Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Prev Med Public Health > Volume 45(2); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
Interaction Between Persistent Organic Pollutants and C-reactive Protein in Estimating Insulin Resistance Among Non-diabetic Adults - Ki-Su Kim1, Nam-Soo Hong1, David R Jacobs2,3, Duk-Hee Lee1
-
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health 2012;45(2):62-69.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.2012.45.2.62
Published online: March 31, 2012
1Department of Preventive Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
2Division of Epidemiology, University of Minnesota School of Public Health, Minneapolis, MN, USA.
3Department of Nutrition, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway.
- Corresponding author: Duk-Hee Lee, MD, PhD. 680 Gukchaebosang-ro, Jung-gu, Daegu 700-842, Korea. Tel: +82-53-420-6960, Fax: +82-53-425-2447, lee_dh@knu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society for Preventive Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Objectives
- Chronic inflammation is now thought to play a key pathogenetic role in the associations of obesity with insulin resistance and diabetes. Based on our recent findings on persistent organic pollutants (POPs) including the lack of an association between obesity and either insulin resistance or diabetes prevalence among subjects with very low concentrations of POPs, we hypothesized that POP concentrations may be associated with inflammation and modify the associations between inflammation and insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects.
-
Methods
- Cross-sectional associations among serum POPs, C-reactive protein (CRP), and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were investigated in 748 non-diabetic participants aged ≥20 years. Nineteen types of POPs in 5 subclasses were selected because the POPs were detectable in ≥60% of the participants.
-
Results
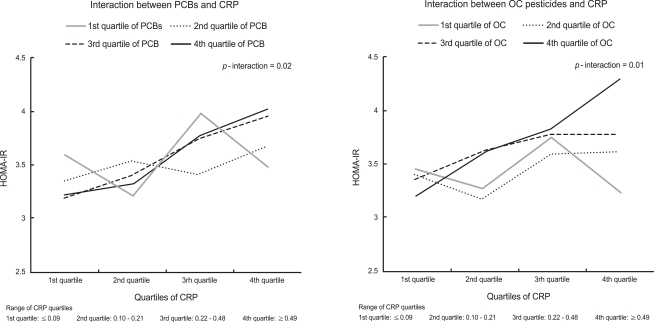
- Among the five subclasses of POPs, only organochlorine (OC) pesticides showed positive associations with CRP concentrations, while polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) showed inverse associations with CRP concentrations. There were statistically significant interactions between CRP and OC pesticides and between CRP and PCBs, in estimating HOMA-IR (P for interaction <0.01 and <0.01, respectively). CRP was not associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with low concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs, while CRP was strongly associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with high concentrations of these POPs.
-
Conclusions
- In the current study, OC pesticides were associated with increased levels of CRP, a marker of inflammation, and both OC pesticides and PCBs may also modify the associations between CRP and insulin resistance.
- Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2002 revealed strong associations of serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) with type 2 diabetes and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in the U.S. general population [1,2]. Furthermore, obesity was not associated with either HOMA-IR or diabetes when POP concentrations were low, while in contrast, POPs were associated with both HOMA-IR and diabetes even among non-obese subjects. Our interpretation of these observations was that POPs stored in adipose tissue, rather than obesity itself, may be the more relevant etiologic factor in HOMA-IR and type 2 diabetes [3,4].
- Chronic low grade inflammation has also been considered to be a key factor in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and diabetes in relation to obesity [5,6]. Many experimental and epidemiological studies have demonstrated obesity to be a state of chronic inflammation caused by altered secretion of adipokines [7]. It is well-known that exposure to high concentrations of environmental pollutants can induce inflammation [8,9]. Thus, POPs stored in adipose tissue may also induce pro-inflammatory reactions although it is unknown whether very low concentrations of POPs from background environmental exposure can also exacerbate chronic inflammation in vivo. In addition, given that obesity was unrelated to either HOMA-IR or diabetes in those with low concentrations of POPs [1,2], we suspected that chronic inflammation may be more strongly associated with insulin resistance or diabetes among subjects with higher concentrations of POPs.
- Thus, this cross-sectional study was performed to test two specific hypotheses in participants without diabetes. The first hypothesis was that serum concentrations of POPs are associated with C-reactive protein (CRP), a well-known nonspecific marker of inflammatory response, independent of obesity, and the second was that CRP is positively associated with HOMA-IR primarily in those with higher concentrations of POPs.
INTRODUCTION
- I. Study Population
- The NHANES 1999-2002 conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention was a complex, multi-state probability survey designed to provide national estimates of the health and nutrition status of the U.S. civilian, non-institutionalized population [10,11].
- Serum concentrations of various POPs or their metabolites were measured in subsamples of the NHANES 1999-2002 surveys [12]. Although 49 POPs were measured in both NHANES 1999-2000 and 2001-2002, to avoid bias in estimation among those below the limit of detection (LOD), we selected the 19 POPs for which at least 60% of the study subjects had concentrations higher than the LOD; this was the same criteria used in our previous study [1]: 3 polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), 3 polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs), 9 polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and 4 organochlorine (OC) pesticides. Of the 852 NHANES 1999-2002 participants aged 20 years or older with information on both fasting morning samples and serum concentrations of the 19 selected POPs, 104 subjects who had diabetes (based on fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dL or physician-diagnosed diabetes) were excluded. The remaining 748 participants were included for the current analysis.
- II. Measurement
- The data collection, quality control procedures, and laboratory methods of NHANES have been described in detail elsewhere [10,11]. Briefly, demographic characteristics and health-related information were collected using a standardized questionnaire during inhome interviews. In order to obtain physical examination data, participants had visited a mobile examination center.
- Venous blood samples were collected, processed, frozen, and shipped weekly at -20℃. The POPs were measured by high-resolution gas chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry using isotope dilution quantification. All these analytes were measured in approximately 5 mL of serum using a modification of the method described by Turner et al. [13]. The POPs were reported on a lipid adjusted basis using concentrations of serum total cholesterol and triglycerides. Plasma glucose was measured with the hexokinase enzymatic reference method (Cobas Mira; Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN, USA) and serum insulin by means of a radioimmunoassay (Pharmacia Diagnostics, Uppsala, Sweden). Insulin resistance was estimated using HOMA-IR calculated as (fasting insulin [mU/L]×fasting glucose [mmol/L]/22.5). CRP was measured by a high-sensitivity assay (hsCRP), a latex-enhanced nephelometry method (BN II nephelometer; Dade Behring, Deerfield, IL, USA) with a lower limit of detection (LOD) of 0.01 mg/dL.
- III. Statistical Analysis
- For each of the POPs, subjects with serum concentrations under the LOD were regarded as the reference group, and subjects with detectable values were categorized by cutoff points of the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentile values. To yield a cumulative measure of 3 PCDDs, we summed the ranks of the 3 PCDDs. The summary values were categorized by cutoff points of the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentile values. We assigned and cumulated POP subclasses similarly for the 3 PCDFs, the 4 dioxin-like PCBs, the 5 non-dioxin-like PCBs, and the 4 OC pesticides. Because the findings were similar for the dioxin-like and the non-dioxin-like PCBs, we also cumulated those 9 POPs and referred to them simply as PCBs.
- First, the associations of categories of POPs with CRP were analyzed using linear regression with continuous logarithmic-transformed CRP concentration as the dependent variable. The association of interactions between POPs and CRP with HOMA-IR were then tested using the quartiles of CRP and POPs as continuous variables.
- In the first model, we adjusted for demographic characteristics: age (years, continuous), gender, race and ethnicity (non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, Mexican-American, and others), and poverty income ratio (family income divided by poverty threshold value, continuous). In the second model, we additionally adjusted for obesity markers and health related information, specifically body mass index (BMI, kg/m2, continuous), waist circumference (cm, continuous), cigarette smoking (never, former, or current), alcohol consumption (g/d, continuous), and leisure time or physical activity (vigorous, moderate, or none). In this study, OC pesticides and PCBs showed opposite associations with CRP, and serum concentrations of OC pesticides and PCBs were positively correlated with each other. Therefore, we generated the final model, which adjusted for the relationship between OC pesticides and PCBs. We substituted the median values in 111 study subjects for the missing values of one or more of the following: poverty income ratio, body mass index, waist circumference, or alcohol consumption. Exclusion of these participants did not change any conclusions.
- All statistical analyses were performed with SAS version 9.2 (SAS Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and SUDAAN version 9.0 (RTI International, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA). Estimates of the main results were calculated accounting for stratification and clustering [14], and adjusting for age, race and ethnicity, and poverty income ratio instead of using sample weights. This adjustment has been regarded as a good compromise between efficiency and bias [14,15]. Because SAS and SUDAAN results were similar, we present the results based on SAS.
METHODS
- The general characteristics of the study subjects by quartiles of CRP are presented in Table 1. Of the subjects, 46.3% were men and 49.5% were non-Hispanic white. The mean age was 48.2 years. Subjects with high CRP tended to be older, women, physically inactive, and obese. In addition, they consumed less alcohol. HOMA-IR showed a positive relationship with CRP.
- Among the 5 POP subclasses, only the OC pesticides showed a positive trend with CRP concentrations (Table 2); this association was attenuated to non-significance after additional adjustment for waist circumference and BMI. Unexpectedly, CRP concentrations tended to show inverse associations with both dioxin-like and non-dioxin-like PCBs. In fact, serum concentrations of OC pesticides and PCBs showed a strong positive correlation (correlation coefficient=0.75) in the current dataset. As only PCBs and OC pesticides, not PCDDs or PCDFs, were associated with CRP in opposite directions, we further adjusted OC pesticides and PCBs for each other. After adjusting for PCBs, the positive association of OC pesticides with CRP was accentuated, while adjustment for OC pesticides rendered the association of PCBs with CRP more strongly inverse (model 3, Table 2). In addition, most of the specific POPs belonging to the PCB or OC pesticide subclasses also showed similar associations (Table 3).
- There were statistically significant interactions between PCBs or OC pesticides and CRP in estimation of HOMA-IR (Table 4, Figure 1). Without consideration of POPs, there were positive associations between CRP and HOMA-IR. However, when POPs were considered as modifying factors, CRP was not associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with low concentrations of PCBs or OC pesticides, while CRP was strongly associated with HOMA-IR among participants with high PCBs or OC pesticide concentrations.
RESULTS
- In this study, we observed that serum concentrations of OC pesticides were positively associated with CRP among the general population of the U.S. with background exposure to POPs. More importantly, consistent with previous findings [1,2], CRP was not associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with low concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs, while CRP was strongly associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with high concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs.
- There is no question that the exposure to certain environmental pollutants can induce inflammation [8,9]. At present, the most studied area in both experimental and human studies subsumes the association between exposure to air pollution and system inflammation [16]. In the case of POPs, experimental studies have clearly shown that some POPs can induce inflammation [17,18]. To the best of our knowledge, however, there are no human data on the association between the low environmental exposure to POPs and inflammation.
- In our study, among 5 subclasses of POPs, OC pesticides were the only subclass to be positively associated with CRP, but other POPs were not associated or were even inversely associated with CRP. Based on the current available evidence, it is almost impossible to suggest possible biological mechanisms that would explain how OC pesticides showed positive associations with CRP while PCBs showed inverse associations. What is known is that the inflammatory properties of plasma cytokines including interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor, which are released from around injured tissue, stimulate acute-phase protein production in the liver, leading to a rise in plasma CRP concentrations [19]. Although it has not been studied yet, it is possible that PCBs interfere with the capacity of the liver to mount an acute-phase response. Thus, although these chemicals can induce inflammation in in vitro experiments, their associations with inflammatory markers in vivo, like CRP, may not be positive. Also, it has been consistently reported that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonists activate oxidative stress-sensitive signaling pathways and subsequent inflammatory events in experimental settings [17,18]. However, in our study on the background exposure to low doses of AhR agonists such as PCDDs, PCDFs, or dioxin-like PCBs were not positively associated with CRP.
- As we hypothesized, there was a clear interaction between POPs and CRP on HOMA-IR, suggesting that the biological implications of increased CRP can be different depending on the serum concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs. Several previous studies have reported associations between inflammatory markers including CRP and insulin resistance among non-diabetic subjects and diabetic or cardiovascular disease patients [20-24]. Some researchers have even suggested the possibility that CRP may directly promote insulin resistance and atherothrombosis by increasing plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and activity in the endothelial cells [25]. Alternatively, insulin resistance could contribute to CRP elevation by reducing insulin-induced suppression of hepatic acute phase reactants [26]. However, the lack of an association between CRP and HOMA-IR among subjects with low concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs, observed in this study, suggests that CRP itself may not be directly involved in insulin resistance or vice versa.
- As an entirely nonspecific response to most forms of tissue damage, various factors may be involved in the chronic elevation of CRP. Our study suggested that, without consideration of exposure to POPs, CRP may not be associated with insulin resistance. These interactions were especially interesting because the direction of association with CRP was opposite for OC pesticides than for PCBs. In addition, it is worthwhile to note that this kind of interaction was very similar to the patterns between POPs and obesity for the risk of type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance, which had been reported in our previous studies, although p-values for interactions of our previous studies had failed to reach statistical significance [1,2]. In one study [27], no association was detected between CRP and insulin resistance in youth. The possibility should be considered that this lack of association could reflect low POP concentrations in youth, given that serum concentrations of POPs are strongly associated with age.
- There are several limitations to this study. First, the cross-sectional study design in NHANES does not allow for inferences regarding the temporality of events. However, the associations of interactions between CRP and some POPs with insulin resistance are not easily explained by any known bias due to the cross-sectional design. Second, misclassification bias is possible for subjects with POPs that would have been detectable with a higher sample volume. Such misclassification would be nondifferential if sample volume is unrelated to HOMA-IR. Third, HOMA-IR is a surrogate with insulin resistance measured using the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp method, but it is highly correlated [28]. Third, we assessed the associations between POPs and CRP by examining 5 POP subclasses and 13 individual POPs. Therefore, some significant associations observed in this study may have been due to chance. Finally, as OC pesticides and PCBs showed opposite associations with CRP and were positively correlated, we adjusted OC pesticides and PCBs for each other. This statistical adjustment of OC pesticides or PCBs can lead to the overestimation of the true effects. However, there were still significant associations of the interactions between PCBs or OC pesticides and CRP with HOMA-IR even when OC pesticides and PCBs were not adjusted for each other (p-values for interaction were 0.02 for PCBs and <0.01 for OC pesticides, data not shown).
- In summary, the current study demonstrated that serum concentrations of OC pesticides were positively associated with CRP levels among the general population of the U.S. and CRP was not associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with low concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs, while CRP was strongly associated with HOMA-IR among subjects with high concentrations of OC pesticides or PCBs.
DISCUSSION
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the material presented in this paper.
-
This article is available at http://jpmph.org/.
Notes
- 1. Lee DH, Lee IK, Jin SH, Steffes M, Jacobs DR Jr. Association between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and insulin resistance among nondiabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetes Care 2007;30(3):622-628. 17327331ArticlePubMed
- 2. Lee DH, Lee IK, Song K, Steffes M, Toscano W, Baker BA, et al. A strong dose-response relation between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and diabetes: results from the National Health and Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetes Care 2006;29(7):1638-1644. 16801591ArticlePubMed
- 3. Lee DH, Jacobs DR Jr, Porta M. Could low-level background exposure to persistent organic pollutants contribute to the social burden of type 2 diabetes? J Epidemiol Community Health 2006;60(12):1006-1008. 17108292ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Porta M. Persistent organic pollutants and the burden of diabetes. Lancet 2006;368(9535):558-559. 16905002ArticlePubMed
- 5. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006;444(7121):860-867. 17167474ArticlePubMed
- 6. Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2006;116(7):1793-1801. 16823477ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Tilg H, Moschen AR. Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2006;6(10):772-783. 16998510ArticlePubMed
- 8. Ganey PE, Roth RA. Concurrent inflammation as a determinant of susceptibility to toxicity from xenobiotic agents. Toxicology 2001;169(3):195-208. 11718960ArticlePubMed
- 9. Laskin DL, Laskin JD. Role of macrophages and inflammatory mediators in chemically induced toxicity. Toxicology 2001;160(1-3):111-118. 11246131ArticlePubMed
- 10. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: NHANES 1999-2000. National Center for Health Statistics. cited 2011 Sep 20. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/nhanes1999-2000/nhanes99_00.htmArticle
- 11. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: NHANES 2001-2002. National Center for Health Statistics. cited 2011 Sep 20. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/nhanes2001-2002/nhanes01_02.htmArticle
- 12. Fourth national report on human exposure to environmental chemicals, updated tables, February 2011. National Center for Health Statistics. cited 2011 Sep 20. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/pdf/Updated_Tables.pdf
- 13. Turner W, DiPietro E, Lapeza C, Green V, Gill J, Patterson DG Jr. A fast universal automated cleanup system for the isotope-dilution HRMS analysis of PCDDs, PCDFs, coplanar PCBs, PCB congeners, and persistent pesticides from the same serum sample. Organohalogen Comp 1997;31: 26-31
- 14. Korn EL, Graubard BI. Epidemiologic studies utilizing surveys: accounting for the sampling design. Am J Public Health 1991;81(9):1166-1173. 1951829ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Graubard BI, Korn EL. Analyzing health surveys for cancer-related objectives. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999;91(12):1005-1016. 10379963ArticlePubMed
- 16. Frampton MW. Systemic and cardiovascular effects of airway injury and inflammation: ultrafine particle exposure in humans. Environ Health Perspect 2001;109(Suppl 4):529-532. 11544158ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Hennig B, Meerarani P, Slim R, Toborek M, Daugherty A, Silverstone AE, et al. Proinflammatory properties of coplanar PCBs: in vitro and in vivo evidence. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2002;181(3):174-183. 12079426ArticlePubMed
- 18. Puga A, Barnes SJ, Chang C, Zhu H, Nephew KP, Khan SA, et al. Activation of transcription factors activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Biochem Pharmacol 2000;59(8):997-1005. 10692565ArticlePubMed
- 19. Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Andus T, Geiger T, Trullenque R, et al. Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 1989;242(2):237-239. 2464504ArticlePubMed
- 20. Chen J, Wildman RP, Hamm LL, Muntner P, Reynolds K, Whelton PK, et al. Association between inflammation and insulin resistance in U.S. nondiabetic adults: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care 2004;27(12):2960-2965. 15562214ArticlePubMed
- 21. Hak AE, Pols HA, Stehouwer CD, Meijer J, Kiliaan AJ, Hofman A, et al. Markers of inflammation and cellular adhesion molecules in relation to insulin resistance in nondiabetic elderly: the Rotterdam study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86(9):4398-4405. 11549682ArticlePubMed
- 22. Marques-Vidal P, Mazoyer E, Bongard V, Gourdy P, Ruidavets JB, Drouet L, et al. Prevalence of insulin resistance syndrome in southwestern France and its relationship with inflammatory and hemostatic markers. Diabetes Care 2002;25(8):1371-1377. 12145237ArticlePubMed
- 23. Wannamethee SG, Lowe GD, Shaper AG, Rumley A, Lennon L, Whincup PH. The metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: relationship to haemostatic and inflammatory markers in older non-diabetic men. Atherosclerosis 2005;181(1):101-108. 15939060ArticlePubMed
- 24. McLaughlin T, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Liang L, Reaven G, Schaaf P, et al. Differentiation between obesity and insulin resistance in the association with C-reactive protein. Circulation 2002;106(23):2908-2912. 12460870ArticlePubMed
- 25. Devaraj S, Xu DY, Jialal I. C-reactive protein increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and activity in human aortic endothelial cells: implications for the metabolic syndrome and atherothrombosis. Circulation 2003;107(3):398-404. 12551862ArticlePubMed
- 26. Campos SP, Baumann H. Insulin is a prominent modulator of the cytokine-stimulated expression of acute-phase plasma protein genes. Mol Cell Biol 1992;12(4):1789-1797. 1372389ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Moran A, Steffen LM, Jacobs DR Jr, Steinberger J, Pankow JS, Hong CP, et al. Relation of C-reactive protein to insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in youth. Diabetes Care 2005;28(7):1763-1768. 15983332ArticlePubMed
- 28. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985;28(7):412-419. 3899825ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
|
Quartiles of C-reactive protein (mg/L) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | < 25th (≦0.09) | 25th - <50th (0.10 - 0.21) | 50th - < 75th (0.22 - 0.48) | ≥75th (≧0.49) | p-trend1 | |
| n = 748 | n = 194 | n = 177 | n = 190 | n = 187 | ||
| Mean±standard deviation | ||||||
| Age (y) | 48.2±18.8 | 42.7±18.9 | 49.7±18.1 | 50.3±18.0 | 50.3±19.3 | <0.01 |
| Poverty income ratio | 2.7±1.6 | 3.0±1.6 | 2.7±1.6 | 2.5±1.5 | 2.5±1.4 | <0.01 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.6±5.7 | 24.7±4.6 | 26.8±4.4 | 28.2±4.9 | 30.8±6.6 | <0.01 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 95.2±14.3 | 87.0±13.5 | 94.1±12.0 | 97.1±12.5 | 103.0±14.4 | <0.01 |
| Alcohol intake (g/d) | 8.9±24.1 | 11.1±29.2 | 11.7±28.1 | 7.1±19.7 | 5.7±16.8 | <0.01 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.9±2.2 | 2.1±1.2 | 2.5±1.7 | 3.0±1.8 | 3.7±3.1 | <0.01 |
| Proportion (%) | ||||||
| Men | 46.3 | 57.7 | 52.0 | 43.7 | 31.6 | <0.01 |
| Non-Hispanic white | 49.5 | 47.4 | 50.3 | 53.2 | 47.1 | 0.03 |
| Current smoker | 19.1 | 15.0 | 23.2 | 19.0 | 19.8 | 0.27 |
| Physically inactive | 46.3 | 38.7 | 45.2 | 41.6 | 59.9 | <0.01 |
| Analyte |
Quartiles of POPs |
p-trend3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 25th | 25th - < 50th | 50th - < 75th | ≥ 75th | |||
| PCDDs | No. of subject | 187 | 187 | 187 | 187 | |
| Model 1 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.44 | |
| Model 2 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.50 | |
| PCDFs | No. of subject | 187 | 187 | 187 | 187 | |
| Model 1 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.43 | |
| Model 2 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.47 | |
| Dioxin-like PCBs | No. of subject | 186 | 188 | 187 | 187 | |
| Model 1 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.28 | |
| Model 2 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.27 | |
| Model 3 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.04 | |
| Non-dioxin like PCBs | No. of subject | 187 | 187 | 187 | 187 | |
| Model 1 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.04 | |
| Model 2 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.28 | |
| Model 3 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.04 | |
| OC pesticides | No. of subject | 186 | 188 | 187 | 187 | |
| Model 1 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.01 | |
| Model 2 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.05 | |
| Model 3 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.01 | |
PCDD, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin; PCDF, polychlorinated dibenzofuran; PCB, polychlorinated biphenyl; OC, organochlorine; POP, persistent organic pollutant.
1 Model 1: adjusted for age, sex, race, and poverty income ratio; model 2: adjusted for the same variables as in model 1 plus body mass index, waist circumference, smoking status, physical activity, and alcohol consumption; model 3: adjusted for the same variables as in model 3 plus for OC pesticides (in models including dioxin like PCBs and non-dioxin like PCBs) or PCBs (in models including OC pesticides).
2 Detectable values of each POP were individually ranked, and the rank orders of the individual POPs in each subclass were summed to arrive at the subclass value. All undetectable values were ranked as 0. The summary values were categorized by the cutoff points of the 25th, 50th, and 75th values of the sum of ranks.
3 Tested by linear regression.
| Analyte | Not detectable |
Quartiles of POPs |
p-trend3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 25th | 25th - < 50th | 50th - < 75th | ≥ 75th | |||
| Dioxin-like PCBs | ||||||
| PCB74 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| PCB118 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| PCB126 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.62 |
| PCB169 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.17 | <0.01 |
| Non-dioxin like PCBs | ||||||
| PCB138 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.05 |
| PCB153 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| PCB170 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.40 |
| PCB180 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.03 |
| PCB187 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| OC pesticides | ||||||
| p,p’-DDE | - | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Oxychlordane | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.09 |
| Trans-nonachlor | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.03 |
| β-hexachlorocyclohexane | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.01 |
POP, persistent organic pollutant; PCB, polychlorinated biphenyl; OC, organochlorine; DDE, dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene.
1 Adjusted for age, sex, race, poverty income ratio, body mass index, waist circumference, smoking status, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and OC pesticides (in models including dioxin-like PCBs and non-dioxin like PCBs) or PCBs (in models including OC pesticides).
2 Detectable values of each POP were individually categorized by the cutoff points of the 25th, 50th, and 75th values.
3 Tested by linear regression.
| Analyte |
Quartiles of C-reactive protein |
p-interaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <25th | 25th - < 50th | 50th -< 75th | ≥ 75th | ||
| Quartiles3 of PCBs | <0.01 | ||||
| <25th | 3.67 | 3.28 | 4.05 | 3.55 | |
| 25th - <50th | 3.39 | 3.57 | 3.43 | 3.69 | |
| 50th - <75th | 3.18 | 3.39 | 3.70 | 3.90 | |
| ≥75th | 3.15 | 3.27 | 3.67 | 3.90 | |
| Quartiles3 of OC pesticides | <0.01 | ||||
| <25th | 3.42 | 3.23 | 3.74 | 3.20 | |
| 25th - <50th | 3.37 | 3.14 | 3.57 | 3.59 | |
| 50th - <75th | 3.33 | 3.60 | 3.76 | 3.77 | |
| ≥75th | 3.17 | 3.59 | 3.82 | 4.31 | |
HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; PCB, polychlorinated biphenyls; OC, organochlorine.
1 Adjusted for age, sex, race, poverty income ratio, body mass index, waist circumference, smoking status, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and OC pesticides (in models including PCBs) or PCBs (in models including OC pesticides).
2 p-interactions between C-reactive protein and PCBs or OC pesticides on HOMA-IR were tested by a generalized linear model using each quartile of C-reactive protein and persistent organic pollutants (POPs) as continuous variables.
3 Detectable values of each POP were individually ranked, and the rank orders of the individual POPs in each subclass were summed to arrive at the subclass value. All not detectable values were ranked as 0. The summary values were categorized by the cutoff points of the 25th, 50th, and 75th values of the sum of ranks.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
Quentin A. Serrano, Sébastien Le Garf, Vincent Martin, Serge S. Colson, Nicolas Chevalier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 883. CrossRef - The associations between endocrine disrupting chemicals and markers of inflammation and immune responses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhiqin Liu, Yao Lu, Kunxia Zhong, Chenchen Wang, Xi Xu
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2022; 234: 113382. CrossRef - Endocrine Disruptors and the Induction of Insulin Resistance
Rafael Vanni, Renata Maksoud Bussuan, Renato Luiz Rombaldi, Alberto K. Arbex
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides on the inflammatory milieu. A systematic review of in vitro, in vivo and epidemiological studies
F.M. Peinado, F. Artacho-Cordón, R. Barrios-Rodríguez, J.P. Arrebola
Environmental Research.2020; 186: 109561. CrossRef - Associations between persistent organic pollutants and metabolic syndrome in morbidly obese individuals
S. Dusanov, J. Ruzzin, H. Kiviranta, T.O. Klemsdal, L. Retterstøl, P. Rantakokko, R. Airaksinen, S. Djurovic, S. Tonstad
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2018; 28(7): 735. CrossRef - Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants
Omar M.L. Alharbi, Al Arsh Basheer, Rafat A. Khattab, Imran Ali
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2018; 263: 442. CrossRef - The influence of persistent organic pollutants in the traditional Inuit diet on markers of inflammation
L. K. Schæbel, E. C. Bonefeld-Jørgensen, H. Vestergaard, S. Andersen, Jaymie Meliker
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(5): e0177781. CrossRef - Pesticide Use and Age-Related Macular Degeneration in the Agricultural Health Study
Martha P. Montgomery, Eric Postel, David M. Umbach, Marie Richards, Mary Watson, Aaron Blair, Honglei Chen, Dale P. Sandler, Silke Schmidt, Freya Kamel
Environmental Health Perspectives.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemostatic, inflammatory, and oxidative markers in pesticide user farmers
Fatima Zohra Madani, Merzouk Hafida, Sid Ahmed Merzouk, Bouchra Loukidi, Katia Taouli, Michel Narce
Biomarkers.2016; 21(2): 138. CrossRef - Persistent organic pollutants and biomarkers of diabetes risk in a cohort of Great Lakes sport caught fish consumers
Mary Turyk, Giamila Fantuzzi, Victoria Persky, Sally Freels, Anissa Lambertino, Maria Pini, Davina H. Rhodes, Henry A. Anderson
Environmental Research.2015; 140: 335. CrossRef - Vitamin D-rich marine Inuit diet and markers of inflammation – a population-based survey in Greenland
L. K. Schæbel, E. C. Bonefeld-Jørgensen, P. Laurberg, H. Vestergaard, S. Andersen
Journal of Nutritional Science.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Persistent Organic Pollutants and Inflammatory Markers in a Cross-Sectional Study of Elderly Swedish People: The PIVUS Cohort
Jitender Kumar, P. Monica Lind, Samira Salihovic, Bert van Bavel, Erik Ingelsson, Lars Lind
Environmental Health Perspectives.2014; 122(9): 977. CrossRef
 KSPM
KSPM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite


