Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Prev Med Public Health > Volume 48(3); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
Exposure to Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Is Associated With Activation of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases Signaling and Apoptosis in Rat Lungs - Kevin M. Rice1,2,3,4, Siva K. Nalabotu1,5, Nandini D.P.K. Manne1, Madhukar B. Kolli1,5, Geeta Nandyala1, Ravikumar Arvapalli1, Jane Y. Ma6, Eric R. Blough1,2,3,4,5,6,7
-
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health 2015;48(3):132-141.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.15.006
Published online: May 18, 2015
1Center for Diagnostic Nanosystems, Marshall University, Huntington, WV, USA
2School of Kinesiology, College of Health Professions, Marshall University, Huntington, WV, USA
3Biotechnology Department, West Virginia State University, Institute, WV, USA
4Department of Internal Medicine, Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Marshall University, Huntington, WV, USA
5Department of Pharmacology, Physiology and Toxicology, Marshall University, Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV, USA
6Health Effects Laboratory Division, NIOSH, Morgantown, WV, USA
7Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Marshall University School of Pharmacy, Huntington, WV, USA
- Corresponding author: Kevin M. Rice, MS Room #241 D, 1700 3rd Avenue, Huntington, WV 25755-1090, USA Tel: +1-304-638-2982, Fax: +1-304-696-3766 E-mail: rice9@marshall.edu
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Society for Preventive Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Objectives:
- With recent advances in nanoparticle manufacturing and applications, potential exposure to nanoparticles in various settings is becoming increasing likely. No investigation has yet been performed to assess whether respiratory tract exposure to cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles is associated with alterations in protein signaling, inflammation, and apoptosis in rat lungs.
-
Methods:
- Specific-pathogen-free male Sprague-Dawley rats were instilled with either vehicle (saline) or CeO2 nanoparticles at a dosage of 7.0 mg/kg and euthanized 1, 3, 14, 28, 56, or 90 days after exposure. Lung tissues were collected and evaluated for the expression of proteins associated with inflammation and cellular apoptosis.
-
Results:
- No change in lung weight was detected over the course of the study; however, cerium accumulation in the lungs, gross histological changes, an increased Bax to Bcl-2 ratio, elevated cleaved caspase-3 protein levels, increased phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, and diminished phosphorylation of ERK-1/2-MAPK were detected after CeO2 instillation (p<0.05).
-
Conclusions:
- Taken together, these data suggest that high-dose respiratory exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles is associated with lung inflammation, the activation of signaling protein kinases, and cellular apoptosis, which may be indicative of a long-term localized inflammatory response.
- Cerium is a lanthanide metal that can undergo redox cycling depending on the partial pressure of oxygen in the surrounding environment [1]. The industrial production and utilization of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles is increasing rapidly in the polishing, energy, electronic, automobile, and biomedical industries [2]. Recently, CeO2 nanoparticles have been used as catalysts in combustion engines to reduce particulate emissions and increase fuel efficiency [3]. Other work has demonstrated that CeO2 nanoparticles may exhibit antioxidant activity [4], which has led to the suggestion that these particles may be useful for the treatment of cardiovascular disease [5], neuronal injury [6], and the prevention of radiation-induced damage [7].
- In addition to the beneficial applications of CeO2 nanoparticles, some researchers have begun to examine whether these materials may also be toxic. In vitro studies using lung cancer cells (A549) [8] and bronchoalveolar epithelial cells (BEAS2B) [9] have suggested that cellular exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles may be associated with the increased production of reactive oxygen species and the induction of cellular apoptosis. Other work using intact rats has demonstrated that exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles can cause lung inflammation and fibrosis [10-12]. How exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles may induce lung inflammation and remodeling has not been fully elucidated.
- Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2-MAPK, p38 MAPK, and c-Jun amino terminal kinase (JNK), are a family of serine/threonine-specific kinases that transduce extracellular stimuli and are involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, gene expression, and apoptosis [13,14]. Previous work has suggested that several metals, including arsenic, zinc, and chromium, can induce the phosphorylation of MAPK proteins [15]. To the best of our knowledge, no studies have yet investigated whether exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles can elicit similar activity.
- The primary goal of this study was to determine if exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles is associated with the activation of MAPK signaling and cellular apoptosis in the lungs of intact rats. Our data suggest that exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles is associated with cerium accumulation in the lungs, an increased Bax to Bcl-2 ratio, elevated caspase-3 protein levels, increased phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, and diminished phosphorylation of ERK-1/2-MAPK (p<0.05). Taken together, these data suggest that exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles is associated with activation of MAPK signaling along with cellular apoptosis.
INTRODUCTION
- Particle Characterization
- CeO2 nanoparticles with an average hydrodynamic diameter of approximately 20 nm and average physical diameter of approximately 10 nm were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), corresponding to the specifications of nanoparticles used in previous experiments [12]. Normal saline was used to suspend the nanoparticles prior to instillation. Diluted particle suspensions were filtered, sputter-coated, and examined with a Hitachi Model S-4800 Field Emission scanning electron microscope (Schaumburg, IL, USA) at 5 kV and 20 kV, or placed on a formvar-coated copper grid to dry and imaged with a JEOL 1220 transmission electron microscope (Tokyo, Japan), as previously described [16].
- Animal Handling and Instillation of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
- All procedures were performed in accordance with the Marshall University Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines, using the criteria outlined by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC). Five-week-old (150 to 174 g) specific-pathogen-free male Sprague-Dawley (Hla: SD-CVF) rats were purchased from Hilltop Lab Animals, Inc. (Scottdale, PA, USA). Rats were housed two per cage in an AAALAC-approved vivarium with a 12-hour light-dark cycle and maintained at 22±2˚C. Animals were allowed access to food and water ad libitum. All animals were allowed to acclimatize for two weeks before the study began. All animals were examined for precipitous weight loss, failure to thrive, or unexpected gait. Periodic weight measurements were taken throughout the duration of the study.
- After acclimatization, the animals were randomly divided into 12 groups (n=6 per group). After anesthetization, the animals were placed on an inclined restraint board and instilled with 0.3 mL of a saline suspension of CeO2 nanoparticles at a dosage of 7.0 mg/kg or 0.3 mL of saline, as described elsewhere [16]. This dose was selected based on previously published data by Ma et al. [17] demonstrating a dose-dependent response in lung cells.
- Tissue Collection
- Rats were anesthetized at 1, 3, 14, 28, 56, or 90 days post-exposure, using a ketamine (40 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) cocktail (administered intraperitoneally), supplemented as necessary to ensure the loss of reflexive responses. After midline laparotomy, the lungs were removed and placed in Krebs-Ringer bicarbonate buffer, containing 118 mM NaCl, 4.7 mM KCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 1.2 mM KH2PO4, 1.2 mM MgSO4, 24.2 mM NaHCO3, and 10 mM α-D-glucose (pH 7.4), equilibrated with 5% CO2/95% O2, and maintained at 37˚C. Blood and other tissue materials were removed from the isolated lungs, weighed immediately, and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen.
- Determination of Cerium Content in the Lungs
- Cerium content in the lungs was estimated by induction coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) at Elemental Analysis, Inc. (Lexington, KY, USA) according to standard protocols as described elsewhere [16]. The cerium concentration was estimated for the 1, 3, 14, 28, and 90-day post-exposure groups. Briefly, lung samples (n=4 for each group) were prepared using the Environmental Protection Agency method 3050B for the analysis of total cerium by ICP-MS. Samples was weighed and digested with concentrated nitric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid, and 30% hydrogen peroxide. Samples were diluted and compared against a laboratory control sample using an Agilent 7500cx ICP-MS machine (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
- Histopathological Examination
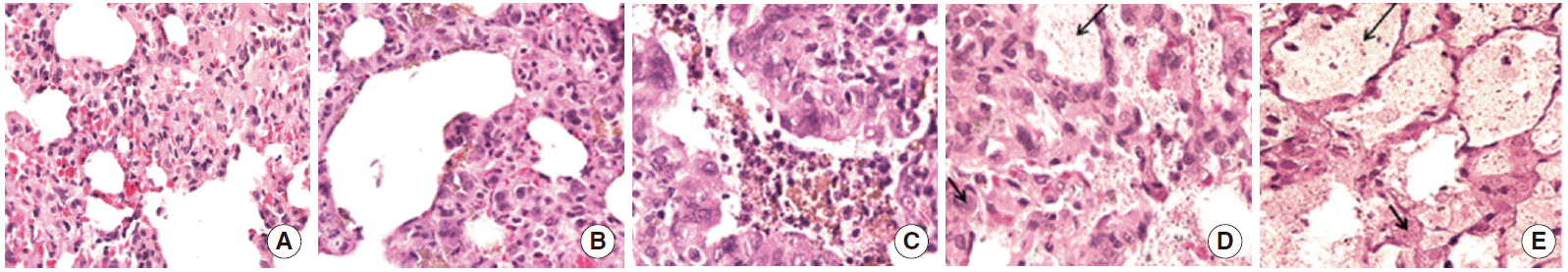
- Histopathological examination was performed on lungs from the day 1 saline control group, and in groups that had been exposed to CeO2 for 1, 3, 14, and 28 days, using hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining on formalin-fixed lung tissues. Using standard histopathological techniques lung tissues were embedded in paraffin wax, sectioned at 5 μm, mounted on glass slides, and stained with H&E. In a blinded fashion, sections were examined by light microscopy by a board-certified pathologist.
- Immunoblotting Analysis
- Portions of individual lung tissues (100 to 150 mg) were homogenized in lysis buffer (T-PER, 8 mL/g of tissue; Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) containing phosphatase inhibitors (Sigma-Aldrich) and protease (Sigma-Aldrich). Tissue homogenates were sonicated for three cycles for 30 seconds at 150 W. The supernatant protein was collected by centrifuging the tissue homogenate at 12 000×g for five minutes at 4˚C. The protein concentration of homogenates was determined via the 660-nm assay method (Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Equal concentrations of the protein samples were prepared from individual animals by adding equal quantities of Laemmli 2X sample buffer (Sigma-Aldrich) and adjusting the protein concentration with the T-PER lysis buffer. Immunoblotting was performed on the prepared samples as described in Kakarla et al. [18] using the primary antibodies against caspase-3 (1:1000 dilution in 5% bovine serum albumin [BSA] in TBST) (#9662), cleaved caspase-3 (1:500 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9661S), Bax (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#2772), Bcl2 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#2870S), caspase-9 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9506), ERK-1/2 Thr 202/Tyr204 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9106S), phosphorylated ERK-1/2 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) Thr 202/Tyr204 (#4377S), JNK (1:500 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9252), phosphorylated JNK Thr 183/Tyr185 (1:500 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9251S), p38 MAPK (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9212), phosphorylated p38 MAPK Thr 180/Tyr 182 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9216L), JAK-2 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#3229), phosphorylated JAK-2 Tyr 1007/100 (1:1000 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#3776), STAT-3 (1:500 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9132), and phosphorylated STAT-3 Tyr 705 (1:500 dilution in 5% BSA in TBST) (#9131S) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA).
- Data Analysis
- Data were analyzed using the SigmaPlot version 11.0 (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). Results are presented as mean±standard error of the mean. To determine overall comparisons one-way analysis of variance and two-way analysis of variance were performed, followed by a Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test to determine differences between groups. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
METHODS
- Nanoparticle Characterization
- Similar to previous research [12,16] using CeO2 nanoparticles made to the same specifications, the analysis of nanoparticle size by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy confirmed the presence of single and agglomerated CeO2 nanoparticles in the suspension. Field emission scanning electron microscopy showed submicron groups dispersion of CeO2 nanoparticles with an average size of 9.26±0.58 nm. Determination of the diameter of the primary CeO2 particles was 10.14±0.76 nm when evaluated by transmission electron microscopy.
- Accumulation of Cerium in the Lung Over Time After Exposure
- The concentration of cerium in the lungs was estimated using ICP-MS (Elemental Analysis). The concentration of cerium in the lungs decreased as post-exposure time increased. The concentration of cerium in lung tissue at 14, 28, and 90 days post-exposure was significantly lower than in tissue obtained one day after exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles, as shown in Figure 1.
- Exposure to Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Alters the Gross Histological Appearance of the Lung
- Alterations in the appearance of the lungs following exposure included the presence of areas of black discoloration and white pustular nodules on the surface of the lungs, which appeared to increase over time (Figure 2). Histological alterations included an increased number of alveolar macrophages, an increased number of polymorphonuclear cells, and an apparent accumulation of particulate material in the alveolar spaces (Figure 3).
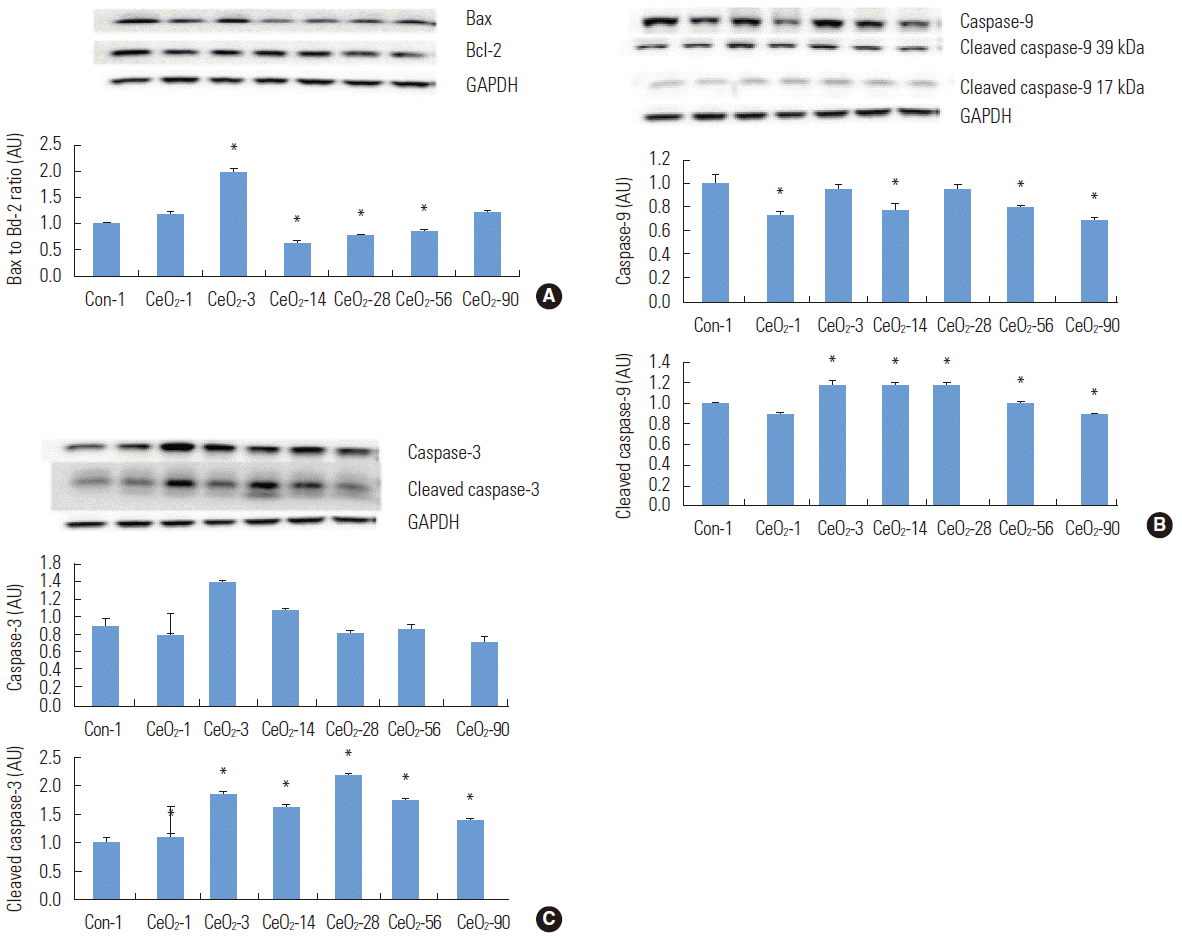
- Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Increase Apoptotic Protein Signaling in the Lung
- Compared to the day 1 saline control group, the Bax to Bcl-2 ratio in exposed animals was 99% higher three days after exposure (p<0.05) before declining thereafter. Compared to the day 1 saline control group, the Bax to Bcl-2 ratio was 37, 23, and 14% lower at days 14, 28, and 56, respectively, in animals exposed to CeO2 nanoparticles (p<0.05) (Figure 4).
- In order to extend these findings, we next examined the regulation of the initiator (caspase-9) and the executor caspases (caspase-3) [18]. Compared to the day 1 saline control group, the total caspase-9 protein levels were reduced by 28, 6, 23, 21, and 32% in the 1, 3, 14, 56, and 90-day post-exposure groups (p<0.05). Compared to the day 1 saline control group, the expression of the 38-kDa and 40-kDa cleaved fragments of caspase-9 was increased by 20% in the 3, 14, and 28-day post-exposure groups (p<0.05) (Figure 4).
- Caspase-3 protein expression levels increased by 56% (p<0.05) and 20% (p<0.05) in the 3 and 14-day exposure groups, when compared to the day 1 saline control group. Compared to the day 1 saline control group, the protein expression of the cleaved fragments of caspase-3 (17 kDa and 19 kDa) were increased by 10, 88, 66, 119, 77, and 39% in the 1, 3, 14, 28, 56, and 90-day post-exposure groups (p<0.05) (Figure 4).
- Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure Is Associated With Activation of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling
- Compared to the day 1 saline control group, the ratio of phosphorylated p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) to total p38 MAPK was reduced by 22 and 14% in the day 1 and day 3 post-exposure groups (p<0.05). However, this ratio was elevated by 52, 15, and 10% in the 14, 28, and 56-day post-exposure groups, before it declined by 19% in the 90-day post-exposure group (p<0.05) (Figure 5).
- The ratio of phosphorylated ERK-1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) to total ERK-1/2 was reduced by 43, 57, 56, 62, 53, and 41% in the 1, 3, 14, 28, 56, and 90-day post-exposure groups compared to the day 1 saline control group (p<0.05) (Figure 5). In contrast, the ratio of phosphorylated (Thr183/Tyr185) JNK to total JNK was unaltered following nanoparticle exposure (Figure 5).
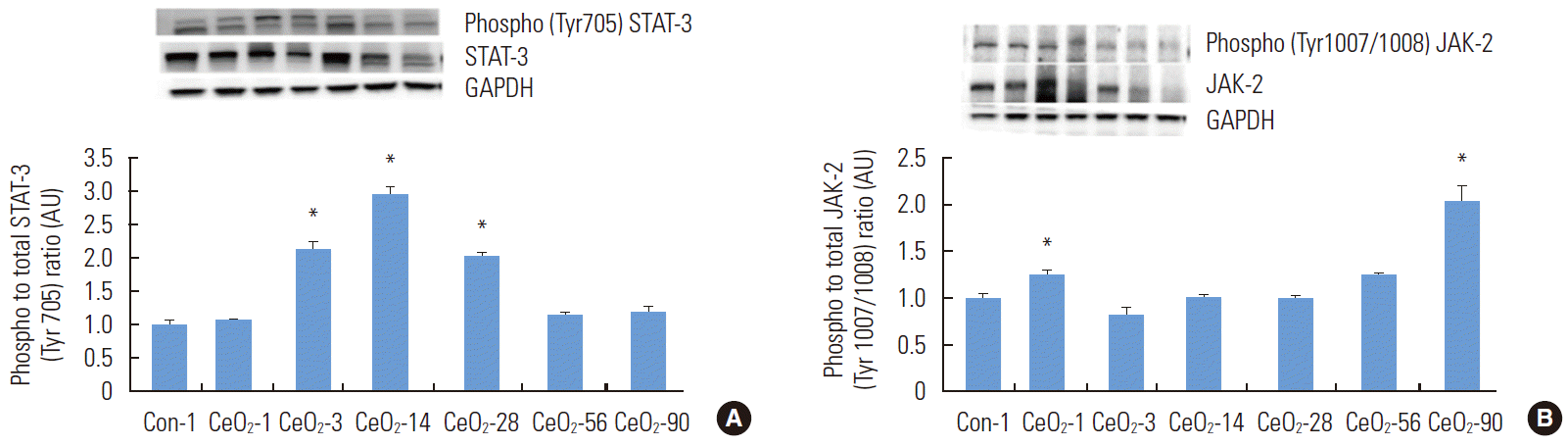
- Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Activate Inflammatory Protein Signaling Through p38 MAPK Mediated STAT-3 Activation
- It is known that JAK-2 and STAT-3 play a crucial role in inflammation [19]. When compared to the day 1 saline control group, the ratio of phosphorylated (Tyr705) to total STAT-3 protein was 111, 193, and 106% higher at 3, 14, and 28 days after exposure (p<0.05) (Figure 6). The ratio of phosphorylated (Tyr1007/1008) JAK-2 to total JAK-2 was 25 and 103% higher in the 1 and 90-day post-exposure groups compared to the control animals (p<0.05) (Figure 6).
RESULTS
- Previous In vitro and in vivo studies have suggested that exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles can elicit toxic effects, although the underlying mechanism is not well understood [3,8,12,20]. The primary finding of the current study is that pulmonary exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles is associated with histological evidence of lung inflammation, the activation of MAPK signaling, the phosphorylation of STAT-3, increased caspase-3 cleavage, and inflammation.
- The data from the current study show that the instillation of CeO2 nanoparticles leads to the deposition of cerium in the lungs, as shown by ICP-MS (Figure 1). We also observed that exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles was associated with the development of white nodular structures on the lung surface (Table 1, Figures 2 and 3). Recent work has shown that nanoparticles such as carbon nanotubes, titanium dioxide nanoparticles, and polyacrylate nanoparticles can induce granulomas on the lung surface [21-23]. It is possible that the white nodules we observed in the present study may be the byproduct of an ongoing inflammatory reaction, which could result in either the clearance of the nanoparticles or their further development into granulomas on the surface of the lungs [22,24]. The aforementioned possibility is consistent with our histopathological analysis, in which we observed an increase in the number of alveolar macrophages and polymorphonuclear white blood cells in the lungs of animals that had been exposed to CeO2 nanoparticles. It is thought that the toxic effects of most nanoparticles (silver, silica, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, and carbonaceous nanoparticles) are characterized by increased oxidative stress [25-29]. Whether these increases in oxidative stress are due to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation or decreased ROS scavenging is currently unclear, although many metallic oxide nanoparticles have been shown to increase ROS production [30,31].
- Increased ROS levels may also induce apoptotic signaling. We observed an increase in the pro-apoptotic Bax to Bcl-2 ratio at one and three days after the exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles, with a subsequent decline. Since the Bax to Bcl-2 ratio is an indicator of whether a cell is likely to undergo apoptosis [18,32], we next examined the possibility that CeO2 nanoparticle exposure may be associated with the activation of caspase-3. Consistent with the Bax/Bcl-2 data, we found that caspase-3 cleavage (activation) was elevated at 3, 14, 28, and 56 days post-exposure. Why caspase-3 cleavage was present in the absence of an elevated Bax/Bcl-2 ratio is currently unclear. Other signaling pathways (extrinsic or intrinsic pathways) that activate the apoptotic pathway may be in play and explain the possible activation of effector caspase-3 in the absence of an elevated Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. It is thought that mild lung injury may elicit the repair of the damaged tissue, whereas excessive apoptosis-induced cell death may lead to the development of lung remodeling and fibrosis [33]. Bearing this in mind, the activation of caspase-3 we identified in the current study may help to explain previous findings that increased lung fibrosis follows exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles [12].
- MAPKs are stress-responsive proteins that can be activated by growth factors, chemicals, ultraviolet radiation, heat, synthesis inhibitors, metals, or foreign organisms [34]. MAPK pathways have been shown to play important roles in oxidative stress and inflammation induced by nanoparticles and metals [15,31]. The three primary members of the MAPK signaling modules are the p38, JNK, and ERK-1/2 MAPKs. MAPK proteins are thought to phosphorylate (activate) transcription factors that are involved in regulating both cell survival and cell death. In the present study, exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles was associated with increased phosphorylation of p38 MAPK at 14, 28, and 56 days after exposure. Conversely, we found that ERK-1/2-MAPK activity appeared to be impaired by CeO2 nanoparticles (Figure 5). Since ERK-1/2-MAPK is thought to play an important role in cell survival and p38 MAPK may play an important role in apoptosis [34], these differences in MAPK signaling may help to explain the sustained caspase-3 cleavage after the pro-apoptotic Bax to Bcl-2 ratio returned to normal.
- It is well known that nanoparticle exposure is often associated with increased levels of cytokines, interleukins, and other mediators of inflammation. The Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway is a particularly important pathway in mediating inflammation [19]. Interestingly, JAK-2 did not appear to play an important role in the toxicological response, as its phosphorylation (Tyr1007/ 1008) was elevated only at day 1 and day 90 (Figure 6). Conversely, the phosphorylation of STAT-3 (Tyr705) seemed to parallel p38 MAPK activation (Figure 6). A previous study has demonstrated that p38 MAPK can act as an upstream activator of STAT-3, which, in turn, can induce apoptosis when activated [35]. Other research has shown that the p38 MAPK and STAT-3 signaling pathways can work in concert or separately to exert apoptotic effects on the cells [36]. These data, considered in light of our findings regarding the increased Bax to Bcl-2 ratio, are consistent with the possibility that apoptosis mediated by CeO2 nanoparticles is mediated through the activation of the p38 MAPK and STAT-3 signaling pathways.
- In summary, our data suggest that lung exposure to CeO2 nanoparticles is associated with the increased accumulation of cerium in the lungs and gross pathological and histological alterations to the lungs. It also appears that CeO2 nanoparticles can induce inflammation and apoptotic protein signaling in the lungs. Overall, the data from the current study indicate that CeO2 nanoparticle-induced inflammation and apoptosis may be mediated through the activation of the stress-responsive MAPK protein signaling pathway, the phosphorylation of STAT-3, and the activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway (Figure 6). Given these findings, additional research to evaluate the role of subcellular organelles in inducing apoptosis in these conditions is likely warranted.
DISCUSSION
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the material presented in this paper.
Notes



| Exposure (d) |
Body weight (g) |
Lung weight (g) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline control | CeO2 (7.0 mg/kg) | Saline control | CeO2 (7.0 mg/kg) | |
| 1 | 319.67±15.92 | 319.67±15.20 | 1.74±0.28 | 1.88±0.08 |
| 3 | 310.33±28.10 | 331.67±24.00 | 1.54±0.27 | 2.19±0.15 |
| 14 | 345.67±27.11 | 332.33±21.07 | 1.90±0.31 | 2.12±0.23 |
| 28 | 411.33±29.21,3 | 403.67±28.941,3 | 1.82±0.09 | 2.43±0.30 |
| 56 | 451.67±26.211-3 | 451.00±34.61-4 | 1.56±0.24 | 2.84±0.58 |
| 90 | 523.33±60.871-5 | 519.33±44.841-5 | 1.62±0.11 | 2.75±0.51 |
Lung tissues were collected from groups of animals that were intratracheally instilled with either normal saline or CeO2 nanoparticles at a dosage of 7.0 mg/kg, at 1, 3, 14, 28, 56, and 90 days after exposure. The lung tissues were cleaned to remove blood and tissue debris with Krebs’s lactate solution and weighed immediately (n=6/group). Two-way analysis of variance was performed for overall comparisons, while the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test was used to determine differences between groups; p<0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
1 Significantly different from the one-day exposure group for a given condition.
2Significantly different from the three-day exposure group for a given condition.
3 Significantly different from the 14-day exposure group for a given condition.
4 Significantly different from the 28-day exposure group.
5 Significantly different from the 56-day exposure group.
- 1. Heckert EG, Seal S, Self WT. Fenton-like reaction catalyzed by the rare earth inner transition metal cerium. Environ Sci Technol 2008;42(13):5014-5019ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Bumajdad A, Eastoe J, Mathew A. Cerium oxide nanoparticles prepared in self-assembled systems. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 2009;147-148: 56-66ArticlePubMed
- 3. Park B, Martin P, Harris C, Guest R, Whittingham A, Jenkinson P, et al. Initial in vitro screening approach to investigate the potential health and environmental hazards of Enviroxtrade mark - a nanoparticulate cerium oxide diesel fuel additive. Part Fibre Toxicol 2007;4: 12ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Karakoti AS, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Aggarwal R, Davis JP, Narayan RJ, Self WT, et al. Nanoceria as antioxidant: synthesis and biomedical applications. JOM (1989) 2008;60(3):33-37ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Niu J, Azfer A, Rogers LM, Wang X, Kolattukudy PE. Cardioprotective effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles in a transgenic murine model of cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 2007;73(3):549-559ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Das M, Patil S, Bhargava N, Kang JF, Riedel LM, Seal S, et al. Auto-catalytic ceria nanoparticles offer neuroprotection to adult rat spinal cord neurons. Biomaterials 2007;28(10):1918-1925ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Colon J, Herrera L, Smith J, Patil S, Komanski C, Kupelian P, et al. Protection from radiation-induced pneumonitis using cerium oxide nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2009;5(2):225-231ArticlePubMed
- 8. Lin W, Huang YW, Zhou XD, Ma Y. Toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Int J Toxicol 2006;25(6):451-457ArticlePubMed
- 9. Eom HJ, Choi J. Oxidative stress of CeO2 nanoparticles via p38-Nrf-2 signaling pathway in human bronchial epithelial cell, Beas-2B. Toxicol Lett 2009;187(2):77-83ArticlePubMed
- 10. He X, Zhang H, Ma Y, Bai W, Zhang Z, Lu K, et al. Lung deposition and extrapulmonary translocation of nano-ceria after intratracheal instillation. Nanotechnology 2010;21(28):285103ArticlePubMed
- 11. Cassee FR, van Balen EC, Singh C, Green D, Muijser H, Weinstein J, et al. Exposure, health and ecological effects review of engineered nanoscale cerium and cerium oxide associated with its use as a fuel additive. Crit Rev Toxicol 2011;41(3):213-229ArticlePubMed
- 12. Ma JY, Zhao H, Mercer RR, Barger M, Rao M, Meighan T, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation and alveolar macrophage functional change in rats. Nanotoxicology 2011;5(3):312-325ArticlePubMed
- 13. Guyton KZ, Liu Y, Gorospe M, Xu Q, Holbrook NJ. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by H2O2. Role in cell survival following oxidant injury. J Biol Chem 1996;271(8):4138-4142PubMed
- 14. Tournier C, Thomas G, Pierre J, Jacquemin C, Pierre M, Saunier B. Mediation by arachidonic acid metabolites of the H2O2-induced stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase). Eur J Biochem 1997;244(2):587-595ArticlePubMed
- 15. Samet JM, Graves LM, Quay J, Dailey LA, Devlin RB, Ghio AJ, et al. Activation of MAPKs in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to metals. Am J Physiol 1998;275(3 Pt 1):L551-L558ArticlePubMed
- 16. Nalabotu SK, Kolli MB, Triest WE, Ma JY, Manne ND, Katta A, et al. Intratracheal instillation of cerium oxide nanoparticles induces hepatic toxicity in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Nanomedicine 2011;6: 2327-2335ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Ma JY, Zhao H, Mercer RR, Barger M, Rao M, Meighan T, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation and alveolar macrophage functional change in rats. Nanotoxicology 2011;5(3):312-325ArticlePubMed
- 18. Wu M, Liu H, Fannin J, Katta A, Wang Y, Arvapalli RK, et al. Acetaminophen improves protein translational signaling in aged skeletal muscle. Rejuvenation Res 2010;13(5):571-579ArticlePubMed
- 19. Kakarla SK, Fannin JC, Keshavarzian S, Katta A, Paturi S, Nalabotu SK, et al. Chronic acetaminophen attenuates age-associated increases in cardiac ROS and apoptosis in the Fischer Brown Norway rat. Basic Res Cardiol 2010;105(4):535-544ArticlePubMed
- 20. Rawlings JS, Rosler KM, Harrison DA. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 2004;117(Pt 8):1281-1283ArticlePubMed
- 21. Park EJ, Choi J, Park YK, Park K. Oxidative stress induced by cerium oxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicology 2008;245(1-2):90-100ArticlePubMed
- 22. Donaldson K, Aitken R, Tran L, Stone V, Duffin R, Forrest G, et al. Carbon nanotubes: a review of their properties in relation to pulmonary toxicology and workplace safety. Toxicol Sci 2006;92(1):5-22ArticlePubMed
- 23. Park EJ, Yoon J, Choi K, Yi J, Park K. Induction of chronic inflammation in mice treated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles by intratracheal instillation. Toxicology 2009;260(1-3):37-46ArticlePubMed
- 24. Ren H, Huang X. Polyacrylate nanoparticles: toxicity or new nanomedicine? Eur Respir J 2010;36(1):218-221ArticlePubMed
- 25. Bergamaschi E, Bussolati O, Magrini A, Bottini M, Migliore L, Bellucci S, et al. Nanomaterials and lung toxicity: interactions with airways cells and relevance for occupational health risk assessment. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2006;19(4 Suppl):3-10PubMed
- 26. Stone V, Johnston H, Clift MJ. Air pollution, ultrafine and nanoparticle toxicology: cellular and molecular interactions. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 2007;6(4):331-340ArticlePubMed
- 27. Folkmann JK, Risom L, Jacobsen NR, Wallin H, Loft S, Møller P. Oxidatively damaged DNA in rats exposed by oral gavage to C60 fullerenes and single-walled carbon nanotubes. Environ Health Perspect 2009;117(5):703-708ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Jeong YS, Oh WK, Kim S, Jang J. Cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and ROS generation with silica/conducting polymer core/shell nanospheres. Biomaterials 2011;32(29):7217-7225ArticlePubMed
- 29. Koike E, Kobayashi T. Chemical and biological oxidative effects of carbon black nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2006;65(6):946-951ArticlePubMed
- 30. Li N, Xia T, Nel AE. The role of oxidative stress in ambient particulate matter-induced lung diseases and its implications in the toxicity of engineered nanoparticles. Free Radic Biol Med 2008;44(9):1689-1699ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Buzea C, Pacheco II, Robbie K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2007;2(4):MR17-MR71ArticlePubMed
- 32. Marano F, Hussain S, Rodrigues-Lima F, Baeza-Squiban A, Boland S. Nanoparticles: molecular targets and cell signalling. Arch Toxicol 2011;85(7):733-741ArticlePubMed
- 33. Lenaz G. The mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species: mechanisms and implications in human pathology. IUBMB Life 2001;52(3-5):159-164ArticlePubMed
- 34. Kuwano K. Epithelial cell apoptosis and lung remodeling. Cell Mol Immunol 2007;4(6):419-429PubMed
- 35. Kang KA, Wang ZH, Zhang R, Piao MJ, Kim KC, Kang SS, et al. Myricetin protects cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via regulation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 2010;11(11):4348-4360ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Blank VC, Peña C, Roguin LP. STAT1, STAT3 and p38MAPK are involved in the apoptotic effect induced by a chimeric cyclic interferon-alpha2b peptide. Exp Cell Res 2010;316(4):603-614ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Toxic Effects of Rare Earth Elements on Human Health: A Review
Wenyu Wang, Yanfang Yang, Donglei Wang, Lihua Huang
Toxics.2024; 12(5): 317. CrossRef - Blood multiple heavy metals exposure and lung function in young adults: A prospective Cohort study in China
Minghao Wang, Lailai Yan, Siqi Dou, Liu Yang, Yiwen Zhang, Wenzhong Huang, Shanshan Li, Peng Lu, Yuming Guo
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2023; 459: 132064. CrossRef - Effects of contaminated surface water and groundwater from a rare earth mining area on the biology and the physiology of Sprague-Dawley rats
Xiaoying He, Ting Yuan, Xinying Jiang, Hui Yang, Chun Li Zheng
Science of The Total Environment.2021; 761: 144123. CrossRef - Effects of radiation and role of plants in radioprotection: A critical review
Mohammed Junaid Hussain Dowlath, Sathish Kumar Karuppannan, Pamela Sinha, Nihala Sultana Dowlath, Kantha Deivi Arunachalam, B. Ravindran, S. Woong Chang, Phuong Nguyen-Tri, D. Duc Nguyen
Science of The Total Environment.2021; 779: 146431. CrossRef - Methods to evaluate the toxicity of engineered nanomaterials for biomedical applications: a review
Gaurang Patel, Chayan Patra, S. P. Srinivas, Mamta Kumawat, P. N. Navya, Hemant Kumar Daima
Environmental Chemistry Letters.2021; 19(6): 4253. CrossRef - Biocompatible dextran-coated gadolinium-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents with high T1 relaxivity and selective cytotoxicity to cancer cells
A. L. Popov, M. A. Abakumov, I. V. Savintseva, A. M. Ermakov, N. R. Popova, O. S. Ivanova, D. D. Kolmanovich, A. E. Baranchikov, V. K. Ivanov
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2021; 9(33): 6586. CrossRef - Influence of Ce3+ Substitution on Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Properties of ZnCexFe2−xO4 Nanoparticles (X = 0.0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, and 0.08) Conjugated with Ebselen and Its Role Subsidised with γ-Radiation in Mitigating Human TNBC and Colorectal Adenoca
Mohamed K. Abdel-Rafei, Noura M. Thabet, M. I. A. Abdel Maksoud, M. Abd Elkodous, Go Kawamura, Atsunori Matsuda, A. H. Ashour, Ahmed I. El-Batal, Gharieb S. El-Sayyad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(18): 10171. CrossRef - Protection effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles against radiation-induced acute lung injuries in rats
Fatemeh Kadivar, Gholamhassan Haddadi, Mohammad Amin Mosleh-Shirazi, Fatemeh Khajeh, Alireza Tavasoli
Reports of Practical Oncology & Radiotherapy.2020; 25(2): 206. CrossRef - Nanoceria distribution and effects are mouse-strain dependent
Robert A. Yokel, Michael T. Tseng, D. Allan Butterfield, Matthew L. Hancock, Eric A. Grulke, Jason M. Unrine, Arnold J. Stromberg, Alan K. Dozier, Uschi M. Graham
Nanotoxicology.2020; 14(6): 827. CrossRef - Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Importance in Cell Signaling Pathways for Predicting Cellular Behavior
Atefeh Pesaraklou, Maryam M Matin
Nanomedicine.2020; 15(17): 1709. CrossRef - Hepatotoxic Effect of Oral Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and the Ameliorating Role of Selenium in Rats: A histological, immunohistochemical and molecular study
Basma Emad Aboulhoda, Dina Adel Abdeltawab, Laila Ahmed Rashed, Marwa Fathi Abd Alla, Hanan Dawood Yassa
Tissue and Cell.2020; 67: 101441. CrossRef - Pulmonary toxicity of inhaled nano-sized cerium oxide aerosols in Sprague–Dawley rats
Chang Guo, Sarah Robertson, Ralf J. M. Weber, Alison Buckley, James Warren, Alan Hodgson, Joshua Z. Rappoport, Konstantin Ignatyev, Kirsty Meldrum, Isabella Römer, Sameirah Macchiarulo, James Kevin Chipman, Tim Marczylo, Martin O. Leonard, Timothy W. Gant
Nanotoxicology.2019; 13(6): 733. CrossRef - The first inorganic mitogens: Cerium oxide and cerium fluoride nanoparticles stimulate planarian regeneration via neoblastic activation
Artem Ermakov, Anton Popov, Olga Ermakova, Olga Ivanova, Alexander Baranchikov, Kristina Kamenskikh, Taisiya Shekunova, Alexander Shcherbakov, Nelli Popova, Vladimir Ivanov
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 104: 109924. CrossRef - Subchronic toxicity of cerium nitrate by 90-day oral exposure in wistar rats
Yu Wu, Xiaoqiao Tang, Wenxiang Yang, Jun Fan, Lijun Tang, Chunhong Wang, Zhou Yu, Xu-Dong Jia, Bolin Fan
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology.2019; 108: 104474. CrossRef - High‐dimensional single cell mapping of cerium distribution in the lung immune microenvironment of an active smoker
Adeeb H. Rahman, Yonit Lavin, Soma Kobayashi, Andrew Leader, Miriam Merad
Cytometry Part B: Clinical Cytometry.2018; 94(6): 941. CrossRef - Intranasal Delivery of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Induces Pulmonary Toxicity and Fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice
Xiaofeng Lai, Hu Zhao, Yong Zhang, Kai Guo, Yuqiao Xu, Suning Chen, Jian Zhang
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis Via Mediating Diverse Cellular Pathways
Liang Chen, Liu-Yun Wu, Wan-Xi Yang
Nanomedicine.2018; 13(22): 2939. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle–Poly I:C RNA Complexes: Implication as Therapeutics against Experimental Melanoma
Meghana Ramani, Miranda C. Mudge, R. Tyler Morris, Yuntao Zhang, Stanislaw A. Warcholek, Miranda N. Hurst, Jim E. Riviere, Robert K. DeLong
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2017; 14(3): 614. CrossRef - Fine Particulate Matter and Sulfur Dioxide Coexposures Induce Rat Lung Pathological Injury and Inflammatory Responses Via TLR4/p38/NF-κB Pathway
Ruijin Li, Lifang Zhao, Jinlong Tong, Yuchao Yan, Chong Xu
International Journal of Toxicology.2017; 36(2): 165. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of cerium dioxide nanoparticles immobilized on the surface of silica nanoparticles in rat experimental pneumonia
Z. Serebrovska, R.J. Swanson, V. Portnichenko, A. Shysh, S. Pavlovich, L. Tumanovska, A. Dorovskych, V. Lysenko, V. Tertykh, Y. Bolbukh, V. Dosenko
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2017; 92: 69. CrossRef - Effects from a 90-day inhalation toxicity study with cerium oxide and barium sulfate nanoparticles in rats
Daniela Schwotzer, Heinrich Ernst, Dirk Schaudien, Heiko Kock, Gerhard Pohlmann, Clemens Dasenbrock, Otto Creutzenberg
Particle and Fibre Toxicology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
 KSPM
KSPM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite







