Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Prev Med Public Health > Volume 53(3); 2020 > Article
-
Special Section: COVID-19Systematic Review
Estimate of the Basic Reproduction Number for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis -
Yousef Alimohamadi1,2
 , Maryam Taghdir3
, Maryam Taghdir3 , Mojtaba Sepandi3,4
, Mojtaba Sepandi3,4
-
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health 2020;53(3):151-157.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.20.076
Published online: March 20, 2020
1Pars Advanced and Minimally Invasive Medical Manners Research Center, Pars Hospital, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
2Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
3Health Research Center, Lifestyle Institute, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
4Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Faculty of Health, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- Corresponding author: Mojtaba Sepandi, PhD Health Research Center, Lifestyle Institute, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran 143591-13189, Iran E-mail: msepandi@gmail.com
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Society for Preventive Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Objectives
- The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is one of the main public health challenges currently facing the world. Because of its high transmissibility, COVID-19 has already caused extensive morbidity and mortality in many countries throughout the world. An accurate estimation of the basic reproduction number (R0) of COVID-19 would be beneficial for prevention programs. In light of discrepancies in original research on this issue, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to estimate the pooled R0 for COVID-19 in the current outbreak.
-
Methods
- International databases (including Google Scholar, Science Direct, PubMed, and Scopus) were searched to identify studies conducted regarding the R0 of COVID-19. Articles were searched using the following keywords: “COVID-19” and “basic reproduction number” or “R0.” The heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the I2 index, the Cochran Q test, and T2. A random-effects model was used to estimate R0 in this study.
-
Results
- The mean reported R0 in the identified articles was 3.38±1.40, with a range of 1.90 to 6.49. According to the results of the random-effects model, the pooled R0 for COVID-19 was estimated as 3.32 (95% confidence interval, 2.81 to 3.82). According to the results of the meta-regression analysis, the type of model used to estimate R0 did not have a significant effect on heterogeneity among studies (p=0.81).
-
Conclusions
- Considering the estimated R0 for COVID-19, reducing the number of contacts within the population is a necessary step to control the epidemic. The estimated overall R0 was higher than the World Health Organization estimate.
- In December 2019, a series of pneumonia cases with no identified cause appeared in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, with clinical symptoms similar to viral pneumonia [1-3]. Most of the reported cases were in patients who worked or lived around the local Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, where live animals were also sold [4]. This new virus infecting humans was initially named the 2019 novel coronavirus, and the World Health Organization (WHO) subsequently issued updated nomenclature, in which the virus is referred to as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the disease that it causes is referred to as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) [5]. Because of its high contagiousness and morbidity, this infection is considered by WHO as a global emergency [6]. As a reflection of the high transmissibility of this viral infection, by January 26, 2020 more than 2000 confirmed cases of COVID-19 had been identified in China, mainly in Wuhan [7]. This number then dramatically increased, with the number of confirmed cases in China reaching 66 580 by February 15, 2020, with 1524 deaths [8]. Human-to-human transmission of COVID-19 was confirmed [9] and cases were reported in countries other than China [10]. Because of the high infectiousness of SARS-CoV-2 among the susceptible population, the calculation of the basic reproduction number (R0) is essential for implementing prevention measures [1]. R0 is an epidemiological metric that can be used to assess the contagiousness of infectious agents. This index presents the average number of new cases generated by an infected person [11,12]. Therefore, a high R0 indicates that an infectious agent is highly contagious. Since the epidemic began in China, numerous papers have been published on this issue. However, because of discrepancies in the results of those studies, the current systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to estimate the pooled R0 for the COVID-19 outbreak, using original articles published during 2020.
INTRODUCTION
- Search Strategy
- This systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to estimate the pooled R0 of COVID-19 in articles published in international journals. International databases (including Google Scholar, Science Direct, PubMed, and Scopus) were searched to obtain studies conducted regarding the reproduction number of COVID-19. Articles were searched using the keywords “COVID-19” AND “basic reproduction number” OR “R0”.
- Study Selection and Data Extraction
- In the current study, all studies published in 2020 that estimated R0 for COVID-19 were entered into the meta-analysis. The name of the first author, country, year of the study, model used to estimate R0, and the estimated R0 value (with a 95% confidence interval, CI) were extracted from the articles.
- Statistical Analysis
- Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using the I2 index, the Cochran Q test, and T2. According to the I2 results, heterogeneity can classified into the following 3 categories: I2<25% (low heterogeneity), I2=25-75% (average heterogeneity), and I2>75% (high heterogeneity) [13]. Because of the high I2 value that was calculated (99.4%), as well as the significance of the Cochran Q test (p<0.001), a random-effects model was used to estimate R0 in this study. The impact of covariates on the estimated R0 was also assessed by univariate meta-regression. Data were analyzed using Stata version 11 (StataCorp., College Station, TX, USA).
- Ethics Statement
- As a systematic review, this study did not need ethical approval.
METHODS
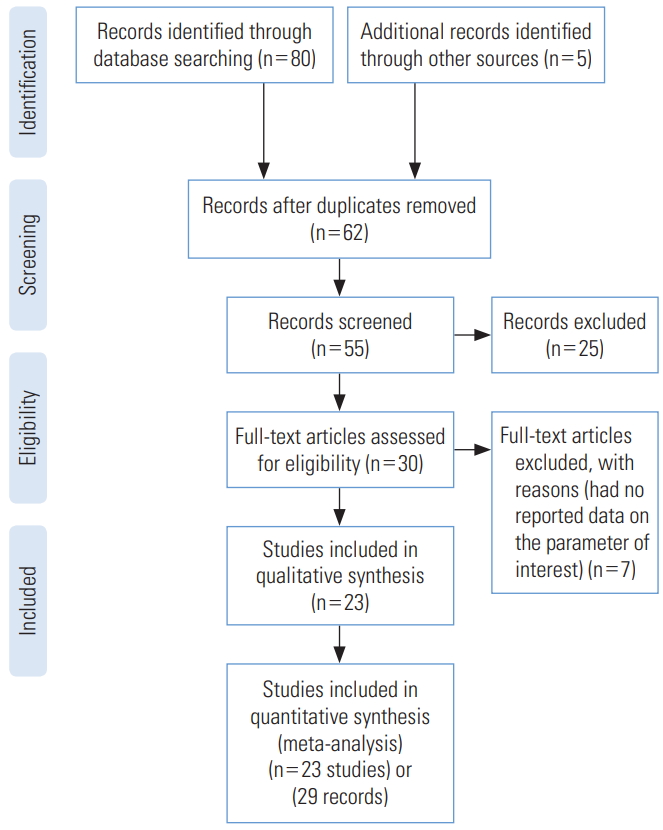
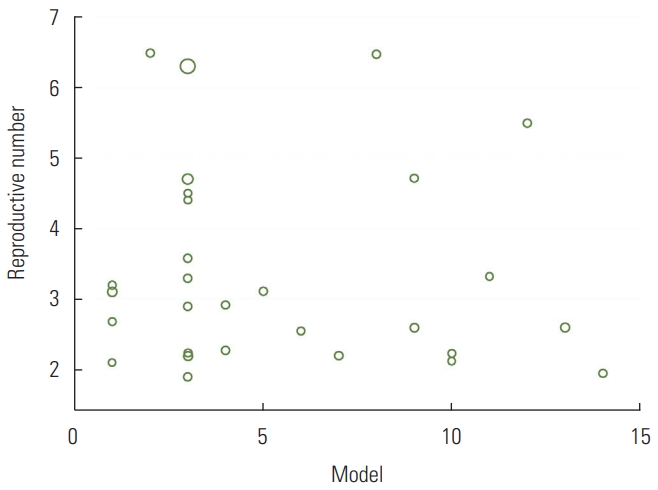
- We identified 85 studies, of which 23 were duplicates, leaving 62 reports. A total of 55 reports passed the initial screening, and 23 reports passed the full-text assessment for eligibility (Figure 1). The reasons for exclusion were as follows: reporting of effective reproductive number instead of R₀ and insufficient data. Finally, we included 23 studies in this systematic review (Table 1). No studies were excluded due to poor quality. In the current study, 23 studies with 29 records that estimated the R0 of COVID-19 were entered into the analysis. The studies used a broad range of methods to estimate R0 for COVID-19. All the studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in 2020 in China. The mean R0 reported in the articles was calculated as 3.38±1.40, with a range of 1.90 to 6.49. More information is shown in Table 1.
RESULTS
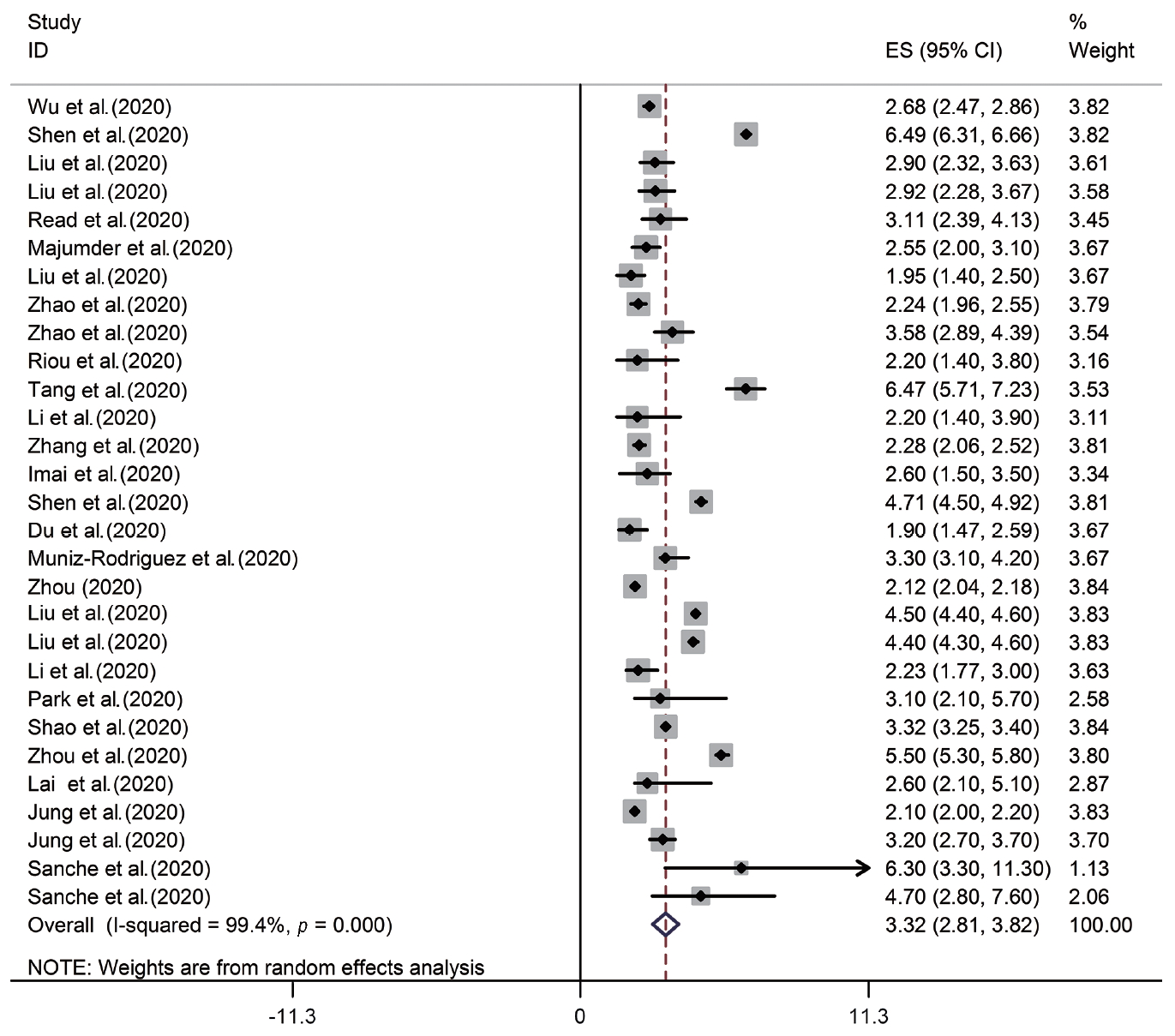
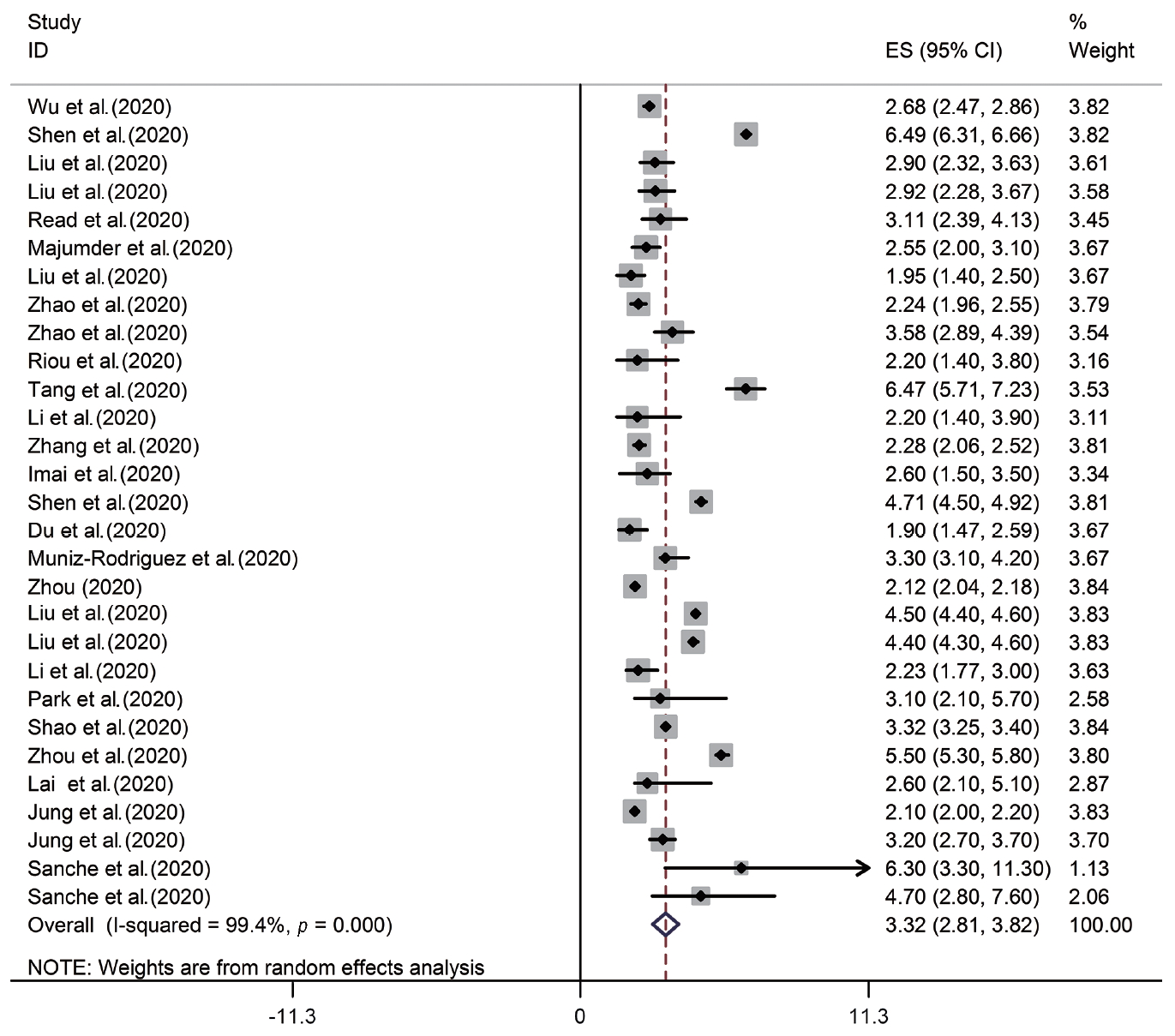
- According to the results of the random-effects model, the pooled R0 for COVID-19 was estimated as 3.32 (95% CI, 2.81 to 3.82). This means that each person infected with COVID-19 transmitted the infection to between 3 and 4 susceptible people on average (Figure 2, Table 2). There was significant heterogeneity among studies (I2=99.4%, p from the chi-square test for heterogeneity <0.001, and T2=1.72) (Table 2).
- Meta-regression
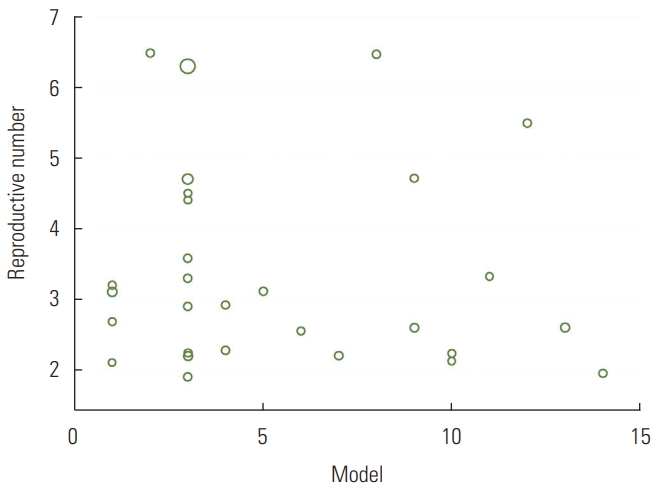
- The meta-regression analysis showed that the type of model used to estimate R0 did not have a significant effect on heterogeneity among studies (p=0.81). The distribution of the estimated R0 according to the model used is shown in Figure 3. The numbers on the χ-axis in Figure 3 represent the type of method used to estimate R0, using the following coding: stochastic Markov chain Monte Carlo method: 1, dynamic compartmental model; 2, statistical exponential growth model; 3, statistical maximum likelihood estimation; 4, mathematical transmission model; 5, mathematical incidence decay and exponential adjustment; 6, stochastic simulation of early outbreak trajectories; 7, mathematical susceptible, exposed, infected, and resistant (SEIR)-type epidemiological model; 8, other mathematical models; 9, networked dynamics metapopulation model; 10, Fudan-Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention model; 11, susceptible, exposed, infected and quarantined (SEIQ) model; 12, coalescent-based exponential growth and a birth-death skyline model; 13, coalescent-based exponential growth and a birth-death skyline model; and 14, type of model not mentioned.
Pooled Estimation of Basic Reproduction Number
- It is necessary to estimate the R0 of COVID-19 to determine the severity and size of the pandemic, as well as to design appropriate interventions and responses to protect the population and to control the spread of the disease [35]. The estimated R0 value is important in infectious disease epidemiology because the intensity of transmission must be reduced by 1-1/R0 to eliminate the outbreak. For example, at R0=2.5, this fraction is 60.0%, but at R0=3.2, this fraction is 68.7%. Mathematical models play an important role in decision-making during outbreak control [36]. Our systematic review and meta-analysis found that the overall R0 was 3.32 (95% CI, 2.81 to 3.82), which is higher than the WHO estimates of 1.4 to 2.5 (11) but similar to the results of an earlier review of 12 articles that were conducted in China (11). Our estimation is similar to the R0 values estimated for the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic in Beijing, China (R0=4.91) [37], and for Middle East respiratory syndrome in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia (R0=3.5 to 6.7) [38]. Such a high R0 indicates that the virus can go through at least 3 to 4 generations of transmission [22]. Similar to reviews of R0 for other pathogens [39-41], it is important to highlight regarding our results that R0 is not an intrinsic characteristic of a given pathogen, but rather describes the transmissibility of that pathogen within a specific population and setting. The estimated R0 depends on factors such as social and demographic variables, the estimation method used, the validity of the underlying assumptions, and the biology of the infectious agent. For example, the frequency of contacts may depend on population size and cultural factors, which can vary across regions. In addition, estimates of R0 may be somewhat error-prone for reasons such as data insufficiency and the short time period analyzed. As more studies are done and more data are produced, the hope is that this error will be reduced. Our results showed significant heterogeneity among studies (I2=99.3%, p from the chi-square test for heterogeneity <0.001, and T2=1.72). One reason for this issue is that it is difficult to calculate the exact number of infected cases during an outbreak. The variation in R0 values reported by different studies indicates that precisely estimating R0 is rather difficult. Additionally, R0 can be affected by environmental factors and modeling methodology [12]. There are many calculation methods for R0 [42]. Our review was restricted to Chinese articles. For other countries, surveillance data are needed either to calculate R0 or to extrapolate R0 estimates from a comparable setting.
- It also seems necessary to consider the reasons why high R0 values were reported in some studies. Modeling assumptions may be a reason for this issue. Usually, high R0 values are calculated in the early stages of an epidemic, both because of the small sample size and the lack of awareness about the disease, which results in inadequate preventive measures being taken. Since the number and patterns of people’s contacts in different populations vary because of factors including culture and the level of literacy in the community, R0 values vary among different populations and even among subgroups of a single population. In fact, the total value of R0 in a population is the average of the R0 subtypes in that community. It is therefore important to note that even if the total R0 value in a population is low (even less than 1), the likelihood of transmission in some subgroups of that population may still be high. Given the rapid spread of the disease and the dependency of the effectiveness of control measures on factors such as the frequency of asymptomatic infections and the potential for disease transmission before symptom onset, COVID-19 seems to be relatively difficult to control. As a measure used to quantify the transmissibility of a disease in a population, R0 is dependent on the population as well as the method of calculation. Our findings suggest that measures such as preventing large gatherings, restricting transportation, and closing schools and universities may be necessary to control this pandemic.
DISCUSSION
- Considering the estimated R0 for COVID-19, reducing the number of contacts within the population is a necessary step to control the epidemic. So Implementation of the social distancing program, preventing large gatherings, restricting transportation, and closing schools and universities may be necessary to control this pandemic. The estimated overall R0 was higher than the WHO estimate.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
-
FUNDING
None.
Notes
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: YA, MS. Data curation: YA, MS, MT. Formal analysis: YA, MS. Funding acquisition: None. Methodology: YA, MS. Project administration: MS. Writing - original draft: YA, MS, MT. Writing - review & editing: YA, MS, MT.
Notes

| Study | Country | Model | No. of reproduction | LCL | UCL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al., 2020 [14] | China | MCMC | 2.68 | 2.47 | 2.86 |
| Shen et al., 2020 [15] | China | Dynamic compartmental model | 6.49 | 6.31 | 6.66 |
| Liu et al., 2020 [16] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 2.90 | 2.32 | 3.63 |
| Liu et al., 2020 [16] | China | Statistical maximum likelihood estimation | 2.92 | 2.28 | 3.67 |
| Read et al., 2020 [17] | China | Mathematical transmission model | 3.11 | 2.39 | 4.13 |
| Majumder et al., 2020 [18] | China | IDEA | 2.55 | 2.00 | 3.10 |
| Liu et al., 2020 [11] | China | Mathematical model | 1.95 | 1.40 | 2.50 |
| Zhao et al., 2020 [19] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 2.24 | 1.96 | 2.55 |
| Zhao et al., 2020 [19] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 3.58 | 2.89 | 4.39 |
| Imai et al., 2020 [20] | China | Mathematical model | 2.50 | 1.50 | 3.50 |
| Riou et al., 2020 [21] | China | Stochastic simulations of early outbreak trajectories | 2.20 | 1.40 | 3.80 |
| Tang et al., 2020 [22] | China | Mathematical SEIR-type epidemiological model | 6.47 | 5.71 | 7.23 |
| Li et al., 2020 [23] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 2.20 | 1.40 | 3.90 |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [24] | China | Statistical maximum likelihood estimation | 2.28 | 2.06 | 2.52 |
| Shen et al., 2020 [15] | China | Mathematical model | 4.71 | 4.50 | 4.92 |
| Du et al., 2020 [25] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 1.90 | 1.47 | 2.59 |
| Muniz-Rodriguez et al., 2020 [26] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 3.30 | 3.10 | 4.20 |
| Zhou, 2020 [27] | China | SEIR model | 2.12 | 2.04 | 2.18 |
| Liu et al., 2020 [28] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 4.50 | 4.40 | 4.60 |
| Liu et al., 2020 [28] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 4.40 | 4.30 | 4.60 |
| Li et al., 2020 [29] | China | Networked dynamic metapopulation model | 2.23 | 1.77 | 3.00 |
| Park et al., 2020 [30] | China | MCMC | 3.10 | 2.10 | 5.70 |
| Shao et al., 2020 [31] | China | Fudan-CCDC model | 3.32 | 3.25 | 3.40 |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [32] | China | SEIQ model | 5.50 | 5.30 | 5.80 |
| Lai et al., 2020 [33] | China | Coalescent-based exponential growth and a birth-death skyline method | 2.60 | 2.10 | 5.10 |
| Jung et al., 2020 [9] | China | MCMC | 2.10 | 2.00 | 2.20 |
| Jung et al., 2020 [9] | China | MCMC | 3.20 | 2.70 | 3.70 |
| Sanche et al., 2020 [34] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 6.30 | 3.30 | 11.30 |
| Sanche et al., 2020 [34] | China | Statistical exponential growth model | 4.70 | 2.80 | 7.60 |
| Pooled estimate (95% CI) | Q | I2 | T2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.32 (2.81, 3.82) | <0.001 | 99.4 | 1.72 |
- 1. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020;395(10223):497-506ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Pan F, Ye T, Sun P, Gui S, Liang B, Li L, et al. Time course of lung changes on chest CT during recovery from 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia. Radiology 2020;295(3):715-721ArticlePubMed
- 3. Boldog P, Tekeli T, Vizi Z, Dénes A, Bartha FA, Röst G. Risk assessment of novel coronavirus COVID-19 outbreaks outside China. J Clin Med 2020;9(2):571ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 2020;395(10223):507-513ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H, Yang J, et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020;395(10223):514-523ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Chen H, Guo J, Wang C, Luo F, Yu X, Zhang W, et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records. Lancet 2020;395(10226):809-815ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020;395(10224):565-574ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8(4):420-422ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Jung SM, Akhmetzhanov AR, Hayashi K, Linton NM, Yang Y, Yuan B, et al. Real-time estimation of the risk of death from novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: inference using exported cases. J Clin Med 2020;9(2):523ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020;395(10223):470-473ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Liu Y, Gayle AA, Wilder-Smith A, Rocklöv J. The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus. J Travel Med 2020;27(2):taaa021ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Delamater PL, Street EJ, Leslie TF, Yang YT, Jacobsen KH. Complexity of the basic reproduction number (R0). Emerg Infect Dis 2019;25(1):1-4Article
- 13. Ghanei Gheshlagh R, Aslani M, Shabani F, Dalvand S, Parizad N. Prevalence of needlestick and sharps injuries in the healthcare workers of Iranian hospitals: an updated meta-analysis. Environ Health Prev Med 2018;23(1):44ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Wu JT, Leung K, Leung GM. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet 2020;395(10225):689-697ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Shen M, Peng Z, Xiao Y, Zhang L. Modelling the epidemic trend of the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in China. bioRxiv 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.23.916726Article
- 16. Liu T, Hu J, Kang M, Lin L, Zhong H, Xiao J, et al. Transmission dynamics of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). bioRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.25.919787Article
- 17. Read JM, Bridgen JR, Cummings DA, Ho A, Jewell CP. Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic predictions. MedRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.23.20018549Article
- 18. Majumder M, Mandl KD. Early transmissibility assessment of a novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. SSRN 2020. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3524675Article
- 19. Zhao S, Lin Q, Ran J, Musa SS, Yang G, Wang W, et al. Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: a data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. Int J Infect Dis 2020;92: 214-217ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Imai N, Cori A, Dorigatti I, Baguelin M, Donnelly CA, Riley S, et al. Report 3: transmissibility of 2019-nCoV. 2020 Jan 25 [cited 2020 Apr 20]. Available from: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrcglobal-infectious-disease-analysis/covid-19/report-3-transmissibility-of-covid-19/
- 21. Riou J, Althaus CL. Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020. Euro Surveill 2020;25(4):2000058ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Tang B, Wang X, Li Q, Bragazzi NL, Tang S, Xiao Y, et al. Estimation of the transmission risk of the 2019-nCoV and its implication for public health interventions. J Clin Med 2020;9(2):462ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med 2020;382(13):1199-1207ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Zhang S, Diao M, Yu W, Pei L, Lin Z, Chen D. Estimation of the reproductive number of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) and the probable outbreak size on the Diamond Princess cruise ship: a data-driven analysis. Int J Infect Dis 2020;93: 201-204ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Du Z, Wang L, Cauchemez S, Xu X, Wang X, Cowling BJ, et al. Risk for transportation of coronavirus disease from Wuhan to other cities in China. Emerg Infect Dis 2020;26(5):1049-1052ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Muniz-Rodriguez K, Chowell G, Cheung CH, Jia D, Lai PY, Lee Y, et al. Epidemic doubling time of the COVID-19 epidemic by Chinese province. medRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.05.20020750Article
- 27. Zhou C. Evaluating new evidence in the early dynamics of the novel coronavirus COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan, China with real time domestic traffic and potential asymptomatic transmissions. medRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.15.2002344Article
- 28. Liu T, Hu J, Xiao J, He G, Kang M, Rong Z, et al. Time-varying transmission dynamics of novel coronavirus pneumonia in China. bioRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.25.919787Article
- 29. Li R, Pei S, Chen B, Song Y, Zhang T, Yang W, et al. Substantial undocumented infection facilitates the rapid dissemination of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV2). Science 2020;368(6490):489-493ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Park SW, Bolker BM, Champredon D, Earn DJ, Li M, Weitz JS, et al. Reconciling early-outbreak estimates of the basic reproductive number and its uncertainty: framework and applications to the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) outbreak. medRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.30.20019877Article
- 31. Shao N, Cheng J, Chen W. The reproductive number R0 of COVID-19 based on estimate of a statistical time delay dynamical system. medRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.17.20023747Article
- 32. Zhang KK, Xie L, Lawless L, Zhou H, Gao G, Xue C. Characterizing the transmission and identifying the control strategy for COVID-19 through epidemiological modeling. medRxiv 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.24.20026773Article
- 33. Lai A, Bergna A, Acciarri C, Galli M, Zehender G. Early phylogenetic estimate of the effective reproduction number of SARS-CoV-2. J Med Virol 2020;92(6):675-679ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Sanche S, Lin YT, Xu C, Romero-Severson E, Hengartner NW, Ke R. The novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, is highly contagious and more infectious than initially estimated. arXiv 2002;03268Article
- 35. Kwok KO, Tang A, Wei VW, Park WH, Yeoh EK, Riley S. Epidemic models of contact tracing: systematic review of transmission studies of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2019;17: 186-194ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Egger M, Johnson L, Althaus C, Schöni A, Salanti G, Low N, et al. Developing WHO guidelines: time to formally include evidence from mathematical modelling studies. F1000Res 2017;6: 1584ArticlePubMed
- 37. Gumel AB, Ruan S, Day T, Watmough J, Brauer F, van den Driessche P, et al. Modelling strategies for controlling SARS outbreaks. Proc Biol Sci 2004;271(1554):2223-2232ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Majumder MS, Rivers C, Lofgren E, Fisman D. Estimation of MERS-coronavirus reproductive number and case fatality rate for the Spring 2014 Saudi Arabia outbreak: insights from publicly available data. PLoS Curr 2014;6: ecurrents.outbreaks.98d2f8f3382d84f390736cd5f5fe133c
- 39. Ridenhour B, Kowalik JM, Shay DK. Unraveling R0: considerations for public health applications. Am J Public Health 2014;104(2):e32-e41Article
- 40. Biggerstaff M, Cauchemez S, Reed C, Gambhir M, Finelli L. Estimates of the reproduction number for seasonal, pandemic, and zoonotic influenza: a systematic review of the literature. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14: 480ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 41. Johansson MA, Hombach J, Cummings DA. Models of the impact of dengue vaccines: a review of current research and potential approaches. Vaccine 2011;29(35):5860-5868ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Breban R, Vardavas R, Blower S. Theory versus data: how to calculate R0? PLoS One 2007;2(3):e282ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Optimal resource allocation model for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yu-Yuan Wang, Wei-Wen Zhang, Ze-xi Lu, Jia-lin Sun, Ming-xia Jing
BMC Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Building a Simple Model to Assess the Impact of Case Investigation and Contact Tracing for Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Lessons From COVID-19
François M. Castonguay, Harrell W. Chesson, Seonghye Jeon, Gabriel Rainisch, Leah S. Fischer, Biswha B. Adhikari, Emily B. Kahn, Bradford Greening, Thomas L. Gift, Martin I. Meltzer
AJPM Focus.2024; 3(1): 100147. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 incidence monitoring and statistical estimation of the basic and time-varying reproduction number at the early onset of the pandemic in 45 sub-Saharan African countries
Michael Safo Oduro, Seth Arhin-Donkor, Louis Asiedu, Damazo T. Kadengye, Samuel Iddi
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Looking under the lamp-post: quantifying the performance of contact tracing in the United States during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
Henry Bayly, Madison Stoddard, Debra Van Egeren, Eleanor J Murray, Julia Raifman, Arijit Chakravarty, Laura F White
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic analysis of generalized epidemic models with latent period, quarantine, governmental intervention and Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process
Tan Su, Xinhong Zhang, Daqing Jiang
Nonlinear Dynamics.2024; 112(9): 7749. CrossRef - A Dynamic Reaction-restore-type Transmission-rate Model for COVID-19
Fernando Córdova-Lepe, Juan Pablo Gutiérrez-Jara
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON BIOLOGY AND BIOMEDICINE.2024; 21: 118. CrossRef - Optimal non-pharmaceutical interventions considering limited healthcare system capacity and economic costs in the Republic of Korea
Yuna Lim, Youngsuk Ko, Victoria May P. Mendoza, Renier Mendoza, Jongmin Lee, Eunok Jung
Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena.2024; 19: 6. CrossRef - GAME-THEORETICAL MODEL OF COVID-19 VACCINATION IN THE ENDEMIC EQUILIBRIUM
RENEE MARIA ARGANA MARQUEZ, MARIA SEANNA CABERO MINAS, JORDAN VANCE TAITANO SANTOS, KANGSAN YOON, VINCE NICOLAS S. CAMPO, HYUNJU OH, JAN RYCHTÁŘ, DEWEY TAYLOR
Journal of Biological Systems.2024; 32(02): 349. CrossRef - Estimating the COVID-19 prevalence from wastewater
Jan Mohring, Neele Leithäuser, Jarosław Wlazło, Marvin Schulte, Maximilian Pilz, Johanna Münch, Karl-Heinz Küfer
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A tree-based explainable AI model for early detection of Covid-19 using physiological data
Manar Abu Talib, Yaman Afadar, Qassim Nasir, Ali Bou Nassif, Haytham Hijazi, Ahmad Hasasneh
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Airline safety: Still getting better?
Arnold Barnett, Jan Reig Torra
Journal of Air Transport Management.2024; 119: 102641. CrossRef - An SIR‐based Bayesian framework for COVID‐19 infection estimation
Haoyu Wu, David A. Stephens, Erica E. M. Moodie
Canadian Journal of Statistics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling SARS‐CoV‐2 True Infections in Catalonia through a Digital Twin
Pau Fonseca i Casas, Joan Garcia i Subirana, Victor Garcia i Carrasco
Advanced Theory and Simulations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Mitigation Strategy against SARS-CoV-2 Infection for Healthcare Provider at Harapan Bersama General Hospital, Singkawang, Indonesia
Rizki Rahim, Andreasta Meliala
Hospital Topics.2023; 101(4): 381. CrossRef - Reducing the basic reproduction number of COVID-19: a model simulation focused on QALYs, hospitalisation, productivity costs and optimal (soft) lockdown
Jose Robles-Zurita
The European Journal of Health Economics.2023; 24(4): 647. CrossRef - Waco COVID Survey: A Community-Based SARS-CoV-2 Serological Surveillance Study in Central Texas
Michael P. Muehlenbein, Jeffrey Gassen, Tomasz J. Nowak, Alexandria D. Henderson, Sally P. Weaver, Erich J. Baker
Journal of Community Health.2023; 48(1): 104. CrossRef - COVID-19 epidemic and public health interventions in Shanghai, China: Statistical analysis of transmission, correlation and conversion
Dali Yi, Xicheng Chen, Haojia Wang, Qiuyue Song, Ling Zhang, Pengpeng Li, Wei Ye, Jia Chen, Fang Li, Dong Yi, Yazhou Wu
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bounding pandemic spread by heat spread
Teddy Lazebnik, Uri Itai
Journal of Engineering Mathematics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Macroeconomic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic
Terrie Walmsley, Adam Rose, Richard John, Dan Wei, Jakub P. Hlávka, Juan Machado, Katie Byrd
Economic Modelling.2023; 120: 106147. CrossRef - Monkeypox 2022: Emerging zoonotic epidemic threat, future implications, and way ahead
Suraj Kapoor, Ashvin Varadharajan
Journal of Public Health and Primary Care.2023; 4(1): 8. CrossRef - Forty‐seven year trend of measles in Iran: An interrupted time series analysis
Yousef Alimohamadi, Mojtaba Sepandi
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A mathematical model for the spread of Omicron virus based on grey prediction algorithm
Haotian Lin, Jianze Lin, Kewei You
Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology.2023; 36: 1386. CrossRef - Household transmission dynamics of COVID-19 among residents of Delhi, India: a prospective case-ascertained study
Farzana Islam, Yasir Alvi, Mohammad Ahmad, Faheem Ahmed, Anisur Rahman, Farishta Hannah D. Singh, Ayan Kumar Das, Mridu Dudeja, Ekta Gupta, Rashmi Agarwalla, Iqbal Alam, Sushovan Roy
IJID Regions.2023; 7: 22. CrossRef - Study of optimal vaccination strategies for early COVID-19 pandemic using an age-structured mathematical model: A case study of the USA
Giulia Luebben, Gilberto González-Parra, Bishop Cervantes
Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering.2023; 20(6): 10828. CrossRef - A Stochastic Mobility-Driven spatially explicit SEIQRD COVID-19 model with VOCs, seasonality, and vaccines
Tijs W. Alleman, Michiel Rollier, Jenna Vergeynst, Jan M. Baetens
Applied Mathematical Modelling.2023; 123: 507. CrossRef - Using advanced analysis together with fractional order derivative to investigate a smoking tobacco cancer model
Ismail Shah, Eiman, Hussam Alrabaiah, Burhanettin Ozdemir, Ateeq ur Rehman Irshad
Results in Physics.2023; 51: 106700. CrossRef - Trajectories of COVID-19: A longitudinal analysis of many nations and subnational regions
David Burg, Jesse H. Ausubel, Rajnesh Lal
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(6): e0281224. CrossRef - Influence spreading model for partial breakthrough effects on complex networks
Into Almiala, Henrik Aalto, Vesa Kuikka
Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications.2023; 630: 129244. CrossRef - A Brighton Collaboration standardized template with key considerations for a benefit/risk assessment for the Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine (NVX-CoV2373), a recombinant spike protein vaccine with Matrix-M adjuvant to prevent disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 viruses
Bethanie Wilkinson, Kinjal S. Patel, Katherine Smith, Robert Walker, Chengbin Wang, Ann M. Greene, Gale Smith, Emily R. Smith, Marc Gurwith, Robert T. Chen
Vaccine.2023; 41(45): 6762. CrossRef - Modelling influenza and SARS-CoV-2 interaction: Analysis for Catalonia region
Pau Fonseca i Casas, Victor Garcia i Carrasco, Joan Garcia i Subirana
Journal of Algorithms & Computational Technology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Measuring the efficacy of a vaccine during an epidemic
Antonio Scala, Pierpaolo Cavallo, Tiago Pereira
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(9): e0290652. CrossRef - Fast bilateral weighted least square for the detail enhancement of COVID-19 chest X-rays
Wenyan Bian, Yang Yang
DIGITAL HEALTH.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Econometric Estimation of the Basic Reproduction Number for COVID-19 Across U.S. States and Selected Countries
Ida Johnsson, M. Hashem Pesaran, Cynthia Fan Yang
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2: An Update on the Biological Interplay with the Human Host
Giuseppe Lippi, Fabian Sanchis-Gomar, Camilla Mattiuzzi, Brandon M. Henry
COVID.2023; 3(10): 1586. CrossRef - A data-driven semi-parametric model of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the United States
John M. Drake, Andreas Handel, Éric Marty, Eamon B. O’Dea, Tierney O’Sullivan, Giovanni Righi, Andrew T. Tredennick, Gerardo Chowell
PLOS Computational Biology.2023; 19(11): e1011610. CrossRef - Reaction–Diffusion Equations in Mathematical Models Arising in Epidemiology
Vasyl’ Davydovych, Vasyl’ Dutka, Roman Cherniha
Symmetry.2023; 15(11): 2025. CrossRef - Multivariate Forecasting Model for COVID-19 Spread Based on Possible Scenarios in Ecuador
Juan Guamán, Karen Portilla, Paúl Arias-Muñoz, Gabriel Jácome, Santiago Cabrera, Luis Álvarez, Bolívar Batallas, Hernán Cadena, Juan Carlos García
Mathematics.2023; 11(23): 4721. CrossRef - Direct indicators of social distancing effectiveness in COVID-19 outbreak stages: a correlational analysis of case contacts and population mobility
Sojin Choi, Chanhee Kim, Kun-Hee Park, Jong-Hun Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2023; : e2023065. CrossRef - Screening multi‐dimensional heterogeneous populations for infectious diseases under scarce testing resources, with application to COVID‐19
Hussein El Hajj, Douglas R. Bish, Ebru K. Bish, Hrayer Aprahamian
Naval Research Logistics (NRL).2022; 69(1): 3. CrossRef - COVID-19 Global Humanitarian Response Plan: An optimal distribution model for high-priority countries
Ibrahim M. Hezam
ISA Transactions.2022; 124: 1. CrossRef - Health and Public Health Implications of COVID‐19 in Asian Countries
Atsushi Miyawaki, Yusuke Tsugawa
Asian Economic Policy Review.2022; 17(1): 18. CrossRef - Implications for clinical dental practice during the coronavirus disease pandemic: A scoping review
Kazumichi Yonenaga, Shunsuke Itai, Kazuto Hoshi
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2022; 66(1): 6. CrossRef - Objective Evaluation of Olfactory and Taste Dysfunction Among COVID-19 Patients: A Cross Sectional Study from Tribal India
Izhar Khan, Vikas Gupta, Sanjay Kumar Shukla
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2022; 74(S2): 3193. CrossRef - A strict mask policy for hospital staff effectively prevents nosocomial influenza infections and mortality: monocentric data from five consecutive influenza seasons
A. Ambrosch, D. Luber, F. Klawonn, M. Kabesch
Journal of Hospital Infection.2022; 121: 82. CrossRef - Effectiveness of social distancing interventions in containing COVID-19 incidence: International evidence using Kalman filter
Navendu Prakash, Bhavya Srivastava, Shveta Singh, Seema Sharma, Sonali Jain
Economics & Human Biology.2022; 44: 101091. CrossRef - Validación preclínica de un respirador de turbina para la ventilación invasiva: el respirador ACUTE-19
J.M. Alonso-Iñigo, G. Mazzinari, M. Casañ-Pallardó, J.I. Redondo-García, J. Viscasillas-Monteagudo, A. Gutierrez-Bautista, J. Ramirez-Faz, P. Alonso-Pérez, S. Díaz-Lobato, A.S. Neto, O. Diaz-Cambronero, P. Argente-Navarro, M. Gama de Abreu, P. Pelosi, M.J
Revista Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación.2022; 69(9): 544. CrossRef - An algorithm for the direct estimation of the parameters of the SIR epidemic model from the I(t) dynamics
François G. Schmitt
The European Physical Journal Plus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficacy of deep learning based LSTM model in forecasting the outbreak of contagious diseases
Nurul Absar, Nazim Uddin, Mayeen Uddin Khandaker, Habib Ullah
Infectious Disease Modelling.2022; 7(1): 170. CrossRef - Quantifying transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 and impact of intervention within long-term healthcare facilities
Jessica E. Stockdale, Sean C. Anderson, Andrew M. Edwards, Sarafa A. Iyaniwura, Nicola Mulberry, Michael C. Otterstatter, Naveed Z. Janjua, Daniel Coombs, Caroline Colijn, Michael A. Irvine
Royal Society Open Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost-effective proactive testing strategies during COVID-19 mass vaccination: A modelling study
Zhanwei Du, Lin Wang, Yuan Bai, Xutong Wang, Abhishek Pandey, Meagan C. Fitzpatrick, Matteo Chinazzi, Ana Pastore y Piontti, Nathaniel Hupert, Michael Lachmann, Alessandro Vespignani, Alison P. Galvani, Benjamin J. Cowling, Lauren Ancel Meyers
The Lancet Regional Health - Americas.2022; 8: 100182. CrossRef - Epidemiological Characteristics and Transmissibility for SARS-CoV-2 of Population Level and Cluster Level in a Chinese City
Shanshan Yu, Shufeng Cui, Jia Rui, Zeyu Zhao, Bin Deng, Chan Liu, Kangguo Li, Yao Wang, Zimei Yang, Qun Li, Tianmu Chen, Shan Wang
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-time pandemic surveillance using hospital admissions and mobility data
Spencer J. Fox, Michael Lachmann, Mauricio Tec, Remy Pasco, Spencer Woody, Zhanwei Du, Xutong Wang, Tanvi A. Ingle, Emily Javan, Maytal Dahan, Kelly Gaither, Mark E. Escott, Stephen I. Adler, S. Claiborne Johnston, James G. Scott, Lauren Ancel Meyers
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety Linked to COVID-19: A Systematic Review Comparing Anxiety Rates in Different Populations
Hafsah Saeed, Ardalan Eslami, Najah T. Nassif, Ann M. Simpson, Sara Lal
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2189. CrossRef - A simple electrical-circuit analogous phenomenological COVID-19 model valid
for all observed pandemic phases
J. C. Nolasco, J. T. García, A. Castro-Chacón, A. Castro-Carranza, J. Gutowski
AIP Advances.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in a Canadian suburban tertiary hospital necessitating full facility closure: a descriptive observational study
Jamil N. Kanji, Y.L. Elaine Chan, Lesia R. Boychuk, Curtiss Boyington, Sebora Turay, Melissa Kobelsky, Carolyn Doroshuk, Philana Choo, Susan Jacka, Erin Roberts, Karen Leighton, Stephanie W. Smith, Christopher Sikora, Robert Black
CMAJ Open.2022; 10(1): E137. CrossRef - Local Surveillance of the COVID-19 Outbreak
Caifen Liu, Lingfeng Xu, Yuan Bai, Xiaoke Xu, Eric H. Y. Lau, Benjamin J. Cowling, Zhanwei Du
Frontiers in Physics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A review on COVID-19 transmission, epidemiological features, prevention and vaccination
Yuqin Zhang, Gonghua Wu, Shirui Chen, Xu Ju, Wumitijiang Yimaer, Wangjian Zhang, Shao Lin, Yuantao Hao, Jing Gu, Jinghua Li
Medical Review.2022; 2(1): 23. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness analysis on COVID-19 surveillance strategy of large-scale sports competition
Xuechun Wang, Yiru Cai, Bo Zhang, Xiangyu Zhang, Lianhao Wang, Xiangyu Yan, Mingchen Zhao, Yuan Zhang, Zhongwei Jia
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Social and Policy Determinants of COVID-19 Infection Across 23 Countries: An Ecological Study
Kyungsik Kim, Young-Do Jeung, Jeoungbin Choi, Sue K. Park
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2022; 55(2): 144. CrossRef - Perspectives on factors influencing transmission of COVID-19 in Zambia: a qualitative study of health workers and community members
Cephas Sialubanje, Doreen C Sitali, Nawa Mukumbuta, Libonda Liyali, Phyllis Ingutu Sumbwa, Harvey Kakoma Kamboyi, Mary Ng'andu, Fastone Matthew Goma
BMJ Open.2022; 12(4): e057589. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Mortality Among the COVID-19 Patients Treated at Gulu Regional Referral Hospital: A Retrospective Study
Steven Baguma, Christopher Okot, Nelson Onira Alema, Paska Apiyo, Paska Layet, Denis Acullu, Johnson Nyeko Oloya, Denis Ochula, Pamela Atim, Patrick Odong Olwedo, Smart Godfrey Okot, Freddy Wathum Drinkwater Oyat, Janet Oola, Eric Nzirakaindi Ikoona, Judi
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal intervention strategies to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic effects
Andreas Kasis, Stelios Timotheou, Nima Monshizadeh, Marios Polycarpou
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID‐19 infection in an infant with cystic fibrosis: A case report and possible therapeutic effect of hypertonic saline
Seyed Javad Seyedi, Hossein Sadeghi, Hamid‐Reza Kianifar, Abdolkarim Hamedi, Amin Saeidinia
Clinical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Data analysis and prediction of the COVID-19 outbreak in the first and second waves for top 5 affected countries in the world
Ashabul Hoque, Abdul Malek, K. M. Rukhsad Asif Zaman
Nonlinear Dynamics.2022; 109(1): 77. CrossRef - The influence of gender on COVID-19 infections and mortality in Germany: Insights from age- and gender-specific modeling of contact rates, infections, and deaths in the early phase of the pandemic
Achim Doerre, Gabriele Doblhammer, Siew Ann Cheong
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0268119. CrossRef - The impact of vaccination against the new coronavirus infection on the morbidity of university students
Sergey A. Sayganov, Anna V. Lubimova, Alexandr V. Meltser, Zakhar V. Lopatin, Olga Yu. Kuznetsova, Olga V. Kovaleva
Russian Family Doctor.2022; 26(1): 21. CrossRef - COVID-19: Clinical features, case fatality, and the effect of symptoms on mortality in hospitalized cases in Iran
Yousef Alimohamadi, Mojtaba Sepandi, Roya Rashti, Homeira Sedighinezhad, Sima Afrashteh
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2022; 17(5): 725. CrossRef - The Basic Reproduction Number and Delayed Action of T Cells for Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2
Yingdong Yin, Yupeng Xi, Cheng Xu, Qiwen Sun
Mathematics.2022; 10(12): 2017. CrossRef - Understanding Dynamics of Pandemic Models to Support Predictions of COVID-19 Transmission: Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of SIR-Type Models
Chunfeng Ma, Xin Li, Zebin Zhao, Feng Liu, Kun Zhang, Adan Wu, Xiaowei Nie
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2022; 26(6): 2458. CrossRef - Estimating the course of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany via spline-based hierarchical modelling of death counts
Tobias Wistuba, Andreas Mayr, Christian Staerk
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adding a reaction-restoration type transmission rate dynamic-law to the basic SEIR COVID-19 model
Fernando Córdova-Lepe, Katia Vogt-Geisse, Fabio A Sanchez
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269843. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 Risk Quantification Model and Validation Based on Large-Scale Dutch Test Events
Bas Kolen, Laurens Znidarsic, Andreas Voss, Simon Donders, Iris Kamphorst, Maarten van Rijn, Dimitri Bonthuis, Merit Clocquet, Maarten Schram, Rutger Scharloo, Tim Boersma, Tim Stobernack, Pieter van Gelder
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(12): 7238. CrossRef - Testing and isolation to prevent overloaded healthcare facilities and reduce death rates in the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in Italy
Arnab Bandyopadhyay, Marta Schips, Tanmay Mitra, Sahamoddin Khailaie, Sebastian C. Binder, Michael Meyer-Hermann
Communications Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Autoregressive count data modeling on mobility patterns to predict cases of COVID-19 infection
Jing Zhao, Mengjie Han, Zhenwu Wang, Benting Wan
Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment.2022; 36(12): 4185. CrossRef - Epidemiological investigation of the COVID-19 outbreak in Vellore district in South India using Geographic Information Surveillance (GIS)
Malathi Murugesan, Padmanaban Venkatesan, Senthil Kumar, Premkumar Thangavelu, Winsley Rose, Jacob John, Marx Castro, T. Manivannan, Venkata Raghava Mohan, Priscilla Rupali
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2022; 122: 669. CrossRef - Burden of hospital-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infections in Germany: occurrence and outcomes of different variants
M. Bonsignore, S. Hohenstein, C. Kodde, J. Leiner, K. Schwegmann, A. Bollmann, R. Möller, R. Kuhlen, I. Nachtigall
Journal of Hospital Infection.2022; 129: 82. CrossRef - Lessons from a pandemic
Yves Eggli, Valentin Rousson, Reuben Kiggundu
PLOS Global Public Health.2022; 2(7): e0000404. CrossRef - Update on COVID-19 and Effectiveness of a Vaccination Campaign in a Global Context
Ioannis Alexandros Charitos, Andrea Ballini, Roberto Lovero, Francesca Castellaneta, Marica Colella, Salvatore Scacco, Stefania Cantore, Roberto Arrigoni, Filiberto Mastrangelo, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(17): 10712. CrossRef - Overview of the Role of Spatial Factors in Indoor SARS-CoV-2 Transmission: A Space-Based Framework for Assessing the Multi-Route Infection Risk
Qi Zhen, Anxiao Zhang, Qiong Huang, Jing Li, Yiming Du, Qi Zhang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(17): 11007. CrossRef - Different forms of superspreading lead to different outcomes: Heterogeneity in infectiousness and contact behavior relevant for the case of SARS-CoV-2
Elise J. Kuylen, Andrea Torneri, Lander Willem, Pieter J. K. Libin, Steven Abrams, Pietro Coletti, Nicolas Franco, Frederik Verelst, Philippe Beutels, Jori Liesenborgs, Niel Hens, Miles P. Davenport
PLOS Computational Biology.2022; 18(8): e1009980. CrossRef - Adjusting non-pharmaceutical interventions based on hospital bed capacity using a multi-operator differential evolution
Victoria May P. Mendoza, Renier Mendoza, Jongmin Lee, Eunok Jung
AIMS Mathematics.2022; 7(11): 19922. CrossRef - Estimation and worldwide monitoring of the effective reproductive number of SARS-CoV-2
Jana S Huisman, Jérémie Scire, Daniel C Angst, Jinzhou Li, Richard A Neher, Marloes H Maathuis, Sebastian Bonhoeffer, Tanja Stadler
eLife.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioral responses to risk promote vaccinating high‐contact individuals first
Hazhir Rahmandad
System Dynamics Review.2022; 38(3): 246. CrossRef - Pre-clinical validation of a turbine-based ventilator for invasive ventilation—The ACUTE-19 ventilator
J.M. Alonso-Iñigo, G. Mazzinari, M. Casañ-Pallardó, J.I. Redondo-García, J. Viscasillas-Monteagudo, A. Gutierrez-Bautista, J. Ramirez-Faz, P. Alonso-Pérez, S. Díaz-Lobato, A.S. Neto, O. Diaz-Cambronero, P. Argente-Navarro, M. Gama de Abreu, P. Pelosi, M.J
Revista Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación (English Edition).2022; 69(9): 544. CrossRef - Why COVID-19 modelling of progression and prevention fails to translate to the real-world
Carl J. Heneghan, Tom Jefferson
Advances in Biological Regulation.2022; 86: 100914. CrossRef - The impact of demographic factors on the courseof COVID-19 infection
Karolina Goroszkiewicz, Grażyna Lisowska, Natalia Zięba, Grażyna Stryjewska-Makuch, Kinga Szopińska, Maciej Misiołek
Polski Przegląd Otorynolaryngologiczny.2022; 11(3): 1. CrossRef - COVID-19 cluster size and transmission rates in schools from crowdsourced case reports
Paul Tupper, Shraddha Pai, Caroline Colijn
eLife.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - No magic bullet: Limiting in-school transmission in the face of variable SARS-CoV-2 viral loads
Debra Van Egeren, Madison Stoddard, Abir Malakar, Debayan Ghosh, Antu Acharya, Sk Mainuddin, Biswajit Majumdar, Deborah Luo, Ryan P. Nolan, Diane Joseph-McCarthy, Laura F. White, Natasha S. Hochberg, Saikat Basu, Arijit Chakravarty
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for in-hospital mortality among patients with coronavirus-19 in Isfahan City, Iran
Roya Riahi, Marziye Ghasemi, Zahra Montazeri Shatouri, Mojgan Gharipour, Mahboobeh Maghami, Hamid Melali, Ramin Sami, Aminreza Tabatabaei, SayedMohsen Hosseini
Advanced Biomedical Research.2022; 11(1): 121. CrossRef - Comparison of the Basic Reproduction Numbers for COVID-19 through Four Waves of the Pandemic in Vietnam
Ngan Thi Mai, Giang Thi Huong Tran, Anh Huu Dang, Phuong Thi Bich Cao, Trung Thanh Nguyen, Huong Thi Lan Pham, Tra Thi Thu Vu, Hieu Van Dong, Le Thi My Huynh
International Journal of Translational Medicine.2022; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Estimating the Basic Reproduction Number for the Second Wave of Covid-19 Pandemic in Nigeria
Ashiribo Senapon Wusu, Olusola Aanu Olabanjo, Manuel Mazzara
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Research.2022; 2(2): 1. CrossRef - COVID-19 and India: what next?
Ramesh Behl, Manit Mishra
Information Discovery and Delivery.2021; 49(3): 250. CrossRef - What the reproductive number R0 can and cannot tell us about COVID-19 dynamics
Clara L. Shaw, David A. Kennedy
Theoretical Population Biology.2021; 137: 2. CrossRef - Ruling out COVID-19 by chest CT at emergency admission when prevalence is low: the prospective, observational SCOUT study
Ulf Teichgräber, Amer Malouhi, Maja Ingwersen, Rotraud Neumann, Marina Reljic, Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer, Bettina Löffler, Wilhelm Behringer, Jan-Christoph Lewejohann, Andreas Stallmach, Philipp Reuken
Respiratory Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The challenges of containing SARS-CoV-2 via test-trace-and-isolate
Sebastian Contreras, Jonas Dehning, Matthias Loidolt, Johannes Zierenberg, F. Paul Spitzner, Jorge H. Urrea-Quintero, Sebastian B. Mohr, Michael Wilczek, Michael Wibral, Viola Priesemann
Nature Communications.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A model for COVID-19 with isolation, quarantine and testing as control measures
M.S. Aronna, R. Guglielmi, L.M. Moschen
Epidemics.2021; 34: 100437. CrossRef - Understanding Viral Infection Mechanisms and Patient Symptoms for the Development of COVID-19 Therapeutics
Hyung Muk Choi, Soo Youn Moon, Hyung In Yang, Kyoung Soo Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(4): 1737. CrossRef - Current understanding of the surface contamination and contact transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in healthcare settings
Hosoon Choi, Piyali Chatterjee, John D. Coppin, Julie A. Martel, Munok Hwang, Chetan Jinadatha, Virender K. Sharma
Environmental Chemistry Letters.2021; 19(3): 1935. CrossRef - Impact of climatic, demographic and disease control factors on the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in large cities worldwide
Soeren Metelmann, Karan Pattni, Liam Brierley, Lisa Cavalerie, Cyril Caminade, Marcus S.C. Blagrove, Joanne Turner, Kieran J. Sharkey, Matthew Baylis
One Health.2021; 12: 100221. CrossRef - Mathematical modelling to inform New Zealand’s COVID-19 response
Shaun Hendy, Nicholas Steyn, Alex James, Michael J. Plank, Kate Hannah, Rachelle N. Binny, Audrey Lustig
Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand.2021; 51(sup1): S86. CrossRef - Meta-analysis on Serial Intervals and Reproductive Rates for SARS-CoV-2
Mohammad Hussein, Eman Toraih, Rami Elshazli, Manal Fawzy, August Houghton, Danielle Tatum, Mary Killackey, Emad Kandil, Juan Duchesne
Annals of Surgery.2021; 273(3): 416. CrossRef - Genomic epidemiology of a densely sampled COVID-19 outbreak in China
Lily Geidelberg, Olivia Boyd, David Jorgensen, Igor Siveroni, Fabrícia F Nascimento, Robert Johnson, Manon Ragonnet-Cronin, Han Fu, Haowei Wang, Xiaoyue Xi, Wei Chen, Dehui Liu, Yingying Chen, Mengmeng Tian, Wei Tan, Junjie Zai, Wanying Sun, Jiandong Li,
Virus Evolution.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimating the basic reproduction number for COVID-19 in Western Europe
Isabella Locatelli, Bastien Trächsel, Valentin Rousson, Yury E. Khudyakov
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0248731. CrossRef - The S(E)IR(D) Models of the COVID-19 Epidemic in Korea
Hee-Young Shin
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Simulation of COVID-19 Propagation Scenarios in the Madrid Metropolitan Area
David E. Singh, Maria-Cristina Marinescu, Miguel Guzmán-Merino, Christian Durán, Concepción Delgado-Sanz, Diana Gomez-Barroso, Jesus Carretero
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The SEIR(D) Model of the COVID-19 Epidemic in Korea
Hee-Young Shin
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Countries with delayed COVID-19 introduction – characteristics, drivers, gaps, and opportunities
Zheng Li, Cynthia Jones, Girum S. Ejigu, Nisha George, Amanda L. Geller, Gregory C. Chang, Alys Adamski, Ledor S. Igboh, Rebecca D. Merrill, Philip Ricks, Sara A. Mirza, Michael Lynch
Globalization and Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Containment efficiency and control strategies for the corona pandemic costs
Claudius Gros, Roser Valenti, Lukas Schneider, Kilian Valenti, Daniel Gros
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of COVID-19 secondary attack rate in household and close contacts compared to current risk stratification guidelines of the Kerala government
Balram Rathish, Arun Wilson, Sonya Joy
Tropical Doctor.2021; 51(3): 461. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of measures to control the novel coronavirus disease 2019 in Jilin Province, China
Qinglong Zhao, Yao Wang, Meng Yang, Meina Li, Zeyu Zhao, Xinrong Lu, Bo Shen, Bo Luan, Yifei Zhao, Bonan Cao, Laishun Yao, Benhua Zhao, Yanhua Su, Tianmu Chen
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Meteorological Conditions on the Dynamics of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Poland
Bogdan Bochenek, Mateusz Jankowski, Marta Gruszczynska, Grzegorz Nykiel, Maciej Gruszczynski, Adam Jaczewski, Michal Ziemianski, Robert Pyrc, Mariusz Figurski, Jarosław Pinkas
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 3951. CrossRef - Mathematical modeling of spatio-temporal population dynamics and application to epidemic spreading
Stefanie Winkelmann, Johannes Zonker, Christof Schütte, Nataša Djurdjevac Conrad
Mathematical Biosciences.2021; 336: 108619. CrossRef - Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: From transmission to control with an interdisciplinary vision
Uttpal Anand, Carlo Cabreros, Joyabrata Mal, Florencio Ballesteros, Mika Sillanpää, Vijay Tripathi, Elza Bontempi
Environmental Research.2021; 197: 111126. CrossRef - Tweet Topics and Sentiments Relating to COVID-19 Vaccination Among Australian Twitter Users: Machine Learning Analysis
Stephen Wai Hang Kwok, Sai Kumar Vadde, Guanjin Wang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(5): e26953. CrossRef - Modelling the impact of household size distribution on the transmission dynamics of COVID-19
Pengyu Liu, Lisa McQuarrie, Yexuan Song, Caroline Colijn
Journal of The Royal Society Interface.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Previsione della propagazione di SARS-CoV-2 nello Stato di Amapá, Amazzonia, Brasile, mediante modellazione matematica
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2021; : 73. CrossRef - Estimation of Transmission of COVID-19 in Simulated Nursing Homes With Frequent Testing and Immunity-Based Staffing
Inga Holmdahl, Rebecca Kahn, James A. Hay, Caroline O. Buckee, Michael J. Mina
JAMA Network Open.2021; 4(5): e2110071. CrossRef - Estimation of novel coronavirus (COVID‐19) reproduction number and case fatality rate: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Tanvir Ahammed, Aniqua Anjum, Mohammad Meshbahur Rahman, Najmul Haider, Richard Kock, Md Jamal Uddin
Health Science Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Modelling the Impact of Robotics on Infectious Spread Among Healthcare Workers
Raul Vicente, Youssef Mohamed, Victor M. Eguíluz, Emal Zemmar, Patrick Bayer, Joseph S. Neimat, Juha Hernesniemi, Bradley J. Nelson, Ajmal Zemmar
Frontiers in Robotics and AI.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Who complies with coronavirus disease 2019 precautions and who does not?
Róbert Urbán, Orsolya Király, Zsolt Demetrovics
Current Opinion in Psychiatry.2021; 34(4): 363. CrossRef - Gamma irradiation-mediated inactivation of enveloped viruses with conservation of genome integrity: Potential application for SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine development
Fouad A. Abolaban, Fathi M. Djouider
Open Life Sciences.2021; 16(1): 558. CrossRef - COVID-19 herd immunity in the absence of a vaccine: an irresponsible approach
Jade Khalife, Derrick VanGennep
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021012. CrossRef - Machine Learning for Analyzing Non-Countermeasure Factors Affecting Early Spread of COVID-19
Vito Janko, Gašper Slapničar, Erik Dovgan, Nina Reščič, Tine Kolenik, Martin Gjoreski, Maj Smerkol, Matjaž Gams, Mitja Luštrek
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(13): 6750. CrossRef - Impact of reduction of susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 on epidemic dynamics in four early-seeded metropolitan regions
Thomas J. Barrett, Karen C. Patterson, Timothy M. James, Peter Krüger
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Asian-Origin Approved COVID-19 Vaccines and Current Status of COVID-19 Vaccination Program in Asia: A Critical Analysis
Chiranjib Chakraborty, Ashish Ranjan Sharma, Manojit Bhattacharya, Govindasamy Agoramoorthy, Sang-Soo Lee
Vaccines.2021; 9(6): 600. CrossRef - Phylodynamics reveals the role of human travel and contact tracing in controlling the first wave of COVID-19 in four island nations
Jordan Douglas, Fábio K Mendes, Remco Bouckaert, Dong Xie, Cinthy L Jiménez-Silva, Christiaan Swanepoel, Joep de Ligt, Xiaoyun Ren, Matt Storey, James Hadfield, Colin R Simpson, Jemma L Geoghegan, Alexei J Drummond, David Welch
Virus Evolution.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The current reproduction number of COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia: is the disease controlled?
Theeb Ayedh Alkahtani, Abdullah Alakeel, Reem Abdullah Alakeel, Faten Abdulrahman Khorshid, Hisham Hamoud Alshammari, Abdullah M. Alguwaihes, Mohammad Almohideb, Eman Merghani Ali, May Bin-Jumah, Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim, Anwar Ali Jammah
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2021; 28(33): 44812. CrossRef - Beyond the new normal: Assessing the feasibility of vaccine-based suppression of SARS-CoV-2
Madison Stoddard, Sharanya Sarkar, Lin Yuan, Ryan P. Nolan, Douglas E. White, Laura F. White, Natasha S. Hochberg, Arijit Chakravarty, Muhammad Adrish
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254734. CrossRef - A multi-stage SEIR(D) model of the COVID-19 epidemic in Korea
Hee-Young Shin
Annals of Medicine.2021; 53(1): 1160. CrossRef - A novel geo-hierarchical population mobility model for spatial spreading of resurgent epidemics
Alexandru Topîrceanu, Radu-Emil Precup
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF COVID 19 FEAR ON QUALITY OF LIFE IN HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS: A CORRELATION STUDY IN TURKEY
Ayşe Gül PARLAK, Zümrüt AKGÜN ŞAHİN
Samsun Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2021; 6(2): 367. CrossRef - Is compulsory home quarantine less effective than centralized quarantine in controlling the COVID-19 outbreak? Evidence from Hong Kong
Pengyu Zhu, Xinying Tan
Sustainable Cities and Society.2021; 74: 103222. CrossRef - Rates of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and vaccination impact the fate of vaccine-resistant strains
Simon A. Rella, Yuliya A. Kulikova, Emmanouil T. Dermitzakis, Fyodor A. Kondrashov
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-adherence to preventive behaviours during the COVID-19 epidemic: findings from a community study
Róbert Urbán, Borbála Paksi, Ádám Miklósi, John B. Saunders, Zsolt Demetrovics
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of neutrophil‐to‐lymphocyte ratio in COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Juan R. Ulloque‐Badaracco, W. Ivan Salas‐Tello, Ali Al‐kassab‐Córdova, Esteban A. Alarcón‐Braga, Vicente A. Benites‐Zapata, Jorge L. Maguiña, Adrian V. Hernandez
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and hesitancy: a cross-sectional study in Saudi Arabia
Amar Ibrahim Omer Yahia, Abdullah Mohammed Alshahrani, Wael Gabir H. Alsulmi, Mohammed Mesfer M. Alqarni, Tamim Khalid Abdullah Abdulrahim, Waleed Faya H Heba, Turki Ayidh A. Alqarni, Khalid Ali Z Alharthi, Abdullah Ali A. Buhran
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2021; 17(11): 4015. CrossRef - Modeling coupling dynamics between the transmission, intervention of COVID-19 and economic development
Zhaowang Zhang, Lingming Kong, Hualiang Lin, Guanghu Zhu
Results in Physics.2021; 28: 104632. CrossRef - Vaccines and variants: Modelling insights into emerging issues in COVID-19 epidemiology
Jamie M. Caldwell, Xuan Le, Lorin McIntosh, Michael T. Meehan, Samson Ogunlade, Romain Ragonnet, Genevieve K. O'Neill, James M. Trauer, Emma S. McBryde
Paediatric Respiratory Reviews.2021; 39: 32. CrossRef - Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 to Close Contacts, China, January–February 2020
Yu Li, Jianhua Liu, Zhongcheng Yang, Jianxing Yu, Chengzhong Xu, Aiqin Zhu, Hao Zhang, Xiaokun Yang, Xin Zhao, Minrui Ren, Zhili Li, Jinzhao Cui, Hongting Zhao, Xiang Ren, Chengxi Sun, Ying Cheng, Qiulan Chen, Zhaorui Chang, Junling Sun, Lance E. Rodewald
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2021; 27(9): 2288. CrossRef - Living with COVID-19: The road ahead
Wycliffe Enli Wei, Wei Keat Tan, Alex Richard Cook, Li Yang Hsu, Yik Ying Teo, Vernon Jian Ming Lee
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2021; 50(8): 619. CrossRef - “Mass gathering events and COVID-19 transmission in Borriana (Spain): A retrospective cohort study”
Salvador Domènech-Montoliu, Maria Rosario Pac-Sa, Paula Vidal-Utrillas, Marta Latorre-Poveda, Alba Del Rio-González, Sara Ferrando-Rubert, Gema Ferrer-Abad, Manuel Sánchez-Urbano, Laura Aparisi-Esteve, Gema Badenes-Marques, Belén Cervera-Ferrer, Ursula Cl
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256747. CrossRef - Effective vaccine allocation strategies, balancing economy with infection control against COVID-19 in Japan
Satoshi Sunohara, Toshiaki Asakura, Takashi Kimura, Shun Ozawa, Satoshi Oshima, Daigo Yamauchi, Akiko Tamakoshi, Martial L. Ndeffo Mbah
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(9): e0257107. CrossRef - THE “FLU SEASONS” AND THE MISSING DATA: A MATCHED-PAIR ANALYSIS FOR THE PANDEMIC SEASON 2019_2020
Vincent Kay Lo Ip
International Journal of Research -GRANTHAALAYAH.2021; 9(8): 268. CrossRef - A simple model for control of COVID-19 infections on an urban campus
Robert A. Brown
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and CT Imaging Features of COVID-19 on Admission: A Retrospective Study
Changchun Liu, Jianping Cai, Mengmeng Zhang, Huizhen Li, Chunyan Liu, Jian Dong, Jinghui Dong
Current Medical Imaging Formerly Current Medical Imaging Reviews.2021; 17(11): 1324. CrossRef - Network models to evaluate vaccine strategies towards herd immunity in COVID-19
Josephine N.A. Tetteh, Van Kinh Nguyen, Esteban A. Hernandez-Vargas
Journal of Theoretical Biology.2021; 531: 110894. CrossRef - Examining SARS-CoV-2 Interventions in Residential Colleges Using an Empirical Network
Hali L. Hambridge, Rebecca Kahn, Jukka-Pekka Onnela
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 113: 325. CrossRef - Immunization using a heterogeneous geo-spatial population model: A qualitative perspective on COVID-19 vaccination strategies
Alexandru Topîrceanu
Procedia Computer Science.2021; 192: 2095. CrossRef - Epidemiological characterization of COVID-19 – Pune, 2020-2021
SumitD Bhardwaj, ManoharLal Choudhary, YogeshK Gurav, Priya Abraham, VarshaA Potdar
Indian Journal of Medical Research.2021; 153(5): 542. CrossRef - Synergistic interventions to control COVID-19: Mass testing and isolation mitigates reliance on distancing
Emily Howerton, Matthew J. Ferrari, Ottar N. Bjørnstad, Tiffany L. Bogich, Rebecca K. Borchering, Chris P. Jewell, James D. Nichols, William J. M. Probert, Michael C. Runge, Michael J. Tildesley, Cécile Viboud, Katriona Shea, Jennifer A. Flegg
PLOS Computational Biology.2021; 17(10): e1009518. CrossRef - Low case numbers enable long-term stable pandemic control without lockdowns
Sebastian Contreras, Jonas Dehning, Sebastian B. Mohr, Simon Bauer, F. Paul Spitzner, Viola Priesemann
Science Advances.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapid relaxation of pandemic restrictions after vaccine rollout favors growth of SARS-CoV-2 variants: A model-based analysis
Debra Van Egeren, Madison Stoddard, Alexander Novokhodko, Michael S. Rogers, Diane Joseph-McCarthy, Bruce Zetter, Arijit Chakravarty, Martial L Ndeffo Mbah
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(11): e0258997. CrossRef - Stability, Bifurcation, and a Pair of Conserved Quantities in a Simple Epidemic System with Reinfection for the Spread of Diseases Caused by Coronaviruses
Jorge Fernando Camacho, Cruz Vargas-De-León, Hassan A. El Morshedy
Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Knowledge, Awareness, and Practices (KAP) towards COVID-19 among the marine fishers of Maharashtra State of India: An online cross-sectional Analysis
Suhas Wasave, Sangita Wasave, Ketankumar Chaudhari, Prakash Shingare, Bharat Yadav, Sandesh Patil, Bhalchandra Naik, Amitava Mukherjee
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(12): e0261055. CrossRef - Estimating the impact of influenza on the epidemiological dynamics of SARS-CoV-2
Matthieu Domenech de Cellès, Jean-Sebastien Casalegno, Bruno Lina, Lulla Opatowski
PeerJ.2021; 9: e12566. CrossRef - Ruling Out COVID-19 by Chest CT at Emergency Admission to Prevent In-Hospital Spread When Prevalence is Low – The Prospective, Observational SCOUT Study
Ulf Karl-Martin Teichgräber, Amer Malouhi, Maja Ingwersen, Rotraud Neumann, Marina Reljic, Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer, Bettina Löffler, Wilhelm Behringer, Jan-Christoph Lewejohann, Andreas Stallmach, Philipp A. Reuken
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and forecast of COVID-19 in India, USA and Italy - an application of ARIMA Model
Elbin Siby, Maria Joseph, Aneena Thankachan, K. K. Jose
Biometrics & Biostatistics International Journal.2021; 10(2): 75. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in IRAN: A single center study
Mohamad Nikpouraghdam, Alireza Jalali Farahani, GholamHossein Alishiri, Soleyman Heydari, Mehdi Ebrahimnia, Hossein Samadinia, Mojtaba Sepandi, Nematollah Jonaidi Jafari, Morteza Izadi, Ali Qazvini, Ruhollah Dorostkar, Mahdi Tat, Alireza Shahriary, Gholam
Journal of Clinical Virology.2020; 127: 104378. CrossRef - Preventing major outbreaks of COVID-19 in jails
Justin T Okano, Sally Blower
The Lancet.2020; 395(10236): 1542. CrossRef - Predição da propagação do SARS-CoV-2 no Estado do Amapá, Amazônia, Brasil, por modelagem matemática
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 73. CrossRef - Prediction of the propagation of SARS-CoV-2 in Amapá State, Amazon Region, Brazil, by mathematical modeling
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 73. CrossRef - Price of Delay in Covid-19 Lockdowns: Delays Spike Total Cases, Natural Experiments Reveal
Gerard J. Tellis, Ashish Sood, Nitish Sood
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing the R0 of COVID‐19: mathematics fights back
J. J. Pandit
Anaesthesia.2020; 75(12): 1643. CrossRef - Estimating COVID-19 outbreak risk through air travel
Yair Daon, Robin N Thompson, Uri Obolski
Journal of Travel Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Decrease in Ambient Fine Particulate Matter during COVID-19 Crisis and Corresponding Health Benefits in Seoul, Korea
Changwoo Han, Yun-Chul Hong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5279. CrossRef - “Tomorrow Never Dies”: Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Modalities against Coronavirus (COVID-19) amid Controversies
Partha Laskar, Murali M. Yallapu, Subhash C. Chauhan
Diseases.2020; 8(3): 30. CrossRef - Years of Life Lost Attributable to COVID-19 in High-incidence Countries
In-Hwan Oh, Minsu Ock, Su Yeon Jang, Dun-Sol Go, Young-Eun Kim, Yoon-Sun Jung, Ki Beom Kim, Hyesook Park, Min-Woo Jo, Seok-Jun Yoon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Corona and the climate: a comparison of two emergencies
Kira Vinke, Sabine Gabrysch, Emanuela Paoletti, Johan Rockström, Hans Joachim Schellnhuber
Global Sustainability.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Imputation method to reduce undetected severe acute respiratory infection cases during the coronavirus disease outbreak in Brazil
Silvano Barbosa de Oliveira, Fabiana Ganem, Wildo Navegantes de Araújo, Jordi Casabona, Mauro Niskier Sanchez, Julio Croda
Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Transmission Dynamics of the COVID-19 Epidemic at the District Level in India: Prospective Observational Study
Suman Saurabh, Mahendra Kumar Verma, Vaishali Gautam, Nitesh Kumar, Akhil Dhanesh Goel, Manoj Kumar Gupta, Pankaj Bhardwaj, Sanjeev Misra
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2020; 6(4): e22678. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Critically Ill Patients Infected with COVID-19 in Rasoul Akram Hospital in Iran: A Single Center Study
Poupak Rahimzadeh, Saied Amniati, Reza Farahmandrad, Seyed Hamid Reza Faiz, Setareh Hedayati Emami, Azadeh Habibi
Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Repeated Testing in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Giuseppe Lippi, Fabian Sanchis-Gomar, Brandon M. Henry
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2020; 95(10): 2283. CrossRef - COVID-19 Transmission: Bangladesh Perspective
Masud M A, Md Hamidul Islam, Khondaker A. Mamun, Byul Nim Kim, Sangil Kim
Mathematics.2020; 8(10): 1793. CrossRef - Early management of critically ill patients with COVID‐19
Damián Gutiérrez‐Zarate, Karina Rosas‐Sánchez, Juan Carlos Flores‐Carrillo, Salvador Medrano‐Ahumada, Michel Martínez‐Franco
Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians Open.2020; 1(6): 1418. CrossRef - Transmissibility of coronavirus disease 2019 in Chinese cities with different dynamics of imported cases
Ka Chun Chong, Wei Cheng, Shi Zhao, Feng Ling, Kirran N. Mohammad, Maggie Wang, Benny CY Zee, Lai Wei, Xi Xiong, Hengyan Liu, Jingxuan Wang, Enfu Chen
PeerJ.2020; 8: e10350. CrossRef - Modelling Excess Mortality in Covid-19-Like Epidemics
Zdzislaw Burda
Entropy.2020; 22(11): 1236. CrossRef - Reproductive number of coronavirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on global level evidence
Md. Arif Billah, Md. Mamun Miah, Md. Nuruzzaman Khan, Maria Elena Flacco
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242128. CrossRef - Compositional cyber-physical epidemiology of COVID-19
Jin Woo Ro, Nathan Allen, Weiwei Ai, Debi Prasad, Partha S. Roop
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Responsible Communication of Romanian Companies for Ensuring Public Health in a COVID-19 Pandemic Context
Camelia-Daniela Hategan, Ruxandra-Ioana Curea-Pitorac, Vasile-Petru Hategan
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8526. CrossRef - COVID-19 lockdown induces disease-mitigating structural changes in mobility networks
Frank Schlosser, Benjamin F. Maier, Olivia Jack, David Hinrichs, Adrian Zachariae, Dirk Brockmann
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2020; 117(52): 32883. CrossRef - Attitudes Toward a Potential SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Kimberly A. Fisher, Sarah J. Bloomstone, Jeremy Walder, Sybil Crawford, Hassan Fouayzi, Kathleen M. Mazor
Annals of Internal Medicine.2020; 173(12): 964. CrossRef - Analysis and Forecast of COVID-19 in India, the US and Italy - An Application of Arima Model
Elbin Siby, Maria Joseph, Noel George, Richu Rajesh, Aneena Thankachan
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, Perceived Beliefs, and Preventive Behaviors Related to COVID-19 Among Chinese Older Adults: Cross-Sectional Web-Based Survey
Ying Chen, Rui Zhou, Boyan Chen, Hao Chen, Ying Li, Zhi Chen, Haihong Zhu, Hongmei Wang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(12): e23729. CrossRef - Vorhersage der Ausbreitung von SARS-CoV-2 im brasilianischen Bundesstaat Amapá, Amazonas, durch mathematische Modellierung
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 73. CrossRef - Predicción de la propagación del SARS-CoV-2 en el estado de Amapá, Amazonas, Brasil, por modelado matemático
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 73. CrossRef - Prédiction de la propagation du SRAS-CoV-2 dans l’État d’Amapá, Amazônia, Brésil, par modélisation mathématique
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 73. CrossRef - Прогнозирование распространения SARS-CoV-2 в штате Amapá, Амазонка, Бразилия, с помощью математического моделирования
Neylan Leal Dias, Edcarlos Vasconcelos da Silva, Marcelo Amanajas Pires, Daniel Chaves, Katsumi Letra Sanada, Amanda Alves Fecury, Cláudio Alberto Gellis de Mattos Dias, Euzébio de Oliveira, Carla Viana Dendasck, Simone Delphim Leal
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 73. CrossRef
 KSPM
KSPM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite