Adverse Events Following Immunizations in Infants Under 1 Year of Age in Lorestan Province, Western Iran
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
Vaccination is an important intervention for preventing disease and reducing disease severity. Universal vaccination programs have significantly reduced the incidence of many dangerous diseases among children worldwide. This study investigated the side effects after immunization in infants under 1 year of age in Lorestan Province, western Iran.
Methods
This descriptive analytical study included data from all children <1 year old in Lorestan Province, Iran who were vaccinated according to the national schedule in 2020 and had an adverse event following immunization (AEFI). Data were extracted from 1084 forms on age, sex, birth weight, type of birth, AEFI type, vaccine type, and time of vaccination. Descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage) were calculated, and the chi-square test and Fisher exact test were used to assess differences in AEFIs according to the above-listed variables.
Results
The most frequent AEFIs were high fever (n=386, 35.6%), mild local reaction (n=341, 31.5%), and swelling and pain (n=121, 11.2%). The least common AEFIs were encephalitis (n=1, 0.1%), convulsion (n=2, 0.2%), and nodules (n=3, 0.3%). Girls and boys only showed significant differences in mild local reactions (p=0.044) and skin allergies (p=0.002). The incidence of lymphadenitis (p<0.001), severe local reaction (p<0.001), mild local reaction (p=0.007), fainting (p=0.032), swelling and pain (p=0.006), high fever (p=0.005), and nodules (p<0.001) showed significant differences based on age at vaccination.
Conclusions
Immunization is a fundamental public health policy for controlling vaccine-preventable infectious diseases. Although vaccines such as the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine, oral poliovirus vaccine, and pentavalent vaccine are well-researched and reliable, AEFIs are inevitable.
INTRODUCTION
As one of the most cost-effective healthcare interventions, vaccines have a major effect on reducing the burden of infectious diseases and their associated mortality, especially in children [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that immunization saves the lives of 2.5 million people each year and protects millions more from illness and disability [2]. In many developed countries, several infectious diseases have been controlled or eliminated through routine vaccination. There are more than 40 vaccines available for the prevention of 25 vaccine-preventable diseases [3] including tuberculosis (TB), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, measles, rubella, rotavirus, hepatitis B, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and human papillomavirus. The diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, TB, and pertussis vaccines have saved an estimated 400 000 years of life [1,4]. Measles vaccination resulted in a 79% reduction in worldwide measles deaths from 2000 to 2015 [5].
Today, more children are being immunized than ever before, resulting in declines in child mortality, birth defects, and lifelong disabilities. According to the WHO, a child is fully immunized if the child receives the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine against TB at birth; 3 doses of oral polio vaccine (OPV); 3 doses of pentavalent vaccine at 6 weeks, 10 weeks and 14 weeks of age; and the measles vaccine at 9 months of age [6,7]. The BCG vaccine is given to newborns at risk of getting TB. The OPV vaccine is used to fight against poliomyelitis. The pentavalent vaccine protects against 5 major diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, and Haemophilus influenza type b. This combined vaccine is a newly introduced vaccine in Iran; it was added to the national vaccination program for Iranian children in 2014.
Any vaccine can cause adverse reactions, which are classified as local, systemic, or allergic. Local reactions (e.g., swelling, pain, redness) are usually the least severe and most common. Systemic reactions (e.g., fever, restlessness, loss of appetite) occur less frequently than local reactions, and severe allergic reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis) are the least frequent type of reaction [8]. In a study by Cunha et al. [9] in Brazil, it was reported that the DTwP/Hib (diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis-Hemophillus influenzae type b) vaccine caused the highest number of systemic (61.4%) and localized events (33.8%) when compared to the BCG, hepatitis B, DPT (diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis), MMR (mumps, measles, rubella), and yellow fever vaccines in children aged ≤1 year, who are more susceptible to adverse events. Berhane et al. [10], in a longitudinal study in Ethiopia, reported 19 side effects after immunization with the 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV-10) and pentavalent vaccines in children <1 year (10 abscesses and 9 deaths). They found no significant difference in the rate of injection-site abscesses in children who received the 2 vaccines. A study by Tosun et al. [11] in Turkey on side effects of the measles vaccine in children aged 7–14 years found that 52% of side effects were local, with pain and swelling at the injection site most common. Fever and headache were the most observed systemic side effects.
A few recent studies in Iran have assessed the adverse effects of vaccines. Karami et al. [12], in a 2015 mixed cohort study on AEFI with the pentavalent vaccine in children aged <1 year in the city of Hamadan, Iran, reported the Incidence of swelling, redness, pain, mild fever, high fever, drowsiness, loss of appetite, irritability, vomiting, and persistent crying. Pain was the most prevalent (44.2%), followed by irritability (32.9%). There was no evidence of convulsion or encephalopathy. Khazaei et al. [13], in a 2013–2015 cross-sectional study comparing the adverse events of the pentavalent and DPT vaccines in healthy infants aged 2–6 months in Iran, found that the pentavalent vaccine had more recorded AEFIs than the DPT vaccine. High fever was most prevalent with the DPT vaccine (47.4%), while mild local reactions were most prevalent with the pentavalent vaccine (31.7%). The 2019 study by Ekrami Noghabi et al. [14] in Sari, northern Iran on the side effects of the pentavalent vaccine in healthy infants, reported that the most common systemic AEFI was fever. In addition, 1 infant had persistent crying (for >3 hours) after the second dose. Other serious side effects were not observed.
Currently, there are pharmacovigilance systems in developed countries for evaluating new vaccines and most suspected AEFIs. An AEFI is any unexpected medical occurrence after immunization and does not necessarily have a causal relationship with use of the vaccine [15]. An AEFI can be any unfavorable or unintended sign, abnormal laboratory finding, symptom or disease. Pharmacovigilance has a low priority in developing countries [16] such as Iran, where the status of pharmacovigilance is unclear [17]. Therefore, more studies on recognizing and reporting AEFIs are needed in these countries to guide legislators and patients in addressing their concerns about the safety of vaccines. AEFIs, which can affect healthy individuals, should be promptly identified and reported to enable additional research and support appropriate action. We found no related study on AEFIs in children in western Iran, specifically for the BCG and OPV vaccines. Therefore, this study surveyed the AEFIs in infants aged <1 year in Lorestan Province, western Iran. We assessed differences in the AEFIs based on sex, birth type (preterm/term), birthweight, vaccination time (at birth, and 2, 4, and 6 months after birth), and vaccine type (BCG, OPV, pentavalent).
METHODS
This was a descriptive analytical study. All data related to children aged <1 year in Lorestan Province, Iran in 2020 who had been vaccinated according to the national vaccination schedule and had an AEFI reported to their comprehensive urban/rural health centers in the province were collected from the reporting forms (n=1122). Of these, 38 infants with incomplete forms were excluded. Finally, data were extracted from 1084 forms. The extracted data were age, sex, birth weight, type of birth, type of AEFI, type of vaccine, and time of vaccination. Descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage) were used for describing data, and the chi-square test and Fisher exact test were used to assess differences in AEFIs according to sex, birth weight, birth type, vaccine type, and vaccination time. SPSS version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used for all statistical analyses.
Ethics Statement
Permission was obtained from the Vice-Chancellor for Research and the Ethics Committee of Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, and a referral was made to the Health Deputy of the university in coordination with the disease control expert of this deputy.
RESULTS
Infants’ Characteristics
The mean age of the infants was 3.7±1.8 months (range, 0–6) and their mean birthweight was 3208.7±368.6 g (range, 1600–6800). Of the 1084 infants with reported AEFI, 497 (45.8%) were girls and 587 (54.2%) were boys. In terms of birthweight, 36 (3.3%) weighed <2500 g, 1036 (95.6%) weighed 2500–4000 g, and only 12 (1.1%) weighed >4000 g. Furthermore, most had a term birth (n=1012, 93.3%) and only 72 (6.7%) had a preterm birth. Most were vaccinated at age 2 months (n=404, 37.3%) and 6 months (n=335, 30.9%), while only 42 (3.9%) were vaccinated at the time of birth. The remaining were vaccinated at age 4 months (n=303, 28%). In terms of vaccine type, 1011 infants (93.2%) received the pentavalent vaccine, 42 (3.9%) received the BCG vaccine, and 31 (2.9%) received the OPV.
Distribution and Causes of Adverse Event Following Immunizations
The most common AEFI in infants was high fever (n=386, 35.6%), followed by mild local reaction (n=341, 31.5%), and swelling and pain (n=121, 11.2%). The least common AEFIs were encephalitis (n=1, 0.1%), convulsion (n=2, 0.2%), and nodules (n=3, 0.3%). The most frequent cause of AEFI was reported as “reaction to vaccine” (n=1401, 96%). Other reported causes were “unknown cause” (n=28, 2.6%) and “programmer error” (n=15, 1.4%).
Incidence of Adverse Event Following Immunization According to Sex, Birthweight, and Birth Type
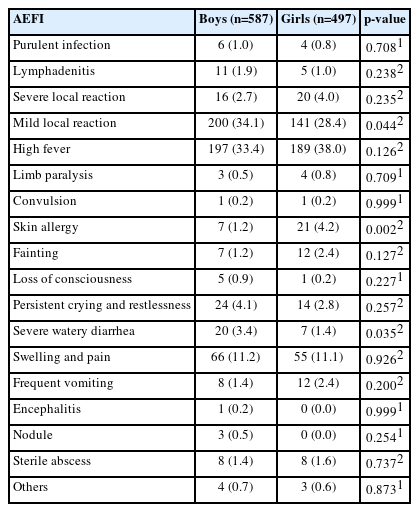
According to the chi-square test results (Table 1), girls and boys only showed significant differences for mild local reactions (p=0.044) and skin allergies (p=0.002). Mild local reactions (n=200, 34.1%) were more common in boys, while skin allergies (n=21, 4.2%) were more common in girls. According to the chi-square test results, infant birthweight only showed significant associations with severe local reactions (p=0.025), mild local reactions (p=0.028), and swelling and pain (p= 0.001) (Table 2). Severe local reactions and swelling and pain were most common in infants with a birthweight of <2500 g (11.1 and 30.6%, respectively) as compared to those weighing 2500–4000 g and >4000 g. Mild local reactions were most common in infants with a birthweight of >4000 g (50.0%) when compared to those weighing <2500 g and 2500–4000 g.

The frequency and percentage of adverse effects following immunizations (AEFIs) according to birth weight and type of birth (n=1084)
The differences in birth type (term and preterm) were significant only for purulent infections (p=0.003), swelling and pain (p=0.021), sterile abscesses (p=0.018), and limb paralysis (p= 0.008) (Table 2). These adverse events were most prevalent in infants with preterm births (5.6, 19.3, 5.6, and 4.2%, respectively).
Incidence of Adverse Effects Following Immunizations in Infants According to Age at Vaccination
The incidence of lymphadenitis (p<0.001), severe local reaction (p<0.001), mild local reaction (p=0.007), fainting (p=0.032), swelling and pain (p=0.006), high fever (p=0.005), and nodules (p<0.001) showed significant differences among infants who received vaccinations at different times (Table 3). Lymphadenitis (14.3%), severe local reaction (31.0%), and nodules (7.1%) were most common when infants received their first dose at the time of birth. High fever (n=115, 38.0%) and mild local reaction (n=105, 34.7%) were seen most in infants who received vaccinations at the age of 4 months, while fainting (n=13, 3.2%) and swelling and pain (n=60, 14.1%) were most common in infants vaccinated at the age of 2 months.
Incidence of Adverse Event Following Immunizations in Infants According to Vaccine Type
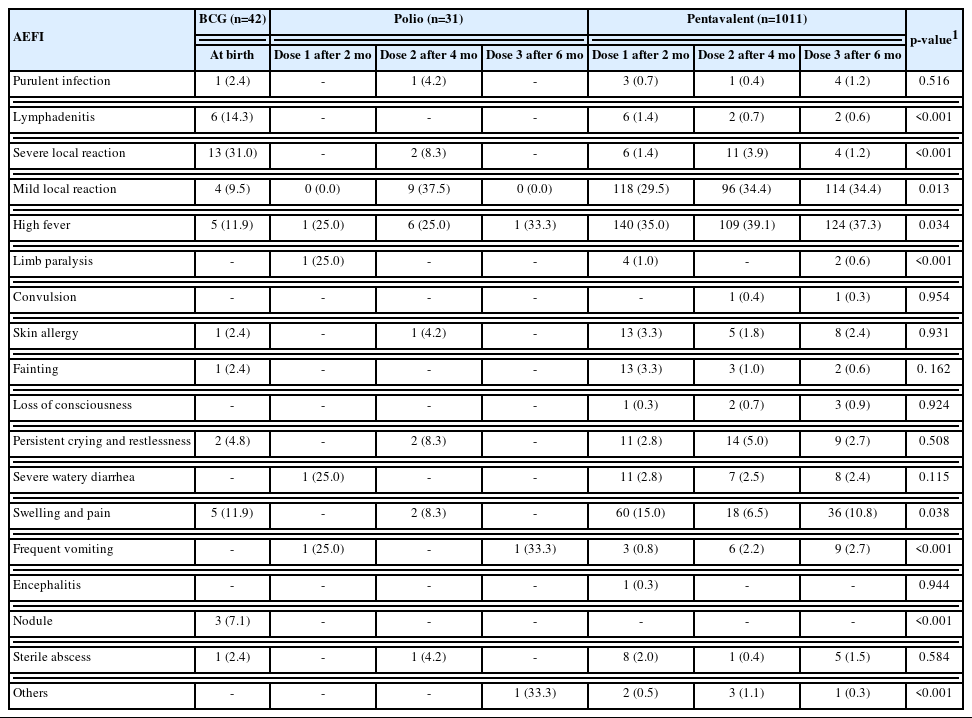
Based on vaccine type, the differences among infants who received the BCG, inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV), OPV, and pentavalent vaccines were significant for the following adverse effects: lymphadenitis (p<0.001), severe local reaction (p<0.001), mild local reaction (p=0.004), high fever (p=0.006), limb paralysis (p<0.001), frequent vomiting (p<0.001), and nodules (p<0.001) (Table 4). Lymphadenitis (n=6, 14.3%), severe local reaction (n=13, 31%), and nodules (n=3, 7.1%) were most common among infants who received the BCG vaccine, while limb paralysis (n=1, 14.3%) and frequent vomiting (n=2, 28.6%) were more prevalent in those who received the OPV. High fever (n=373, 36.8%) was more prevalent in those who received the pentavalent vaccine and mild local reaction (n=9, 37.5%) was more prevalent in those who received the IPV vaccine.
Incidence of Adverse Event Following Immunizations in Infants According to Vaccine Dose
In assessing the differences in AEFI among infants based on vaccine dose (dose number 1, 2, or 3), our results (Table 5) showed statistically significant differences in lymphadenitis (p<0.001), severe local reaction (p<0.001), mild local reaction (p<0.001), limb paralysis (p<0.001), high fever (p=0.034), swelling and pain (p=0.038), frequent vomiting (p<0.001), nodules (p<0.001), and other complications (p<0.001). Among 42 BCG vaccine-related AEFIs, lymphadenitis (n=6), severe local reaction (n=13), and nodules (n=3) were most prevalent when the vaccine was given at birth.
Clusters of Adverse Event Following Immunizations
The occurrence of different AEFIs at the same time was found most with high fever and mild local reaction (n=117, 10.90%), followed by high fever with swelling and pain (n=34, 3.13%), high fever with persistent crying and restlessness (n=28, 2.58%), and mild local reaction with swelling and pain (n=27, 2.49%).
DISCUSSION
The WHO has recommended the surveillance and analysis of AEFIs in developing countries where the current pharmacovigilance systems have low priority [16]. Therefore, this study investigated the AEFIs in infants aged <1 year (mean age, 3.7±1.8 months) in western Iran. By extracting data from the 2020 adverse event forms completed by the comprehensive urban/rural health centers in Lorestan Province, 1084 AEFIs were found. While most infants had received the pentavalent vaccine (n= 1011, 93.2%), the rest had received the BCG vaccine (n=42, 3.9%) and the OPV (n=31, 2.9%). The most common AEFIs were high fever (36.6%), mild local reactions (31.5%), and swelling and pain (11.2%). In the Cunha et al. [9] study in Brazil, the highest number of systemic adverse events (61.4%) and localized adverse events (33.8%) were related to the DTwP/Hib vaccine as compared to the BCG, hepatitis B, and DPT vaccines. In the 2015 study by Karami et al. [12] on pentavalent vaccine-related AEFI in Iranian children, pain was most common (44.2%), followed by irritability (32.9%) and drowsiness (20.0%). Other reported AEFIs were swelling (15.8%), redness (10.9%), mild fever (12.6%), high fever (0.1%), loss of appetite (15.0%), vomiting (4.6%), and persistent crying (5.5%). They found no reports of convulsion or encephalopathy. In our study, among the pentavalent vaccine-related AEFIs, pain and swelling were seen together (10.3%), and the incidence of vomiting and persistent crying was 1.8% and 3.4%, respectively. No loss of appetite, redness, irritability, or drowsiness was reported, while convulsions were reported in 2 infants. These discrepancies may be due to differences in the study location and the data collection method. Our study was conducted in Lorestan Province using data from the comprehensive urban/rural health centers, while their study was conducted in the city of Hamadan with AEFI data reported by the parents of children using a questionnaire. In the study by Khazaei et al. [13], mild local reactions were the most prevalent AEFI with the pentavalent vaccine (31.68%), which is consistent with our study. In the study by Ekrami Noghabi et al. [14], the most common systemic reaction after vaccination with the pentavalent vaccine was fever. Immunization is a fundamental public health policy for controlling vaccine-preventable infectious diseases. Although the vaccines used for immunization (e.g., BCG, IPV, and OPV) are very reliable, it is inevitable that some people will experience AEFIs.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
FUNDING
This study was funded by Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
None.
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Anbari K, Ghanadi K. Data curation: Toulabipour A, Jamebozuorghi D. Funding acquisition: Baharvand P. Methodology: Toulabipour A, Jamebozuorghi D. Project administration: Toulabipour A, Jamebozuorghi D, Baharvand P. Writing – original draft: Toulabipour A, Jamebozuorghi D, Baharvand P. Writing – review & editing: Anbari K, Ghanadi K, Baharvand P.