoV infection in Shenzhen, China. Crit Care 2020;24(1):56ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anaesth 2020;67(5):568-576ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 33. Arabi YM, Fowler R, Hayden FG. Critical care management of adults with community-acquired severe respiratory viral infection. Intensive Care Med 2020;46(2):315-328ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 34. Liew MF, Siow WT, MacLaren G, See KC. Preparing for COVID-19: early experience from an intensive care unit in Singapore. Crit Care 2020;24(1):83ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 35. World Health Organization. Hospital readiness checklist for COVID-19. 2020 Mar. 29. [cited 2020 Aug 11]. Available from: http://www.emro.who.int/images/stories/coronavirus/documents/hospital_readiness_checklist_for_covid_19.pdf?ua=1
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Evaluating the Demand for Nucleic Acid Testing in Different Scenarios of COVID-19 Transmission: A Simulation Study
Yu-Yuan Wang, Wei-Wen Zhang, Ze-xi Lu, Jia-lin Sun, Ming-xia Jing
Infectious Diseases and Therapy.2024; 13(4): 813. CrossRef - Historical evolution of healthcare systems of post-soviet Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, and Azerbaijan: A scoping review
Yuliya Semenova, Lisa Lim, Zhandos Salpynov, Abduzhappar Gaipov, Mihajlo Jakovljevic
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29550. CrossRef - The Role of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Chinese Pharmacopoeia in the
Evaluation and Treatment of COVID-19
Amin Gasmi, Sadaf Noor, Maryam Dadar, Yuliya Semenova, Alain Menzel, Asma Gasmi Benahmed, Geir Bjørklund
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(14): 1060. CrossRef - Using simulation modelling and systems science to help contain COVID‐19: A systematic review
Weiwei Zhang, Shiyong Liu, Nathaniel Osgood, Hongli Zhu, Ying Qian, Peng Jia
Systems Research and Behavioral Science.2023; 40(1): 207. CrossRef - Assessing the medical resources in COVID-19 based on evolutionary game
Keyu Guo, Yikang Lu, Yini Geng, Jun Lu, Lei Shi, Alessandro Borri
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0280067. CrossRef - Restenosis of Coronary Arteries in Patients with Coronavirus Infection: Case Series
Gulnara Batenova, Lyudmila Pivina, Evgeny Dedov, Altay Dyussupov, Zhanar Zhumanbayeva, Yerbol Smail, Tatyana Belikhina, Laura Pak, Diana Ygiyeva, Bruno Megarbane
Case Reports in Medicine.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Is It Possible to Predict COVID-19? Stochastic System Dynamic Model of Infection Spread in Kazakhstan
Berik Koichubekov, Aliya Takuadina, Ilya Korshukov, Anar Turmukhambetova, Marina Sorokina
Healthcare.2023; 11(5): 752. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Antibiotic Consumption in Adult Population of Kazakhstan
Nazym Iskakova, Zaituna Khismetova, Dana Suleymenova, Zhanat Kozhekenova, Zaituna Khamidullina, Umutzhan Samarova, Natalya Glushkova, Yuliya Semenova
Antibiotics.2023; 12(3): 560. CrossRef - Study of seroprevalence of SARS‐CoV‐2 in Kazakhstan
Mukhtar Kulimbet, Timur Saliev, Gulzhan Alimbekova, Dinara Ospanova, Kundyzay Tobzhanova, Dariga Tanabayeva, Baurzhan Zhussupov, Ildar Fakhradiyev
Epidemiology and Infection.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Editorial: Public health challenges in post-Soviet countries during and beyond COVID-19
Natalya Glushkova, Yuliya Semenova, Antonio Sarria-Santamera
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Epidemiological and Economic Impact of COVID-19 in Kazakhstan: An Agent-Based Modeling
Berik Koichubekov, Aliya Takuadina, Ilya Korshukov, Marina Sorokina, Anar Turmukhambetova
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2968. CrossRef - Seropositivity of SARS-CoV-2 in the Population of Kazakhstan: A Nationwide Laboratory-Based Surveillance
Yuliya Semenova, Zhanna Kalmatayeva, Ainash Oshibayeva, Saltanat Mamyrbekova, Aynura Kudirbekova, Ardak Nurbakyt, Ardak Baizhaxynova, Paolo Colet, Natalya Glushkova, Alexandr Ivankov, Antonio Sarria-Santamera
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2263. CrossRef - The lessons of COVID-19, SARS, and MERS: Implications for preventive strategies
Yuliya Semenova, Varvara Trenina, Lyudmila Pivina, Natalya Glushkova, Yersin Zhunussov, Erlan Ospanov, Geir Bjørklund
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2022; 15(4): 314. CrossRef - Coronary Heart Disease and Coronavirus Disease 2019: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, Association with Myocardial Revascularization
Gulnara Batenova, Evgeny Dedov, Maksim Pivin, Igor Nikitin, Olga Ettinger, Yerbol Smail, Diana Ygiyeva , Lyudmila Pivina
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(F): 319. CrossRef - Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak on the Epidemiology and Treatment Outcomes of Fractures of the Proximal Femur in Kazakhstan
Bekzat Beisenov, Maksut Kulzhanov, Tatyana Popova, Assel Yermekbayeva, Nurlat Beikutuly, Kanat Tezekbayev, Shynar Tanabayeva, Ildar Fakhradiyev
Experimental and Applied Biomedical Research (EABR).2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and risk factors for disease severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus in Kazakhstan: A nationwide study
Azhar Dyusupova, Raida Faizova, Oksana Yurkovskaya, Tatiana Belyaeva, Tatiana Terekhova, Amina Khismetova, Antonio Sarria-Santamera, Dmitry Bokov, Alexandr Ivankov, Natalya Glushkova
Heliyon.2021; 7(3): e06561. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Of Triage Systems At Emergency Departments Of Different Countries: Implementation In Kazakhstan
Lyudmila Pivina, Assylzhan M. Messova, Yersin T. Zhunussov, Zhanar Urazalina, Zhanna Muzdubayeva, Diana Ygiyeva, Murat Muratoglu, Gulnara Batenova, Sharbanu Uisenbayeva, Yulia Semenova
Russian Open Medical Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
 KSPM
KSPM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite


