Effects of Antiretroviral Therapy on the Survival of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-positive Adult Patients in Andhra Pradesh, India: A Retrospective Cohort Study, 2007-2013
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
The survival outcomes of antiretroviral treatment (ART) programs have not been systematically evaluated at the state level in India. This retrospective study assessed the survival rates and factors associated with survival among adult human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients in Andhra Pradesh, India.
Methods
The present study used data from 139 679 HIV patients aged ≥15 years on ART who were registered from 2007 to 2011 and were followed up through December 2013. The primary end point was death of the patient. Mortality densities (per 1000 person-years) were calculated. Kaplan-Meier and Cox-regression models were used to estimate survival and explore the factors associated with survival.
Results
The overall median follow-up time was 16.0 months (2.0 months for the deceased and 14.0 months for those lost to follow-up). Approximately 13.2% of those newly initiated on ART died during follow-up. Of those deaths, 56% occurred in the first three months. The crude mortality rate was 80.9 per 1000 person-years at risk. The CD4 count (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR],4.88; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.36 to 5.46 for <100 cells/mm3 vs. >350 cells/mm3), functional status (aHR, 3.05; 95% CI, 2.82 to 3.30 for bedridden vs. normal), and body weight (aHR, 3.69; 95% CI, 3.42 to 3.97 for <45 kg vs. >60 kg) were strongly associated with the survival of HIV patients.
Conclusions
The study findings revealed that high mortality was observed within the first three months of ART initiation. Patients with poor baseline clinical characteristics had a higher risk of mortality. Expanded testing and counseling should be encouraged, with the goal of ensuring early enrollment into the program followed by the initiation of ART in HIV-infected patients.
INTRODUCTION
Morbidity and mortality related to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) remain a global public health concern. Worldwide, the estimated number of people living with HIV (PLHIVs) was nearly 34 million in 2010, a 17% increase from 2001 [1]. With over one million people living with HIV or AIDS (PLHAs) in 2011, India has the third largest number of PLHAs in the world [2]. The national prevalence of HIV in adults (aged ≥15 years) in India is estimated to be 0.27% [2], with approximately 5-fold higher prevalence rates among high-risk groups, including males who have sex with male, female sex workers, and injecting drug users [3]. These population groups are considered important bridging populations for HIV transmission between high-risk and low-risk population groups [4]. The early initiation of antiretroviral treatment (ART) has been shown to enhance the survival of HIV-infected persons worldwide [5,6]. In early 2000, low-income and middle-income countries expanded access to ART through the three by five Initiative of the World Health Organization (WHO) [7]. According to the Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) [8], approximately 300 000 HIV-related deaths have been averted due to ART in Asia. In 2004, the ART program in India was launched under the National AIDS Control Program with the aim of providing free ART services to those with a CD4 count less than 250 or at an advanced stage of disease. At present, more than 450 ART centers provide free ART treatment across the country [9].
In 2007 ART services were scaled up, with new criteria for ART initiation (CD4 ≤200 cells/mm3 or HIV clinical stage III/IV irrespective of CD4 count, including coinfections such as tuberculosis), which resulted in more than seven million PLHIVs accessing ART in 2012 [10]. The ART initiation criteria were further modified in 2009-2010 (to CD4 ≤250 cells/mm3) and 2011-2012 (to CD4 ≤350 cells/mm3), as recommended by UNAIDS [2]. In addition to free treatment, PLHIVs are provided follow-up monitoring, screening for opportunistic infections, and counseling. According to ART guidelines, zidovudine + lamivudine (3TC) + nevirapine (NVP) is the preferred regimen of treatment for patients with a hemoglobin level >9 g/dL, and stavudine + 3TC + NVP is given to those with hemoglobin <9 g/dL. Efavirenz is substituted for nevirapine in those taking anti-tubercular drugs and those with nevirapine toxicity. Despite the considerable increase in the number of PLHAs in India accessing ART from 17% in 2007 to 52% in 2013, ART coverage of people eligible for treatment is still low [2,11].
A recent retrospective cohort analysis from an ART center showed the mortality rate in one year to be 7.7 deaths per 100 patients, with >50% of the deaths occurring during the first three months after ART initiation [12]. A few studies have been conducted investigating the survival benefit of upscaling ART in India. Although the findings demonstrated a higher mortality than that of developed countries, the survival rate of the patients increased and the rate of opportunistic infections decreased [12-15]. No state-level studies have yet been performed in India focusing on the survival outcomes of upscaling ART services. Therefore, the available evidence in the country regarding the survival outcomes of upscaling ART services is limited, despite the large number of patients accessing ART through the National AIDS Control Program. Therefore, large scale state-level survival studies are needed to better understand the HIV control program and to identify priority areas within states for further policy making. This retrospective study explores the survival rates and the factors associated with survival among ART patients in Andhra Pradesh state, including Telengana, a newly created state (separated from Andhra Pradesh), one of the six high-prevalence states of India using the most recent available HIV surveillance data since the scaling-up of ART in this state.
METHODS
Study Settings
Andhra Pradesh has the second highest HIV prevalence (0.75%) after Manipur among the six high HIV prevalence states, with an estimated 490 000 PLHIVs in 2011 [2]. As of December 2014, the state had 56 functional ART and 161 functional ART linkage centers across 25 districts, as compared to 24 ART centers and 21 ART linkage centers in 2007 [16,17]. According to the 2011 census, the population of Andhra Pradesh was 84 665 530 with a density of 308 persons/km2.
Study Participants
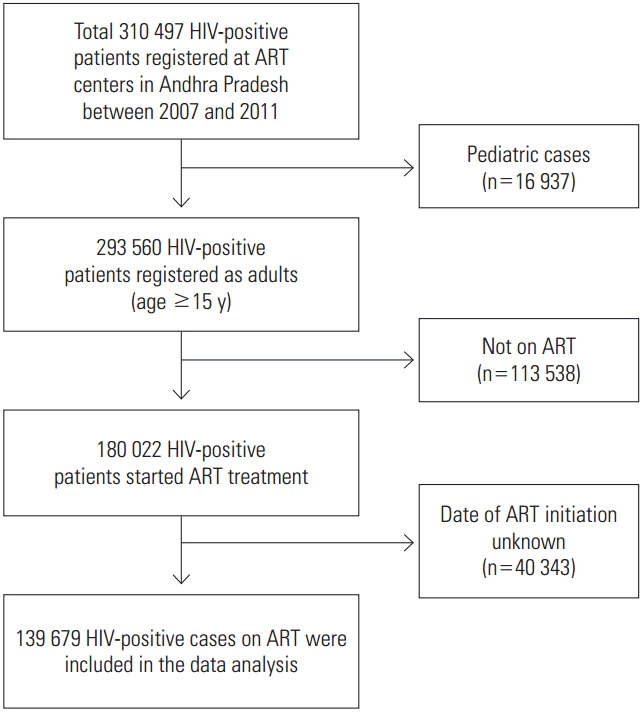
This study used retrospective data from a cohort of HIV-positive patients from 2007 to 2013. Data were extracted from the PLHA database from 51 ART centers, which incorporates information that has been routinely collected by the program since 2004. The database included information on treatment initiation and follow-up of HIV-positive patients who visit ART centers. For every patient, the first follow-up visit was scheduled two weeks after the initiation of treatment, and thereafter, on a monthly basis, the medical records of every patient were updated during each follow-up visit. The total eligible sample was 139 679 adult HIV-infected patients, who were followed up from 2007 to 2013 (Figure 1). The study participants included all adult HIV-positive patients (aged 15 years and older) on ART, who were registered during January 2007 to December 2011 and initiated treatment before December 31, 2013. Participants with a previous treatment history, without a date of ART initiation, and pediatric cases (aged 0-14 years) were excluded from the study.
Ethical Statement
Approval to access the PLHA database was obtained from the National AIDS Control Organization, New Delhi, India. The personal identity of the patients was not accessed and confidentiality was maintained.
Measures
Baseline data were collected on patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics. HIV program-related information was also gathered, including patients’ ART status, date of ART initiation, follow-up status, and the date of their last visit to the ART center.
Socio-demographic variables
The socio-demographic variables used in the analysis were age (<30 years, 30-45 years, and >45 years), education (illiterate, primary, secondary, and college and above), employment status (self-employed and service), and marital status (single [including unmarried/widow/widower] and married/cohabitating).
Clinical characteristics
Clinical characteristics at the time of ART initiation included body weight (kg), functional status, WHO clinical stage, CD4 T-cell count (cells/mm3), and adherence to ART. The patient’s body weight at the time of ART initiation was categorized into three groups: <45 kg, 45-60 kg, and >60 kg. The functional status of the patient was recorded by the counselor at the time of ART initiation and categorized into three groups: normal, ambulatory, and bedridden during the past month. The WHO clinical stage was categorized into four groups (stage I, stage II, stage III, and stage IV), with stage IV considered to be the worst health condition that was assessed by health professionals at ART centers based on the load of clinical symptoms and infections, and recorded using the WHO clinical stage guidelines [18]. CD4 count was categorized as <100 cells/mm3, 101-200 cells/mm3, 201-350 cells/mm3, and >350 cells/mm3, and adherence to ART was categorized as <95% and ≥95% [13].
The date of death for all HIV-infected patients who died from any cause during the study period while on ART was recorded. Patients who missed their follow-up visits for more than three months were considered lost to follow-up, and the date of the last registered follow-up visit was recorded as the date of loss to follow-up. HIV-infected patients on ART who were transferred to another ART center, were recorded as transferred-out cases, and their date of transfer was also recorded. Similarly, patients put on medical advice (due to some complications or any adverse effects) were recorded as being on medical advice and the date when this advice was given was also recorded.
Statistical Analysis
The follow-up time (months) was calculated from the date of initiation of ART to the date of death for patients who died, or the date of the last recorded visit for patients who were censored (alive until the end of the study period, lost to follow-up, transferred out, or on medical advice). The primary end-point of the study was death. Kaplan-Meier methods were used to estimate survival after ART initiation. Patients were stratified by different population subgroups. We used the Wilcoxon log-rank test to assess the statistical differences between subgroups. Mortality density across the study period was estimated as the number of deaths per 1000 person-years of ART initiation to understand the pattern of deaths.
All baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were used as independent variables in the analysis. The proportional hazards assumption was tested using the Schonefild residuals plot, and all the predictor variables satisfied the criterion of being asymptotic. The widely accepted Cox-proportional hazard regression model was applied to identify factors associated with mortality [3,13,14]. The univariate Cox regression analysis was used to estimate the unadjusted hazard ratios (HRs). Stepwise (backward logistic regression) multivariate Cox regression analysis (including all predictor variables) was applied to estimate the adjusted HRs with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The probability for the stepwise regression analysis was 0.05 for entry of the variables and 0.10 for removal of the variables from the model. A sensitivity analysis called ‘the worst-case scenario’ was also performed, in which all patients lost to follow-up were classified as deceased immediately after their last contact with the center and presented separately. All the tests were two-sided and the criterion for statistical significance was set at p-value<0.05. The data were analyzed using Stata version 13.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) and SPSS version 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
RESULTS
The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of adult HIV-positive patients on ART are summarized in Table 1. The mean age of patients at the start of ART was 34.9±9.2 years, 54.7% were male, 45.2 had completed formal education, 68.1% were married or had a live-in partner, and 74.0% voluntarily enrolled in the HIV control program. The median baseline CD4 count was 172 cells/mm3 and the medium body weight was 46 kg. Approximately 32.1% of patients were recorded as being in WHO clinical stage III or IV, and 61.1% of them were adherent (≥95%) to ART treatment.
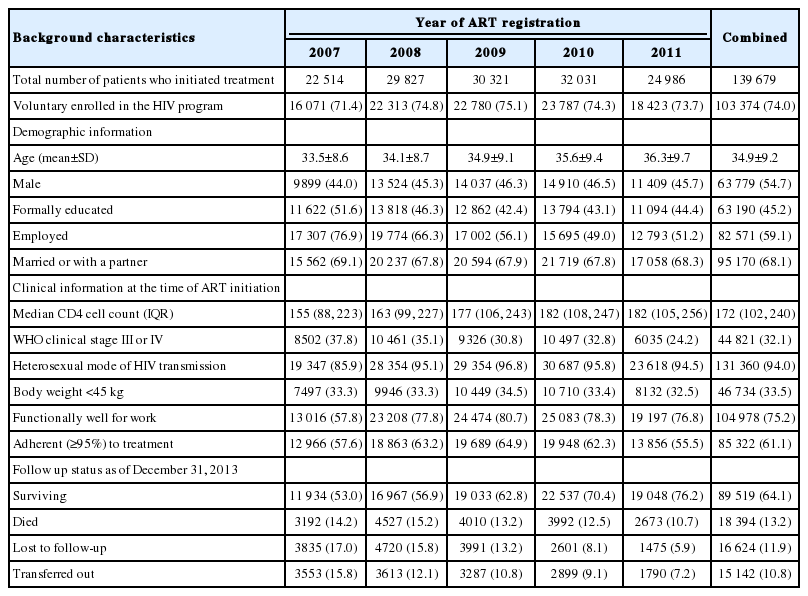
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of HIV-positive patients on ART by number of cases and number of deaths, Andhra Pradesh, 2007-2011
The overall median follow-up time for all patients was 16.0 months or 1.3 years (interquartile range, 0.3 to 2.8 years). The median follow-up time for the deceased was 2.0 months, 14.0 months for those lost to follow-up, and 5.0 months for those who were transferred out, which were lower than the median follow-up time for survivors (23.0 months). The overall survival probability among adult HIV-positive patients decreased over follow-up (Figure 2), and the mean survival over the study period was found to be 70.4 months (95% CI, 70.2 to 70.6 months). The survival probabilities of patients at three months, six months, one year, two years, and five years were 96.5%, 94.8%, 92.0%, 88.9%, and 87.9%, respectively.
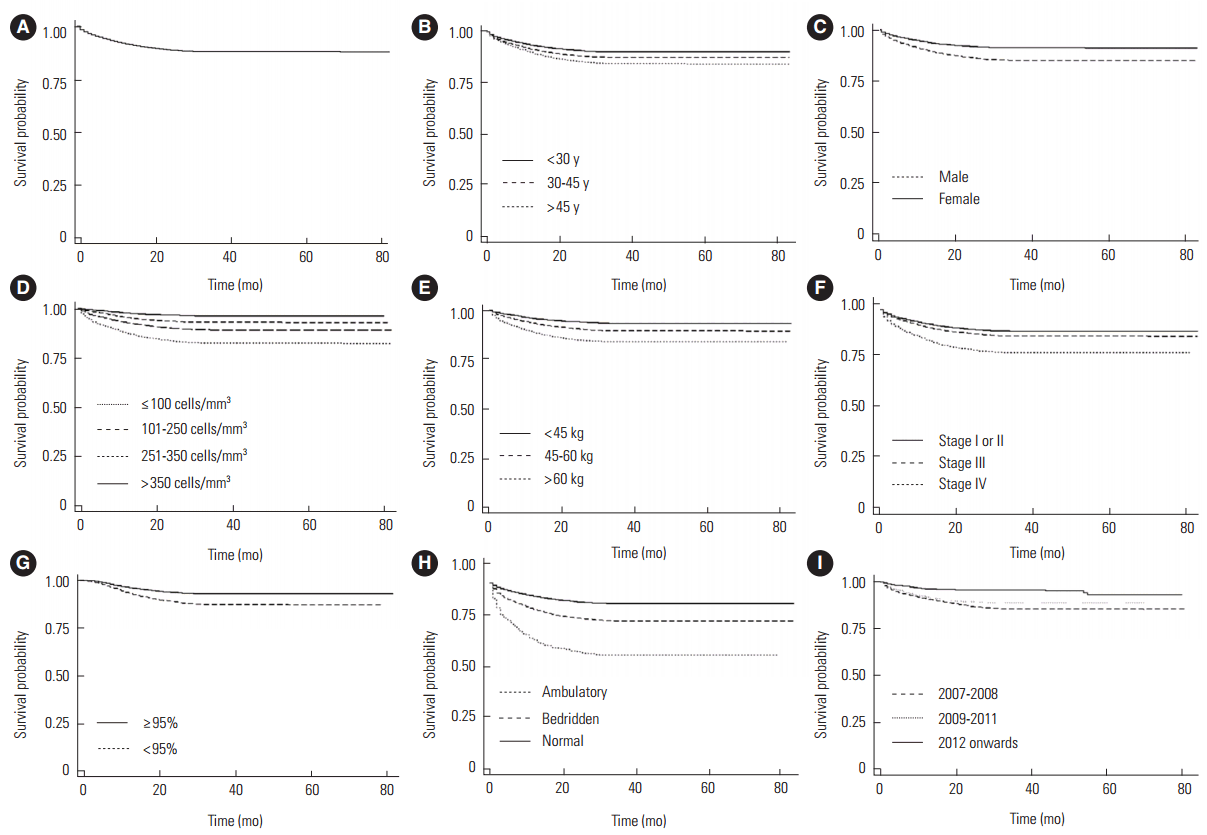
Kaplan-Meier survival plots for overall survival (A), age groups (B), sex (C), baseline CD4 counts (D), baseline body weight (E), baseline WHO clinical stage (F), adherence to HIV treatment (G), baseline functional status (H), and year of CD4 change criterion (I) of HIV-infected individuals after ART initiation in Andhra Pradesh state from 2007 to 2013. HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ART, antiretroviral therapy; WHO, World Health Organization.
As seen in Table 2, of the 18 394 patients who died, 10 305 (56.0%) died within three months of initiating treatment. The study cohort contributed a total of 227 315.9 person-years at risk during the study period. The overall mortality density was 80.9 per 1000 person-years at risk. The mortality rate was higher among patients who were older (>45 years), male, with a low baseline body weight (<45 kg), at baseline WHO clinical stage III or IV, had a baseline ambulatory or bedridden functional status, a CD4 count less than 200 cells/mm3, and initiated treatment according to older ART initiation criteria (≤200 cells/mm3 or ≤250 cells/mm3). The effectiveness of ART in the HIV control program was assessed using the CD4 criteria for ART initiation as the indicator variable. The chances of survival of HIV-positive patients significantly improved (p<0.001) at every time point as the CD4 criterion for ART initiation increased.
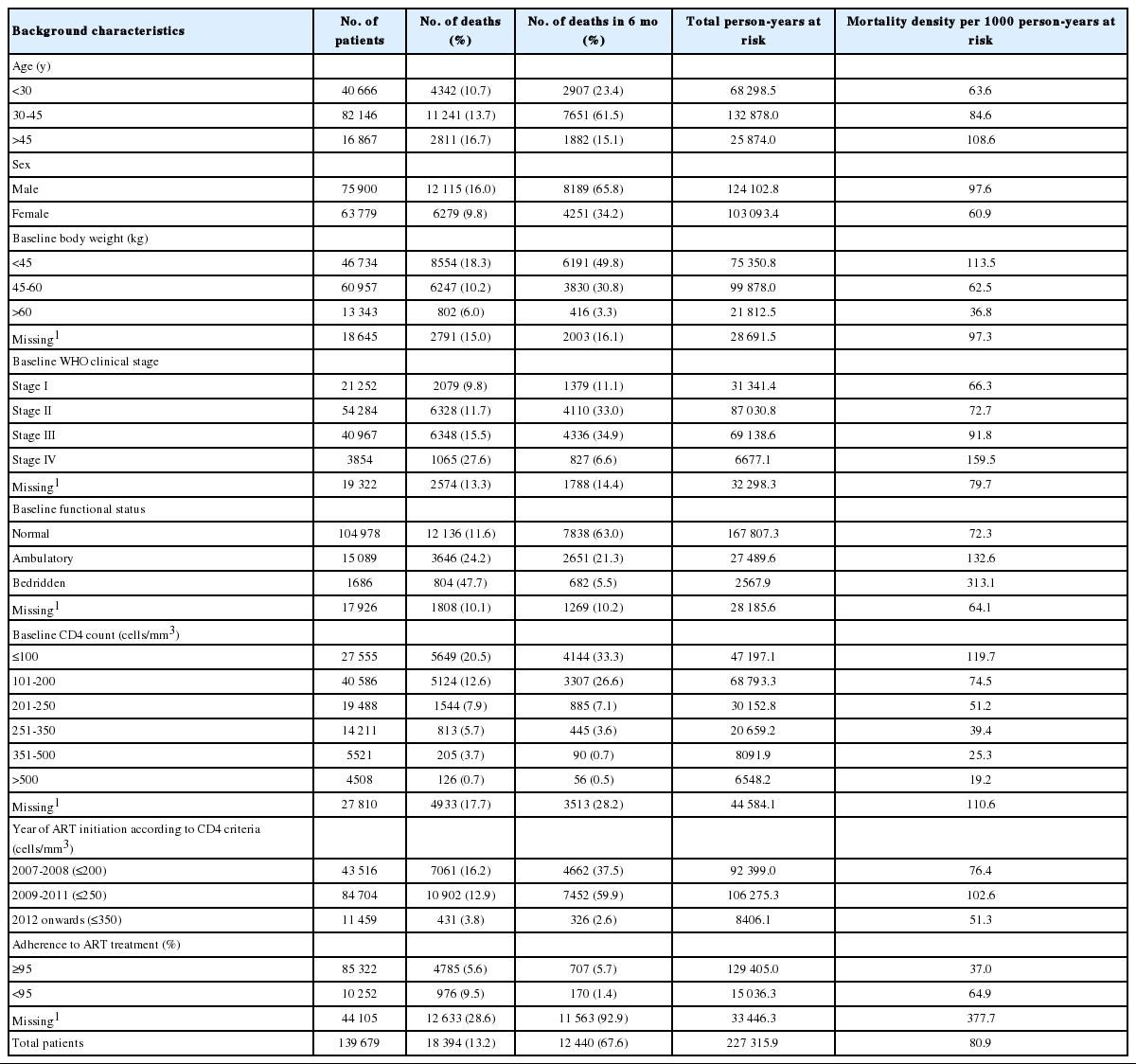
Mortality density (per 1000 person-years) of HIV-positive patients on ART by selected baseline background characteristics
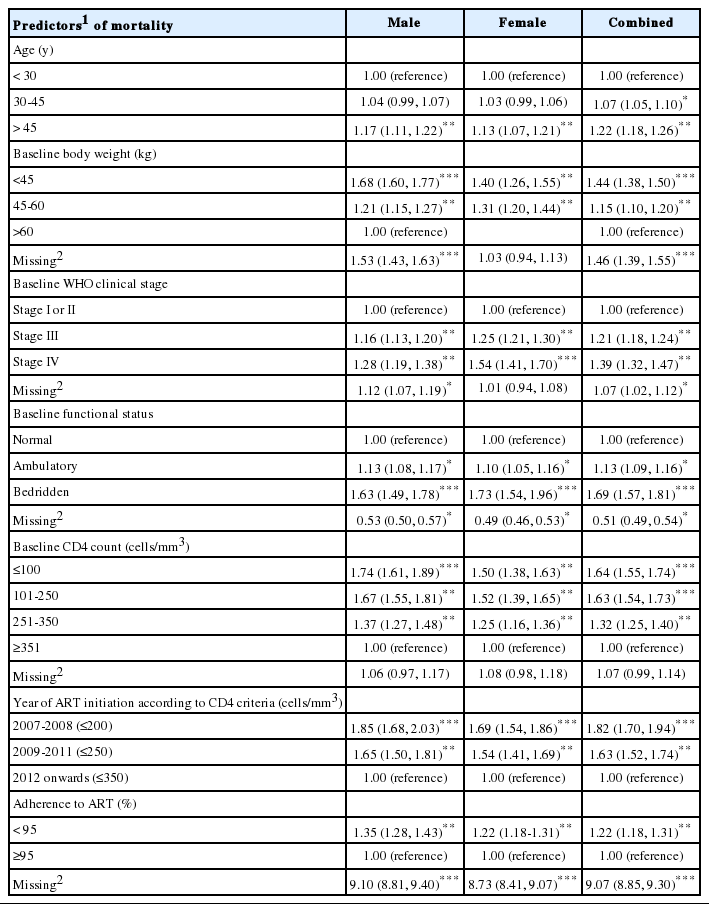
Table 3 shows a stratified analysis of factors associated with survival among adult HIV-infected patients. Multivariable analysis was used to calculate the adjusted hazard ratios for these variables. The risk of mortality was significantly higher among patients in the older age group (age >45 years: HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.34 to1.48). As body weight decreased, the risk of mortality increased, with a risk 3.69 times greater among patients less than 45 kg (95% CI, 3.42 to 3.97) than among those weighing more than 60 kg. Patients at WHO clinical stage IV were at a higher risk (HR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.36 to 1.56) than those at stage I or II. Patients with a baseline bedridden functional status were 3.05 times more likely to die than patients with normal functional status at the start of treatment (95% CI, 2.82 to 3.30). The likelihood of death among those with a baseline CD4 count of ≤100 cells/mm3 increased 4-fold (HR, 4.88; 95% CI, 4.36 to 5.46), and increased 3.02 times (95% CI, 2.70 to 3.38) when the CD4 count was 101-250 cells/mm3, in comparison to those with a CD4 count >350 cells/mm3. Moreover, the risk of mortality was nearly 2-fold greater (HR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.79 to 2.18) in patients with the older CD4 treatment initiation criteria (≤200 cells/mm3) and 1.70 times greater (95% CI, 1.65 to 1.90) in nonadherent (<95%) patients than in adherent (≥95%) patients.

Univariable and multivariable hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals of mortality according to baseline background characteristics using a Cox proportional hazard model
Similarly, Table 4 presents adjusted stratified risks under a worst-case scenario assumption (sensitivity analysis) that all patients lost to follow-up died immediately after discontinuing their treatment. A similar pattern to the real-case scenario in Table 3 emerged in the risk factors. Older age groups, lower body weight, poor clinical stage and functional status, lower CD4 counts, older criteria for treatment initiation, and poor adherence were significantly associated with an elevated risk of mortality.
DISCUSSION
This 7-year retrospective cohort study found a high mortality rate within three months of ART initiation (mortality density of 396.5 per 1000 person-years at risk; 95% CI, 387.4 to 405.5) among HIV-positive patients in Andhra Pradesh, in agreement with other studies conducted in resource-limited settings [3, 13,14,19]. The main predictors of mortality among adult HIV-positive patients on ART were being in the oldest age group, male sex, a low baseline body weight, poor baseline functional status, a poor baseline WHO clinical stage, a low baseline CD4 count, and poor ART adherence (<95%). In the present study, 13.6% of the adult HIV-positive patients on ART died, which is somewhat higher than the overall death rate (7.5%) observed in the ART program in Andhra Pradesh as of 2012 [2]. The cause of death was not investigated in this study; however, it is well-known that opportunistic infections are a major cause of mortality among HIV-positive individuals. In Andhra Pradesh and India, the most prevalent opportunistic infections among HIV-positive individuals are tuberculosis, candidiasis, and cryptosporidiosis [20].
The overall mortality reported in this study is higher than has been found in developed countries [21], but is in line with results from developing countries [15]. This may reflect poor participation of HIV-positive patients in the ART program in Andhra Pradesh. Similar to other studies [12,15], mortality was highest in the first three months after ART initiation. The poor outcomes in the initial few months after ART initiation might be due to delayed diagnosis and/or treatment, and explained by the fact that 60.5% of patients had advanced disease (CD4 count <200 cells/mm3) and 37.2% of patients had advanced clinical symptoms (WHO clinical stage III or IV) at the time of treatment initiation. Several factors such as HIV-related stigma and discrimination [22] may have played a vital role in delaying diagnosis and/or treatment. Moreover, the lack of proper screening diagnostic facilities for opportunistic infections and the limited availability of prophylaxis may have also increased mortality [19,21]. Advanced clinical stage (stage IV) is strongly linked with high mortality during the initial months of treatment [23]. Findings from other countries similarly indicate that the effectiveness of ART in reducing mortality and increasing survival among HIV-infected patients may depend on ART adherence, quality of services, and the clinical characteristics of patients [24,25].
The finding of this study that male HIV-positive patients had a higher risk of mortality than female patients is similar to what has been reported in other studies [3,21,24,26]; however, some previous studies [19,27] reported no significant association between sex and mortality, but rather explained differences in terms of variations in the accessibility and utilization of health services. Moreover, late reporting at ART centers unless one is experiencing extreme HIV-related symptoms might be more common among male than female patients [24]. Stigma and discrimination, economic responsibility, risk behaviors and guilt associated with visiting sex workers, and masculine norms of being strong and healthy may be barriers to males accessing early testing and treatment.
In Andhra Pradesh, while twice the number of male than female HIV-infected persons were registered in integrated counseling and testing centers in 2013, there were only 10% more male than female ART recipients in Andhra Pradesh [16]. This suggests that female patients tend to enroll more frequently than males in ART services, and additionally, they may have initiated early treatment due to linkage between the community-based prevention of parent-to-child transmission (PPTCT) and the HIV treatment and care program. Providing PPTCT services at the community level has considerably increased their utilization by pregnant females, and may have encouraged females to determine their HIV status and start early treatment through awareness and counseling services [28,29].
The positive association between low baseline body weight and mortality documented in the present study is similar to findings of other studies that have found low body weight or body mass index to be significantly associated with high mortality [24,25]. Low body weight could be a proxy marker for advanced disease (low CD4 and poor clinical stage) and a risk factor for opportunistic infections like tuberculosis [30]. Low body weight is associated with malnutrition, poor immunity, and poor living standards, which could also result in an increased risk of mortality. Our finding that patients at an advanced WHO clinical stage (stage III or IV) had a higher risk of mortality than those at stage I or II is supported by several studies in other countries [23-25,28]. Adult HIV-positive patients who were bedridden during the past month had higher risk of mortality than patients with normal baseline functional status at treatment initiation, as has been reported in other studies [3,21,30,31]. Bedridden functional status and being at clinical stage III or IV at ART initiation reflects the worst health condition of patients, and therefore, the combined effect of these clinical conditions could lead to mortality. These findings suggest that patients died mainly due to late initiation of ART, when their health conditions were at their worst.
This study shows that survival has improved significantly according to changes in the CD4 criteria for ART initiation over the study period, suggesting that this criterion plays an important role in affecting the mortality of HIV-positive patients [8,10]. Moreover, the baseline CD4 count was significantly associated with mortality in this study, which is consistent with previous studies [14,21,32]. A study in South Korea [32] showed that patients with a CD4 count of <200 cells/mm3 had mortality rates approximately 5 times higher than those with a CD4 count ≥500 cells/mm3. Another study in Tanzania [27] found a higher likelihood of mortality among patients with a CD4 count <200 cells/mm3 than among patients with a CD4 count ≥200 cells/mm3. In the current study, poor adherence to ART (<95%) was also significantly associated with a higher risk of mortality. This finding is supported by a study conducted in Jharkhand [13] that showed a 3-fold higher risk of mortality among non-adherent patients (<95%).
The main strength of this study is that it documented ART program outcomes across the entire state of Andhra Pradesh, and hence the findings are applicable to other regions with a similar cultural and ecological context outside Andhra Pradesh. This study used routine treatment program data, which is a cost-effective approach that used well-monitored data. However, the results should be interpreted in light of certain limitations. This study did not include information on the cause of death, the baseline treatment regimen, and opportunistic infections in the study population. Although these details are routinely entered in the ART registers, due to incomplete information in the online database, we were unable to include this data in the analysis. Moreover, the mortality outcomes of cases lost to follow-up in this study were not known; these cases may have been at higher risk of death, as shown in a meta-analysis of studies in resource-limited settings that reported that on average 46% of traced patients lost to follow-up on ART had died [33].
The findings of this study provide critical insights for designing effective and efficient HIV treatment, care, and support programs. Our findings show that the mortality rate among adult HIV-positive patients was high, and that the majority of deaths occurred within three months of ART initiation. Patients should be encouraged to be tested early for HIV, and those who test positive should be encouraged to initiate early treatment. Major efforts are required not only to trace those who are lost to follow-up but to initiate mechanisms to trace these patients early, when they have missed their monthly dose of treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) for sharing ART surveillance data under the National Data Analysis Plan (NACO/SIMU/NDAP/2015/02). Furthermore, we would like to thank the Care, Support and Treatment division at NACO for data access and assisting us in understanding the data. The views discussed/expressed in this article are not of NACO or development partners, rather it is completely, the understanding of the authors. We are grateful to the Population Council for facilitating continuous support to enhance our writing skills and reviewing the article, especially Dr. N Saggurti, D Ganju, and Dr. SK Patel. We would like to extend our heartfelt gratitude to Dr. DC Reddy, Dr. S Panda, Dr. V Chakrapani, and Dr. PS Saravanamurthy for their comments during the finalization of the manuscript.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.