Association Between Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers and the Risk of Lung Cancer Among Patients With Hypertension From the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort
Article information
Abstract
Objectives:
The objective of this study was to estimate the risk of lung cancer in relation to angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) use among patients with hypertension from the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study of patients with hypertension who started to take antihypertensive medications and had a treatment period of at least 6 months. We calculated the weighted hazard ratios (HRs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of lung cancer associated with ARB use compared with calcium channel blocker (CCB) use using inverse probability treatment weighting.
Results:
Among a total of 60 469 subjects with a median follow-up time of 7.8 years, 476 cases of lung cancer were identified. ARB use had a protective effect on lung cancer compared with CCB use (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.96). Consistent findings were found in analyses considering patients who changed or discontinued their medication (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.32 to 0.77), as well as for women (HR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.34 to 0.93), patients without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.56 to 1.00), never-smokers (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.99), and non-drinkers (HR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.49 to 0.97). In analyses with different comparison antihypertensive medications, the overall protective effects of ARBs on lung cancer risk remained consistent.
Conclusions:
The results of the present study suggest that ARBs could decrease the risk of lung cancer. More evidence is needed to establish the causal effect of ARBs on the incidence of lung cancer.
INTRODUCTION
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide [1]. In 2016, 48 208 men and 29 986 women died of lung cancer in Korea [2]. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are the most frequently used antihypertensive medications in Korea, accounting for approximately 43.3% of monotherapy and 81.0% of dual therapy from 2002 to 2016 [3]. These medicines mainly target the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), an essential physiological system for maintaining fluid and electrolyte homeostasis and regulating blood pressure [4]. In addition to its effect on the cardiovascular system, the RAS is also associated with cancer development and progression [5-9].
However, the effect of ARBs on the risk of lung cancer is still not established. A large cohort study from the United Kingdom General Practice Research Database reported a protective effect of ARBs compared with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) on lung cancer incidence [10]. However, the effect of ARBs on lung cancer risk may vary depending on the reference medication. Cohort studies from the Taiwanese claims database also reported protective effects of ARBs on lung cancer [11,12]. However, these studies lacked important covariates including smoking status and were based on a user and non-user study design, which could introduce a healthy user bias [13]. A meta-analysis based on observational studies regarding the risk of lung cancer associated with ARBs also reported a protective effect [14]. However, a meta-analysis including randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reported a null effect of ARBs on the incidence of lung cancer [15].
Considering the widespread use of ARBs, it is important to investigate the possible association between the use of ARBs and the risk of lung cancer. The objective of the present study is to provide evidence regarding whether the effects of ARBs are associated with the incidence of lung cancer among patients with hypertension.
METHODS
Database Source and Study Design
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort database (NHIS-HEALS). A description of the database was published elsewhere [16]. Briefly, this database included 514 866 people comprising a 10% random sample of individuals who underwent general health check-ups between 2002 and 2003 and were aged 40-79 years at the time of the check-up. The database included demographic characteristics such as age, gender, residence, and income level and medical information regarding the diagnosis of disease, prescription data about treatment, and health examination data from 2002 to 2015. The diagnostic codes in this database were based on the International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition.
We used an active comparator and new user design to minimize confounding bias by indication and healthy user bias [17-19]. Calcium channel blocker (CCB) users were set as the comparator group for ARB users because during the study period, CCBs were first-line antihypertensive medications along with ARBs, and were the second most commonly used class of antihypertensive medication, prescribed for approximately 42.9% of monotherapy and 63.4% of dual therapy from 2002 to 2016 [3,20]. Furthermore, CCBs were considered to have no influence on cancer development overall [21,22].
Selection of Subjects
We identified patients with hypertension (I10-I13, I15) who started taking antihypertensive medications, including monotherapy or combination therapy, from 2003 to 2015 after excluding prevalent users in 2002. We excluded patients with prevalent or incident cancer before the start date of antihypertensive medication, those who died during the period of defining exposure, and those who did not have health examination data before the start date of antihypertensive medication. We further excluded patients with missing values for continuous variables from the health examination, those who started receiving combination therapy with both ARBs and CCBs, and those who were prescribed antihypertensive medication other than ARBs and CCBs. Finally, among these mutually exclusive ARB users and CCB users, we selected subjects with treatment periods were at least 6 months. The index date was set as the last date of the consecutive 6-month antihypertensive treatment period. We set another lag period of 6 months; thus, subjects with a follow-up period of less than 6 months were excluded because cancer incidence shortly after drug initiation was not considered to be causal [23,24].
Definition of the antihypertensive medication
The use of antihypertensive medication was identified by using insurance claims data for the prescription of treatment in the NHIS-HEALS. Each class of antihypertensive drugs was defined based on the Anatomical Therapeutic Code from the World Health Organization, identified by each corresponding main component code in Korea. The antihypertensive medications in the present study included ARBs (C09C, C09D), ACEIs (C09A, C09B), CCBs (C08C, C08D), beta-blockers (C07), diuretics (C03), and other medications (C02) including alpha-blockers and vasodilators. We aggregated the prescription information of all antihypertensive medications every 3 months for each participant. Antihypertensive medication use was defined based on at least a 30-day prescription of each class of antihypertensive medication during every 3 months.
Follow-up and outcome assessment
Our primary outcome was the incidence of lung cancer. Cases of incident lung cancer were defined as individuals who were admitted to the hospital with a main diagnosis code of C33-C34 [25]. The final subjects were followed-up from the index date until the diagnosis of any cancer, any cause of mortality, drop-out from the cohort, or the last date of the study (December 31, 2015), whichever came first. The cause and date of death were identified through linkage to Korean death statistics.
Statistical Analysis
We used inverse probability treatment weighting (IPTW) to control confounding factors between ARB users and CCB users. The propensity score (PS) of each patient was calculated using a logistic regression model [26]. The variables used to estimate the PS were selected considering their effect on the incidence of lung cancer or their impact on the choice of antihypertensive medications [27]. Demographic variables were gathered during 1 year before the initiation of antihypertensive medication, and the most recent health examinations before the start of follow-up were analyzed. The variables used to construct the PS included age at index date, gender, income level by quintile (lowest, lower, middle, upper-middle, and highest), smoking status (never, ever, current, and missing), alcohol drinking habits (never, 1-2/wk, ≥3/wk, and missing), and physical activity (never, 1-2/wk, ≥3/wk, and missing). The use of other antihypertensive medications and the number of antihypertensive medications were also included. We also included the following comorbidity variables that could influence the choice of antihypertensive medication: diabetes mellitus (DM) (E10-E14), dyslipidemia (E78), myocardial infarction (I21-I23), congestive heart failure (I50, I110, I130, I132), cerebrovascular disease (I60-I69), chronic kidney disease (N18, N19, I12, I13, E102, E112, E132, E142), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (J40-J47), and Charlson Comorbidity Index scores (0, 1, or higher) [28]. Missing values of categorical variables were treated as a separate category. Continuous variables included body mass index (kg/m2), systolic blood pressure (mmHg), diastolic blood pressure (mmHg), levels of fasting blood sugar (mg/dL), total cholesterol (mg/dL), aspartate aminotransferase (U/L), alanine aminotransferase (U/L), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (U/L), and the number of physician visits during 1 year before the index date. We also collected information on the simultaneous prescription of other medications, including metformin, sulfonylurea, insulin, thiazolidinedione, aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and statins.
Stabilized weights for measuring the average treatment effect were estimated for ARB users and CCB users, respectively [27,29]. The weights were trimmed at the lower 1% and upper 99% [27,29]. The absolute standardized mean differences (ASDs) before and after the application of IPTW were estimated for each variable. When the ASDs were less than 0.1, we assumed that the difference in the variables between groups was negligible [30]. The stabilized weights were applied to generate a pseudo-cohort comprising ARB users and CCB users.
We confirmed that there was no significant interaction between time and effect of treatment choice on the incidence of lung cancer. We calculated the hazard ratios (HRs) by weighted Cox regression on the incidence of lung cancer associated with ARB use compared with CCB use. We used a robust sandwich-type variance estimator to calculate the 95% confidence intervals (CIs), accounting for the effect of weights on standard error [27,31]. We also analyzed the risk of lung cancer among ARB users compared with CCB users considering medication change or discontinuation as censoring with a 6-month lag period. Furthermore, we restricted the subjects to monotherapy users (i.e., CCB- and ARB-only users) without any other antihypertensive medications at baseline. We extended the lag period to 1 year and 2 years from the original 6 months. For duration-response analysis, we estimated the weighted HRs of lung cancer among ARB users compared with CCB users by dividing the subjects’ treatment period into at least 30 days, 6 months, and 1 year (the primary analysis was for at least 6-month users). We plotted the weighted cumulative incidence curves of lung cancer among ARB users and CCB users by treatment duration as the Kaplan-Meier estimator.
We performed stratified analyses by gender, age (<60 vs. ≥60 years), COPD, smoking status, drinking status, and use of metformin [32]. Considering the potential effects of CCBs on lung cancer incidence, we included other reference antihypertensive drugs, such as beta-blockers, diuretics, and ACEIs [33]. The weights were recalculated in each group. We also estimated the rate differences and their 95% CIs between ARB users and users of each antihypertensive medication to estimate absolute risk by calculating weighted incidence rates. Additionally, to estimate the effect of ARB use on the risk of lung cancer compared with the general population, we calculated the multivariable HR of lung cancer among overall patients with hypertension compared to those without hypertension based on the treatment period that was compared. Data management and statistical analysis were performed using Statistical Analysis System Enterprise Guide 7.1 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and R version 3.6.2 (https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/old/3.6.2/).
Ethics Statement
The present study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB No. E-1911-001-1074). The database was publicly available, and the subjects were coded anonymously. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
RESULTS
Characteristics of the Study Population
Figure 1 shows the flow of the study for selecting the subjects, including the number of subjects at each step. The final 60 469 subjects included 21 619 ARB users and 38 850 CCB users with a treatment duration of at least 6 months, and total of 51 subjects (0.1%) were lost to follow-up during the study period. Table 1 shows the general characteristics and ASDs of each variable between two groups before and after adjustment by IPTW. Before IPTW adjustment, ARB users were younger than CCB users (58.5 vs. 60.0 years; ASD, 0.159). Diuretics were more frequently prescribed in ARB users than in CCB users (45.2 vs. 18.9%; ASD, 0.587). ARB users were more likely to have DM and dyslipidemia than CCB users (21.3 vs. 12.3%; ASD, 0.242 for DM; 25.6 vs. 16.1%; ASD, 0.237 for dyslipidemia). Metformin was more frequently prescribed for ARB users than for CCB users (12.5 vs. 4.6%; ASD, 0.286). After IPTW was applied to the subjects, 20 614 ARB users and 38 395 CCB users were generated. The ASDs of covariates between two groups after weight adjustment were lower than 0.1, indicating that the characteristics were balanced between two groups.
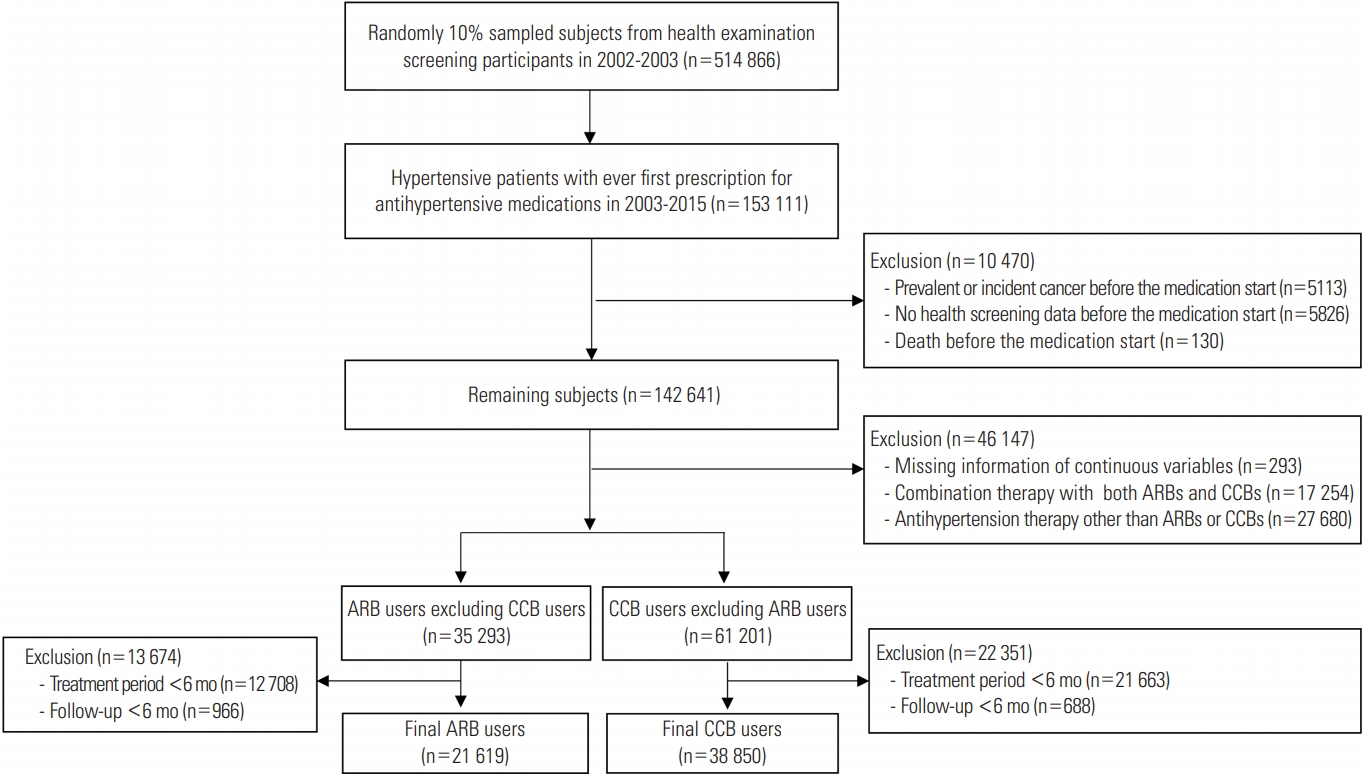
Flow chart for selecting angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) users and calcium channel blocker (CCB) users for the active comparator and new user design in the study.
Risk of Lung Cancer
A total of 476 cases of lung cancer were identified with a median (interquartile range, IQR) follow-up period of 7.8 years (IQR, 4.5 to 10.0). Table 2 shows the main results of the present study regarding the association of ARB use with lung cancer risk. A protective effect of ARB use for lung cancer was found compared with CCB use (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.96 after IPTW and HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.60 to 0.92 before IPTW). When subjects were censored due to discontinuing or changing their original medication, the protective effect of ARBs on the risk of lung cancer remained consistent (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.32 to 0.77). The results were also consistent in the analyses with a 1-year lag period (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.62 to 1.03) and a 2-year lag period (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.54 to 1.02).

Associations of ARB use relative to CCB use with the risk of lung cancer among subjects who had used the drugs for at least 6 months (n=60 469)
In the stratified analysis according to gender, age, comorbid COPD, smoking, alcohol drinking, and use of metformin, there remained an inverse association between ARB use and risk of lung cancer compared with CCB use, though some associations are not significant due to the wide CIs (Table 3). Compared with patients who received CCB treatment, ARB treatment was associated with a lower risk of lung cancer in women (HR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.34 to 0.93), in patients without COPD (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.56 to 1.00), in never-smokers (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.99), in never-drinkers (HR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.49 to 0.97), and in patients without metformin (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54 to 0.94). Figure 2 shows the weighted cumulative incidence curves and IPTW-adjusted HRs of lung cancer among ARB users and CCB users by the treatment duration. The HRs were consistently 0.75 in each group, and we could not find a clear duration-response association.

Stratified analyses associated with ARB use and risk of lung cancer compared with CCB use among subjects who had used the drugs for at least 6 months (n=60 469)
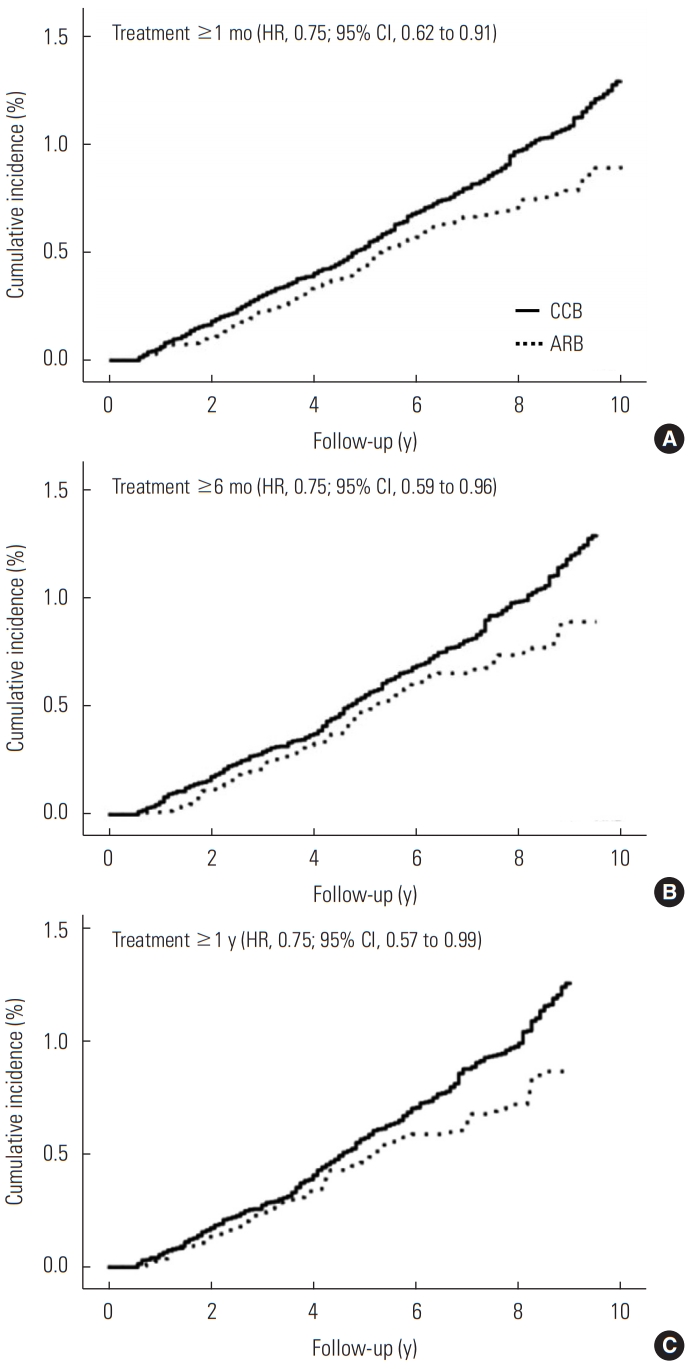
Weighted cumulative incidence of lung cancer among angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) users and calcium channel blocker (CCB) users according to the duration of treatment (A: 1 month, B: 6 months, and C: 1 year). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
In the analyses with different comparison medications, the overall protective effects of ARB on lung cancer risk remained consistent (Supplemental Material 1). The estimated absolute decrease in incidence of lung cancer for ARB users compared with CCB users was 3.6 (95% CI, 1.5 to 5.7) per 10 000 person-years (Supplemental Material 1). In the analysis with a varying washout period to identify new users, we also observed consistent results (Supplemental Material 2). Supplemental Material 3 shows that the risk of lung cancer was not significantly different between people with and without hypertension.
DISCUSSION
In this large-scale cohort study with a long-term follow-up period, we demonstrated a protective effect on the risk of lung cancer associated with the use of ARBs among patients with hypertension using an active comparator and new user design and IPTW. These findings of the protective effect of ARBs on the risk of lung cancer are consistent with those of several previous studies. Observational studies and a meta-analysis reported an inverse association between ARB use and risk of lung cancer [10-12,14]. A cohort study using the Taiwan claims database reported a decreased risk of lung cancer of ARB users compared with ARB non-users (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.53 to 0.73) [11]. Another cohort study from the United Kingdom reported that ARBs were associated with a lower risk of lung cancer compared to ACEIs (HR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.75 to 0.94) [10]. A meta-analysis reported that ARBs decreased lung cancer incidence compared with other antihypertensive medications (odds ratio [OR], 0.81; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.94) [14]. Our finding of a non-significant association between hypertension and lung cancer, which is consistent with a previous meta-analysis [34], could indicate that ARB users have a lower risk of lung cancer than the general population. Although no significant duration-response effect was found in the present study, the consistent protective direction of the effect of ARB use on the incidence of lung cancer in several stratified analyses could support the possibility that ARBs have a real protective effect on lung cancer.
Furthermore, the inverse association between ARBs and the risk of lung cancer can be understood in the context of the action of the RAS. Angiotensin II, one of the main components of the RAS, promotes cellular proliferation, inflammation, and angiogenesis via angiotensin II receptor type 1 [6], which are critical biological processes in lung cancer [35]. Blocking this pathway by ARBs could lower the risk of lung cancer [6]. Another plausible mechanism is through the alternative pathway of the local RAS [36]. Blocking angiotensin II receptor type I by ARB increases the expression of ACE2, which could generate angiotensin‐(1-7) from angiotensin II [5,37]. Preclinical studies demonstrated that angiotensin‐(1-7) significantly reduced lung tumor growth [5].
However, whether ARBs have a chemo-protective effect on the incidence of lung cancer has not been fully resolved, because a meta-analysis including RCTs reported a null effect of ARB on the incidence of lung cancer (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.19) [15]. This indicates the need of further RCTs to elucidate the causal association between the risk of lung cancer and the use of ARBs.
Strengths and limitations
Our study has several strengths. First, the present study observed subjects for a relatively long-term follow-up of a maximum of 10 years with a median follow-up of 7.8 years. Second, the statistical method used in our study, IPTW with an active comparator and new user design, supports high comparability between two groups [27]. Third, immortal time bias was minimal because the definition of the drug exposure period was identical in all subjects [38-40]. Fourth, potential confounding factors including lifestyles and co-medications were considered. Of particular note, important confounding factors including smoking status and the history of COPD were included in calculating the PS. Last, various sensitivity analyses, including different comparison drugs, make our results robust. Although CCBs, as our comparison drug, were assumed not to be associated with lung cancer, it is possible that they could have a potential effect on lung cancer risk [33]. Therefore, we performed further analyses using different comparison drugs (beta-blockers, diuretics, and ACEIs), which showed similar results. We also performed analyses censoring subjects who stopped the original medication and changed or augmented to comparison drugs with a 6-month lag period, which showed consistent results with those of the primary analyses.
However, the results in the present study should also be carefully interpreted in the context of several limitations. The observed association may not be causal because the present study is an observational study, not an RCT, although we tried to minimize confounding bias and selection bias through the study design and the statistical method. A 1-year drug washout period could be insufficient to exclude prevalent antihypertensive medication users to identify new users free of cancer. However, in the analysis with an extended washout period, we found consistent results [19]. Because this study was conducted based on a prescription database, whether the patients took the medicine could not be known, which could introduce misclassification bias. Analysis of the specific histological subtypes of lung cancer was impossible because there was no information regarding the histological subtype of lung cancer.
The results of the present study suggest that ARBs could decrease the risk of lung cancer. More evidence is needed to establish the causal effect of ARBs on the incidence of lung cancer.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
Supplemental materials are available at https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.20.405.
Risk of the lung cancer associated with ARB compared with CCB, BB, DI, and ACEI
Analysis of varying wash-out period regarding association between ARB compared with CCB on the risk of lung cancer
Risk of lung cancer among subjects with hypertension compared with non-hypertensive subjects by treatment period of hypertension
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
FUNDING
This study was funded by the Korean Foundation for Cancer Research (grant No. CB-2017-A-2).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study used the NHIS-HEALS database (NHIS-2020-2-007), which was created and is maintained by the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS). We revised and supplemented “Effect of angiotensin II receptor blockers on the risk of cancer among antihypertensive medication users: a retrospective cohort study in Korea,” the first author’s thesis for a master of science at Seoul National University College of Medicine.
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: SM, HYL, SKP. Data curation: SM, SKP. Formal analysis: SM. Funding acquisition: SKP. Methodology: SM, SKP, JJ. Project administration: SM, SKP. Visualization: SM. Writing – original draft: SM. Writing – review & editing: SM, HYL, SKP, JJ.

